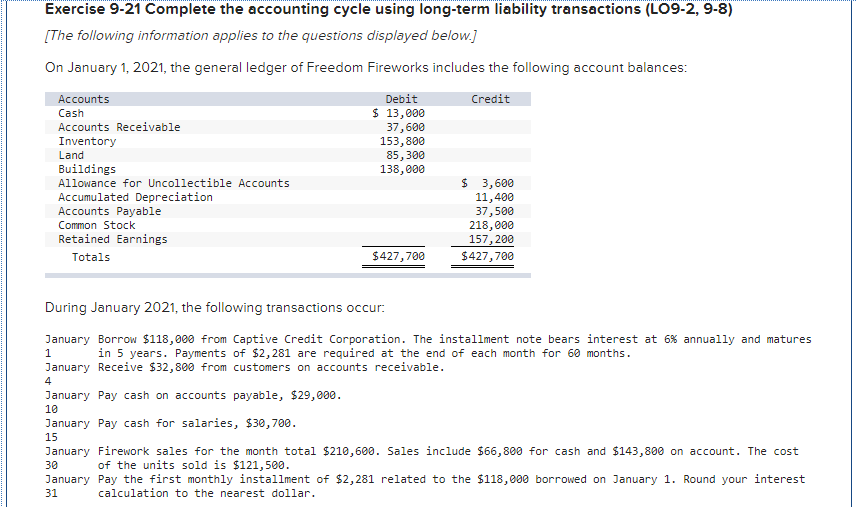
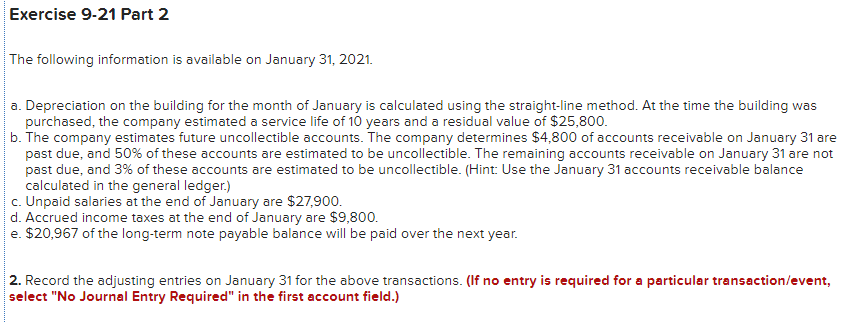
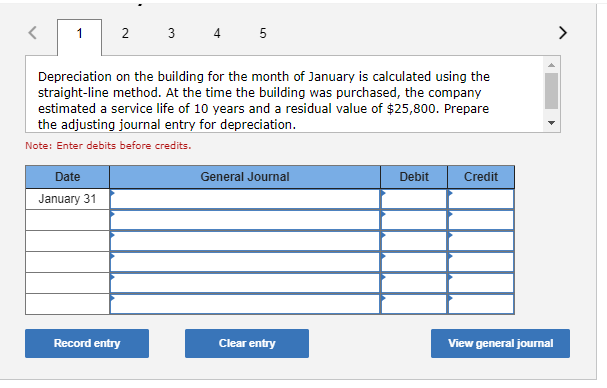
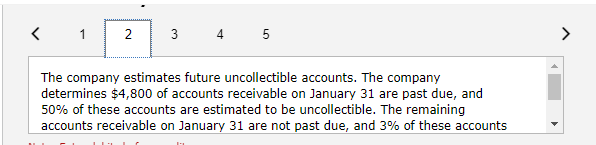
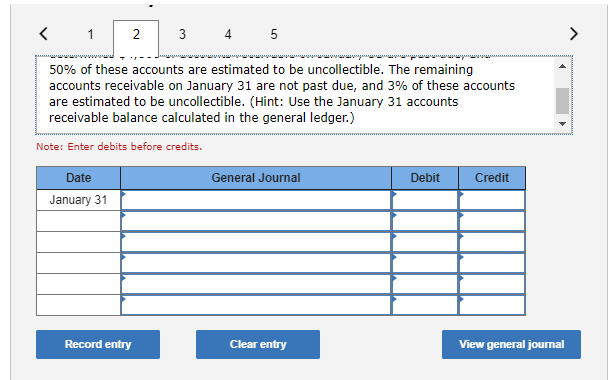
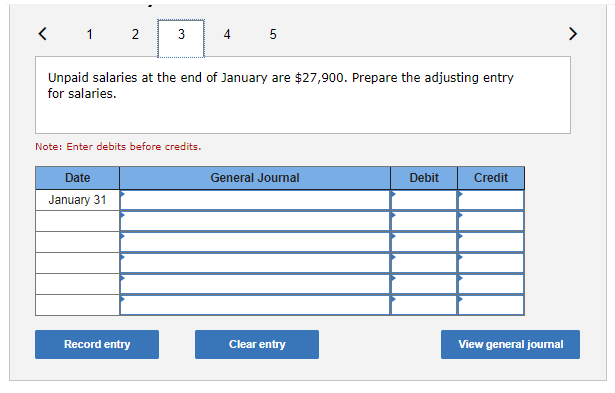
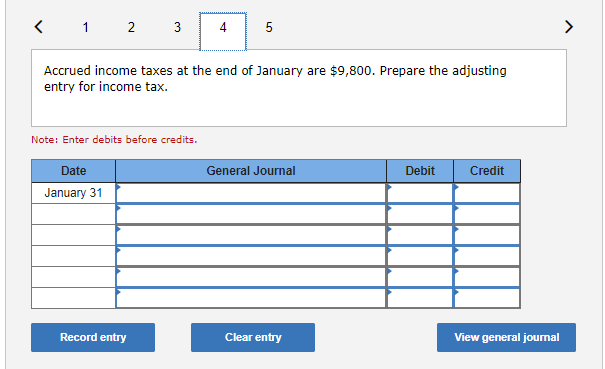
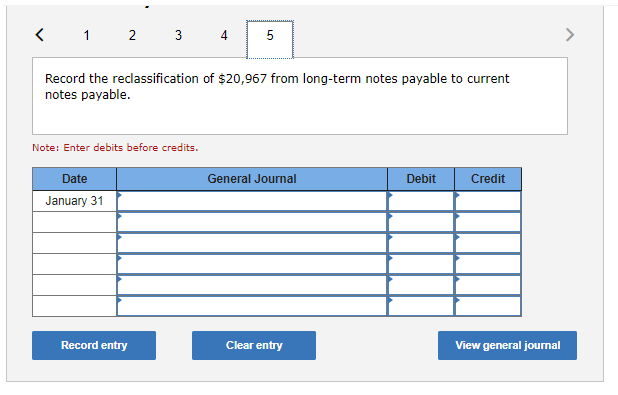
Exercise 9-21 Complete the accounting cycle using long-term liability transactions (LO9-2, 9-8) (The following information applies to the questions displayed below.) On January 1, 2021, the general ledger of Freedom Fireworks includes the following account balances: Credit Debit $ 13,000 37,600 153,800 85,300 138,000 Accounts Cash Accounts Receivable Inventory Land Buildings Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts Accumulated Depreciation Accounts Payable Common Stock Retained Earnings Totals $ 3,600 11,400 37,500 218,000 157,200 $427,700 $427,700 During January 2021, the following transactions occur: January Borrow $118,000 from Captive Credit Corporation. The installment note bears interest at 6% annually and matures 1 in 5 years. Payments of $2,281 are required at the end of each month for 60 months. January Receive $32,800 from customers on accounts receivable. 4 January Pay cash on accounts payable, $29,000. 10 January Pay cash for salaries, $30,700. 15 January Firework sales for the month total $210,600. Sales include $66,800 for cash and $143,800 on account. The cost 30 of the units sold is $121,500. January Pay the first monthly installment of $2,281 related to the $118,000 borrowed on January 1. Round your interest 31 calculation to the nearest dollar. Exercise 9-21 Part 2 The following information is available on January 31, 2021. a. Depreciation on the building for the month of January is calculated using the straight-line method. At the time the building was purchased, the company estimated a service life of 10 years and a residual value of $25,800. b. The company estimates future uncollectible accounts. The company determines $4,800 of accounts receivable on January 31 are past due, and 50% of these accounts are estimated to be uncollectible. The remaining accounts receivable on January 31 are not past due, and 3% of these accounts are estimated to be uncollectible. (Hint: Use the January 31 accounts receivable balance calculated in the general ledger.) c. Unpaid salaries at the end of January are $27,900. d. Accrued income taxes at the end of January are $9,800. e. $20,967 of the long-term note payable balance will be paid over the next year. 2. Record the adjusting entries on January 31 for the above transactions. (If no entry is required for a particular transaction/event, select "No Journal Entry Required" in the first account field.) The company estimates future uncollectible accounts. The company determines $4,800 of accounts receivable on January 31 are past due, and 50% of these accounts are estimated to be uncollectible. The remaining accounts receivable on January 31 are not past due, and 3% of these accounts 50% of these accounts are estimated to be uncollectible. The remaining accounts receivable on January 31 are not past due, and 3% of these accounts are estimated to be uncollectible. (Hint: Use the January 31 accounts receivable balance calculated in the general ledger.) Note: Enter debits before credits. Date General Journal Debit Credit January 31 Record entry Clear entry View general journal Unpaid salaries at the end of January are $27,900. Prepare the adjusting entry for salaries. Note: Enter debits before credits. Date General Journal Debit Credit January 31 Record entry Clear entry View general journal














