
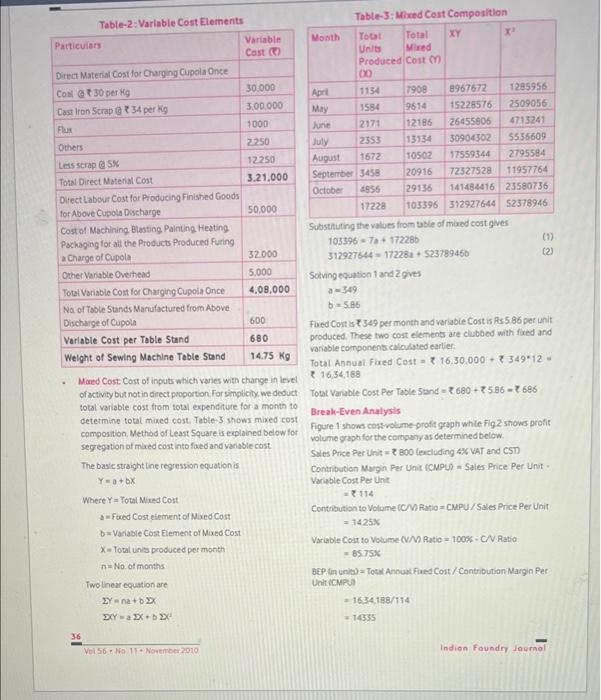

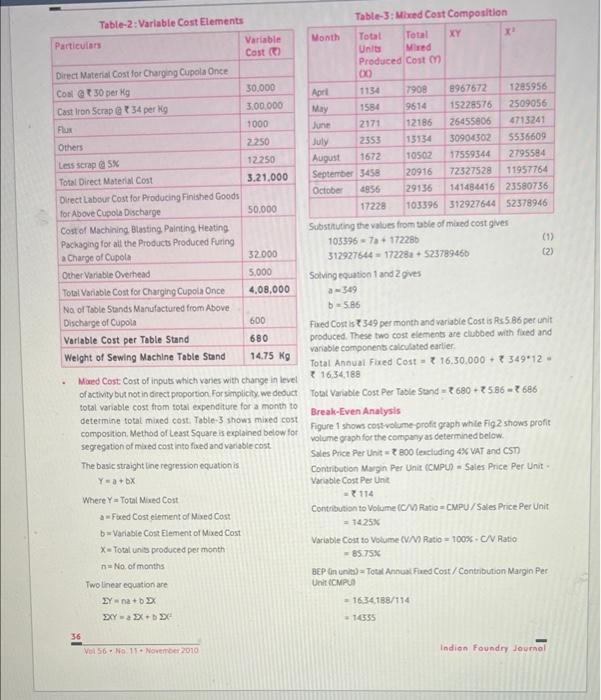
Please read the technical paper named "Short-Term Decision Making in Foundry Unit: A Case Study" and answer the following questions. 1. On Page 36, under the section named "Mixed Cost", the author used the equation method to determine the fixed costs and variable costs. Please use high-low method to determine the fixed costs and variable costs. Specifically, please refer to lecture slides for Chapter 20 and specify all the calculation processes. Table-2: Variable Cost Elements Particulars Variable Cost () Direct Material Cost for Charging Cupola Once Coal 30 per Kg 30.000 Cast Iron Scrap @t34 per kg 3,00,000 Flux 1000 Others 2.250 Less scrap @ 5% 12.250 Total Direct Material Cost 3.21,000 Direct Labour Cost for Producing Finished Goods for Above Cupola Discharge 50.000 Cost of Machining Blasting Painting Heating Packaging for all the Products Produced Furing a Charge of Cupola 32.000 Other Variable Overhead 5.000 Total Variable Cost for Charging Cupola Once 4,08,000 No of Table Stands Manufactured from Above Discharge of Cupola 600 680 Variable Cost per Table Stand Weight of Sewing Machine Table Stand 14.75 Kg Mored Cost: Cost of inputs which varies with change in level of activity but not in direct proportion. For simplicity, we deduct total variable cost from total expenditure for a month to determine total mixed cost. Table-3 shows mixed cost composition. Method of Least Square is explained below for segregation of mixed cost into faxed and variable cost The basic straight line regression equation is Y=a+bX Where Y= Total Mixed Cost a-Fixed Cost element of Mixed Cost b Variable Cost Element of Mixed Cost X-Total units produced per month n No. of months 36 Two linear equation are EY-na+bEx EXY - EX+bX Vol 56 No 11 November 2010 Table-3: Mixed Cost Composition Month Total Total XY X Units Mixed Produced Cost (1) 8 Apri 1134 7908 8967672 1285956 May 1584 9614 15228576 2509056 June 2171 12186 26455806 4713241 July 2353 30904302 5536609 13134 10502 17559344 2795584 August 1672 September 3458 20916 72527528 11957764 October 4856 29136 141484416 23580736 17228 103396 312927644 52378946 Substituting the values from table of mixed cost gives 1033967a+ 17228b 312927644-17228a+523789466 (2) Solving equation 1 and 2 gives a-349 b=5.86 Fixed Cost is 349 per month and variable Cost is Rs5.86 per unit produced. These two cost elements are clubbed with fixed and variable components calculated earlier. Total Annual Fixed Cost t 16.30.000+ 349*12- 16,34,188 Total Variable Cost Per Table Stand-680-586-686 Break-Even Analysis Figure 1 shows cost-volume-profit graph while Fig2 shows profit volume graph for the company as determined below. Sales Price Per Unit-800 (excluding 4% VAT and CST) Contribution Margin Per Unit (CMPU) Sales Price Per Unit- Variable Cost Per Unit . - 114 Contribution to Volume (C/V) Ratio-CMPU/Sales Price Per Unit = 1425% Variable Cost to Volume (V/V) Ratio - 100%-C/V Ratio - 85.75% BEP in unit) Total Annual Fixed Cost/Contribution Margin Per Unit (CMPU - 1634.188/114 - 14355 Indian Foundry Journal










