Question
TUTORIAL 1 & ASSIGNMENT 1QUESTIONS QUESTION 1 1.1Two wires are identical, except that one is aluminum and one is copper. The aluminum wire hasa resistance
TUTORIAL 1 & ASSIGNMENT 1 QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1
1.1 Two wires are identical, except that one is aluminum and one is copper. The aluminum wire has a resistance of 0.20 ῼ. What is the resistance of the copper wire? (4)
1.2 A cylindrical wire has a length of 2.80 m and a radius of 1.03 mm. It carries a current of 1.35 A, when a voltage of 0.0320 V is applied across the ends of the wire. From what material is the wire made? Consult resistivity Table 20.1 (5)
QUESTION 2
2.1 Suppose a single electron orbits about a nucleus containing two protons (+2e), as would be the case for a helium atom from which one of the two naturally occurring electrons is removed. The radius of the orbit is 2.65 x 10 -11m. Determine the magnitude of the electron’s centripetal acceleration. (8)
2.2 A single electron orbits a lithium nucleus that contains three protons (+3e). The radius of the
orbit is 1.76 x 10 -11m. Determine the kinetic energy of the electron. (8)
QUESTION 3
The drawing below shows an equilateral triangle, each side of which has a length of 2.00 cm. Point charges are fixed to each corner, as shown. The 4.00 µC charge experiences a net force due to the charges qA and qB. This net force points vertically downward and has a magnitude of 405 N.
Determine the magnitudes and algebraic signs of the charges qA and qB. (8)
QUESTION 4
4.1 The drawing shows three point charges fixed in place. The charge at the coordinate origin has a value of q1 = +8.00 µC; the other two charges have identical magnitudes, but opposite signs:
q2 = – 5.00 µC and q3 = + 5.00 µC.
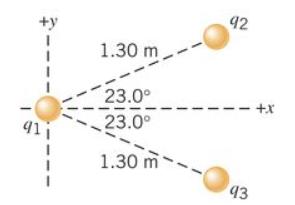
(a) Determine the net force (magnitude and direction) exerted on q1 by the other two charges. (6)
(b) If q1 had a mass of 1.50 g and it were free to move, what would be its acceleration? (2)
4.2 Three charges are placed on the x-axis. The charge q1 = +2.0 µC is placed at x = 0.0 m and the
charge q2 = +5.0 µC is placed at x = 2.0 m.
Determine the position on the x-axis where q3 should be placed to achieve a resultant electric force of zero. Let the distance between q3 and q1 be | (6) |
4.3 P; R and S are three point charges and interact as shown below.
4.3.1 Draw the Free body diagram (Vector diagram) for charge (3)
4.3.2 Calculate the net electrostatic force on charge P due to fields of R and S (10)
4.3.3 Describe any FIVE properties of electric field lines to your Grade 11 learners.
Draw annotated sketch to support your answer. (5)
If charge P is removed while R and S remains; Draw/ sketch
4.3.4 the electric field lines between R and S (4)
4.3.5 the graph relating the force and distance between R and S according to Coulomb’s Law. (2)
4.4 The sketch shows two small metal spheres A and B distance r from their centers and placed on insulated stands. The charge of spheres are q and 2q respectively. Sphere A exerts a force of F on B. What is the magnitude of the force that sphere B exerts on A? The spheres are now placed a distance ¼ r apart. Determine the magnitude of the electrostatic force each sphere experiences. (5)
QUESTION 5
- A negative charge of 2nC is 10 cm from point P. P
– 2nC 10 cm
- Define electric field at a point (2)
- A positive charge is of 3 nC is now positioned 5 cm from point P, as showed in the diagram below
P
10 cm 5 cm
– 2nC
3 nC
Calculate the magnitude of electric field at P due to both charges (12)
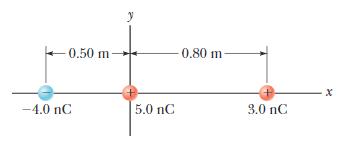
5.2 Use the information in the diagram below to find the electric field at x = -1.0 m; y = 0 m | |
| (9) |
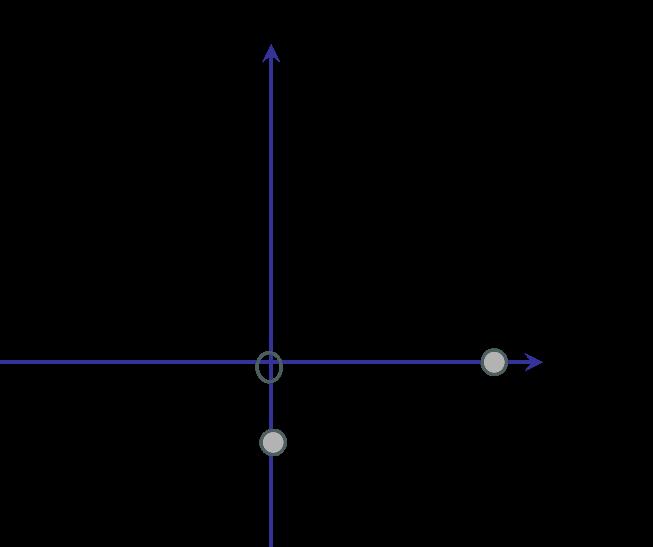
5.3 Drawn in the diagram below are two separate electric fields, field a and b.
Identify the nature of each charge, and estimate the relative magnitude of the charges. Explain your answer. (9)
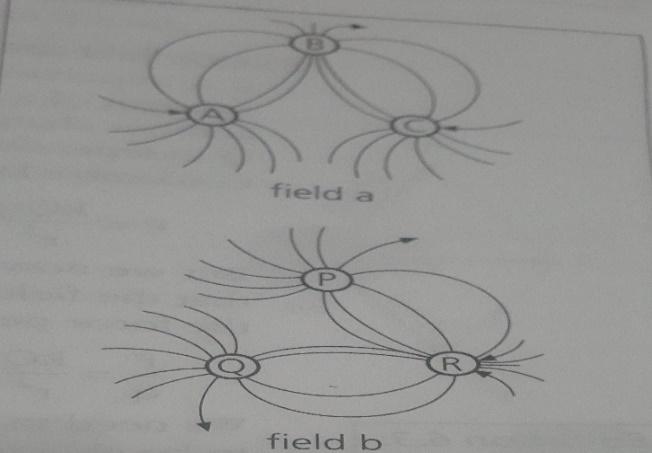
QUESTION 6 [ ELECTRIC FIELD STRENGTH AND ELECTRIC POTENTIAL]
6.1 State the principle of superposition of vectors in words (2)
6.2 Two electric charges are located as follows: q1 = + 30![]() C at (0,0) and
C at (0,0) and
q2 = – 40 ![]() C at the point (0,3). Point P is located at (2,1)
C at the point (0,3). Point P is located at (2,1)
- Draw an annotated sketch to show the position and orientation of q1; q2 and point P in the x - y plane. Indicate the direction of the electric fields as lines of force. (5)
- Determine the net electric field strength at position (2,1) due to q1
and q2 . (8)
QUESTION 7 [ ELECTRIC FIELD STRENGTH AND ELECTRIC POTENTIAL]
7.1 | Find the magnitude and direction of the NET electric field at the origin of the coordinate system due to the two-point charges, q1 and q2. The two charges are located at the x-y coordinate position of (0.0, -2.0 cm) and (+4.00 cm, 0.0), respectively, as shown in the figure. |
| (8) |
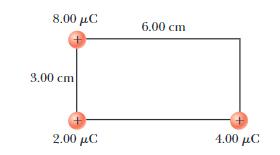
7.2 Find the electric potential, taking zero at infinity, at the empty corner in the rectangle below | |
| (8) |
7.3
Two point charges are held at the corners of a rectangle as shown in the figure. The lengths of the sides of the rectangle are 0.050 m and 0.150 m. Assume that the electric potential is defined to be zero at infinity |
|
QUESTION 8 [ WORK DONE IN ELECTRIC FIED & ELECTRIC POTENTIAL]
8.1 | A particle has a charge of +1.5 µC and moves from point A to point B, a distance 0f 0.20 m. The particle experiences a constant electric force, and its motion is along the line of action of the force. The difference between the particle’s electric potential energy at A and at B is EPEA – EPEB = +9.0 x 10-4 J. | ||
Find the magnitude and direction of
| |||
8.2 | An alpha particle has a positive charge of 2e and a mass of 6.6 x 10-27 kg. With what velocity would an alpha particle reach the negative plate of a parallel plate apparatus with a potential difference of 2.0 x 103 V, if it started, at rest, next to the positive plate? | (6) | |
QUESTION 9
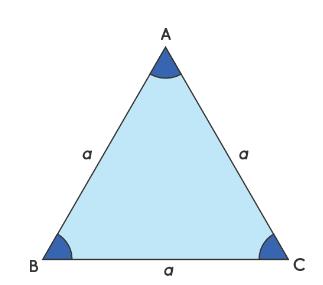
Three charges are at the corners A, B and C of an equilateral triangle. Each charge has a value of +5.00 nC. The length of each side of the triangle a = 4.00 cm. Calculate the electric potential at the midpoint of the base BC. Provide your answer in units of kV. |
| (10) |
QUESTION 10 [ GAUSS LAW & COULOMB’S LAW]
10.1 State Gauss Law in words (2)
10.2 Two gaussian spherical surfaces X and Y of radii 5 cm and 7cm
respectively, are placed distance d from their circumferences. The
charges of each are as indicated in the diagram. The electric field
strength at Y is 3,5 x 10 – 12 NC – 1.
d
X Y
10![]() C – 20
C – 20 ![]() C
C
Determine
10.2.1 the force of attraction or repulsion between X and Y (7)
10.2.2 the net electric field flux due to X and Y. (6)
FORMULA SHEET FOR PHSE 322

![]() F = ma
F = ma
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
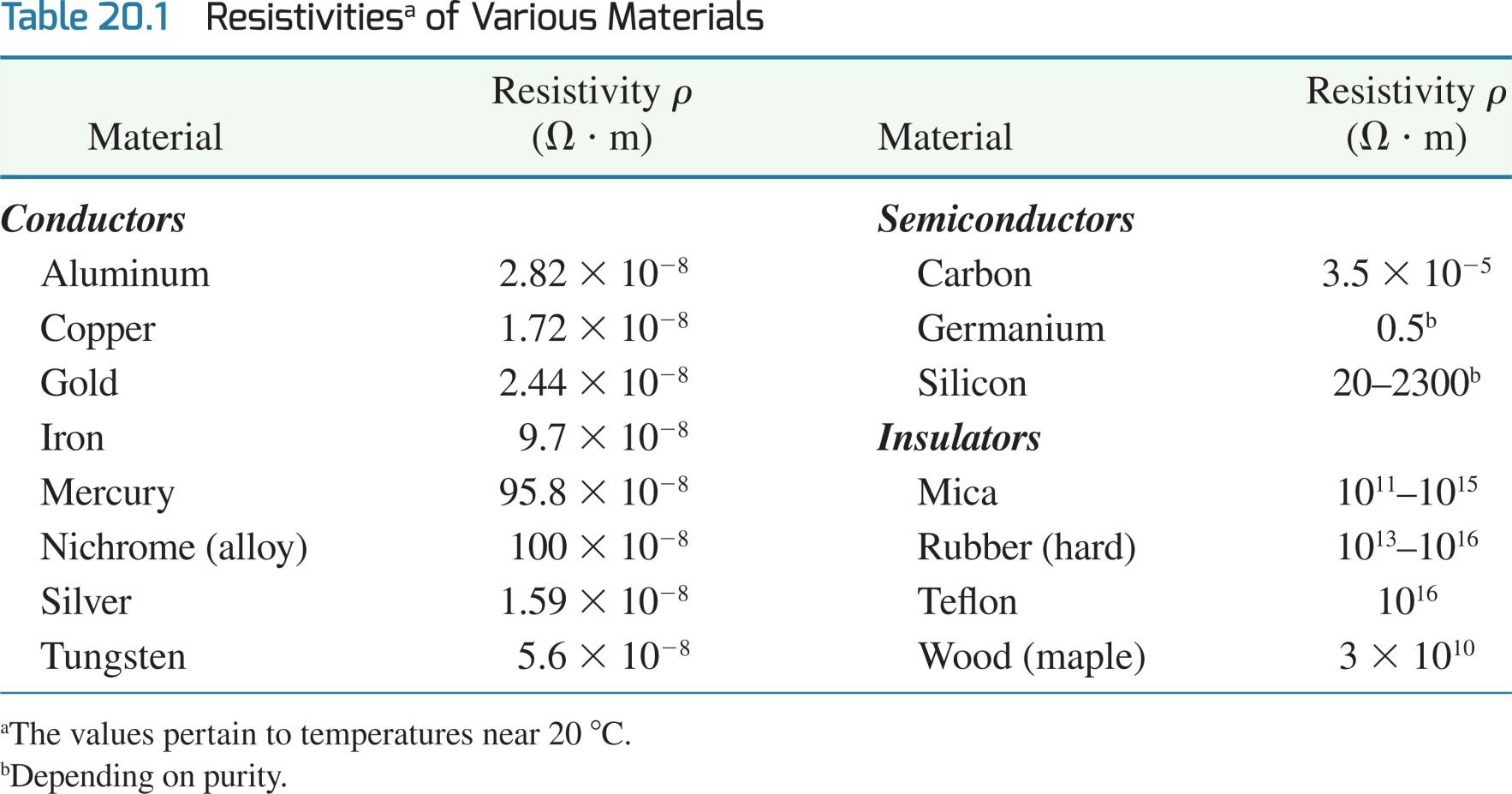
+y 1.30 m 23.0 23.0 92 1.30 m 93 -+x
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started