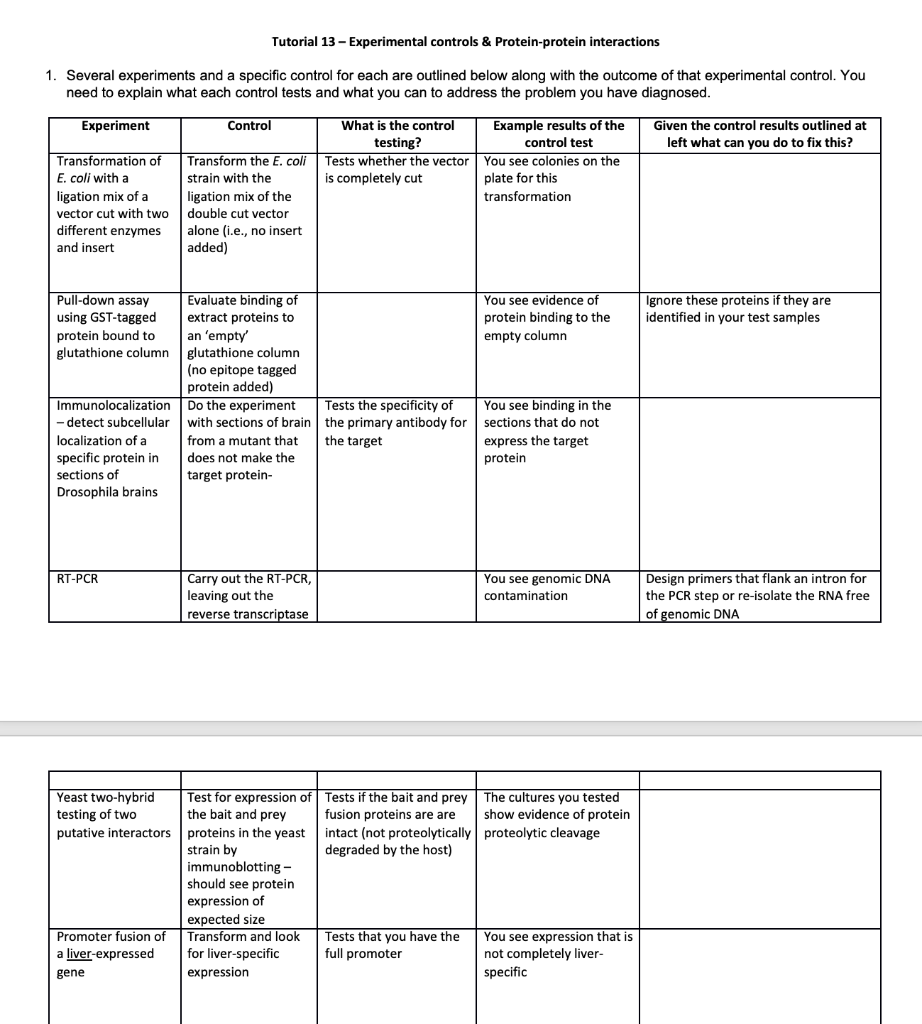
Tutorial 13 - Experimental controls & Protein-protein interactions 1. Several experiments and a specific control for each are outlined below along with the outcome of that experimental control. You need to explain what each control tests and what you can to address the problem you have diagnosed. Experiment Control Given the control results outlined at left what can you do to fix this? What is the control testing? Tests whether the vector is completely cut Transformation of E. coli with a ligation mix of a vector cut with two different enzymes and insert Example results of the control test You see colonies on the plate for this transformation Transform the E. coli strain with the ligation mix of the double cut vector alone (i.e., no insert added) You see evidence of protein binding to the empty column Ignore these proteins if they are identified in your test samples Pull-down assay Evaluate binding of using GST-tagged extract proteins to protein bound to an 'empty' glutathione column glutathione column (no epitope tagged protein added) Immunolocalization Do the experiment Tests the specificity of -detect subcellular with sections of brain the primary antibody for localization of a from a mutant that specific protein in does not make the sections of target protein- Drosophila brains the target You see binding in the sections that do not express the target protein RT-PCR Carry out the RT-PCR. leaving out the reverse transcriptase You see genomic DNA contamination Design primers that flank an intron for the PCR step or re-isolate the RNA free of genomic DNA Yeast two-hybrid testing of two putative interactors Tests if the bait and prey The cultures you tested fusion proteins are are show evidence of protein intact (not proteolytically proteolytic cleavage degraded by the host) Test for expression of the bait and prey proteins in the yeast strain by immunoblotting - should see protein expression of expected size Transform and look for liver-specific expression Promoter fusion of a liver-expressed gene Tests that you have the full promoter You see expression that is not completely liver- specific Tutorial 13 - Experimental controls & Protein-protein interactions 1. Several experiments and a specific control for each are outlined below along with the outcome of that experimental control. You need to explain what each control tests and what you can to address the problem you have diagnosed. Experiment Control Given the control results outlined at left what can you do to fix this? What is the control testing? Tests whether the vector is completely cut Transformation of E. coli with a ligation mix of a vector cut with two different enzymes and insert Example results of the control test You see colonies on the plate for this transformation Transform the E. coli strain with the ligation mix of the double cut vector alone (i.e., no insert added) You see evidence of protein binding to the empty column Ignore these proteins if they are identified in your test samples Pull-down assay Evaluate binding of using GST-tagged extract proteins to protein bound to an 'empty' glutathione column glutathione column (no epitope tagged protein added) Immunolocalization Do the experiment Tests the specificity of -detect subcellular with sections of brain the primary antibody for localization of a from a mutant that specific protein in does not make the sections of target protein- Drosophila brains the target You see binding in the sections that do not express the target protein RT-PCR Carry out the RT-PCR. leaving out the reverse transcriptase You see genomic DNA contamination Design primers that flank an intron for the PCR step or re-isolate the RNA free of genomic DNA Yeast two-hybrid testing of two putative interactors Tests if the bait and prey The cultures you tested fusion proteins are are show evidence of protein intact (not proteolytically proteolytic cleavage degraded by the host) Test for expression of the bait and prey proteins in the yeast strain by immunoblotting - should see protein expression of expected size Transform and look for liver-specific expression Promoter fusion of a liver-expressed gene Tests that you have the full promoter You see expression that is not completely liver- specific







