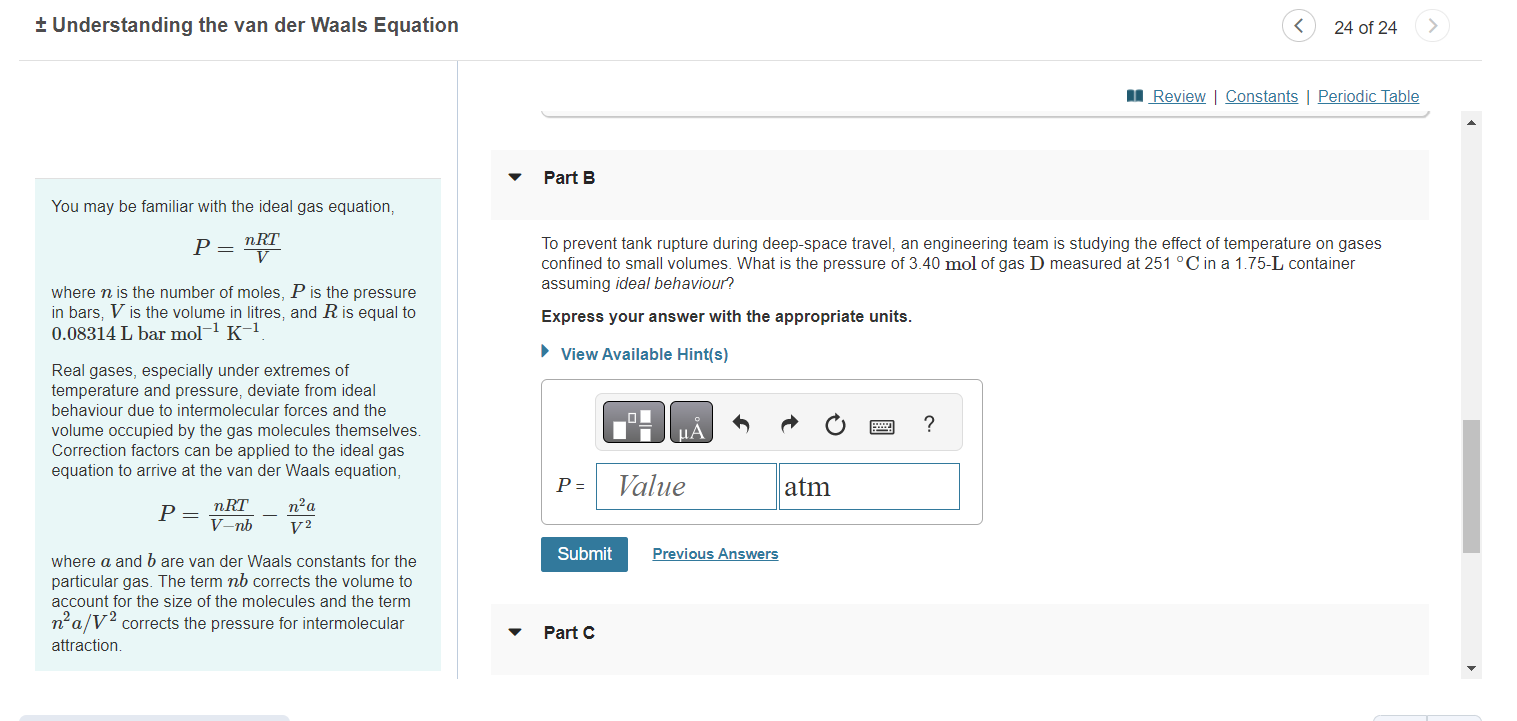
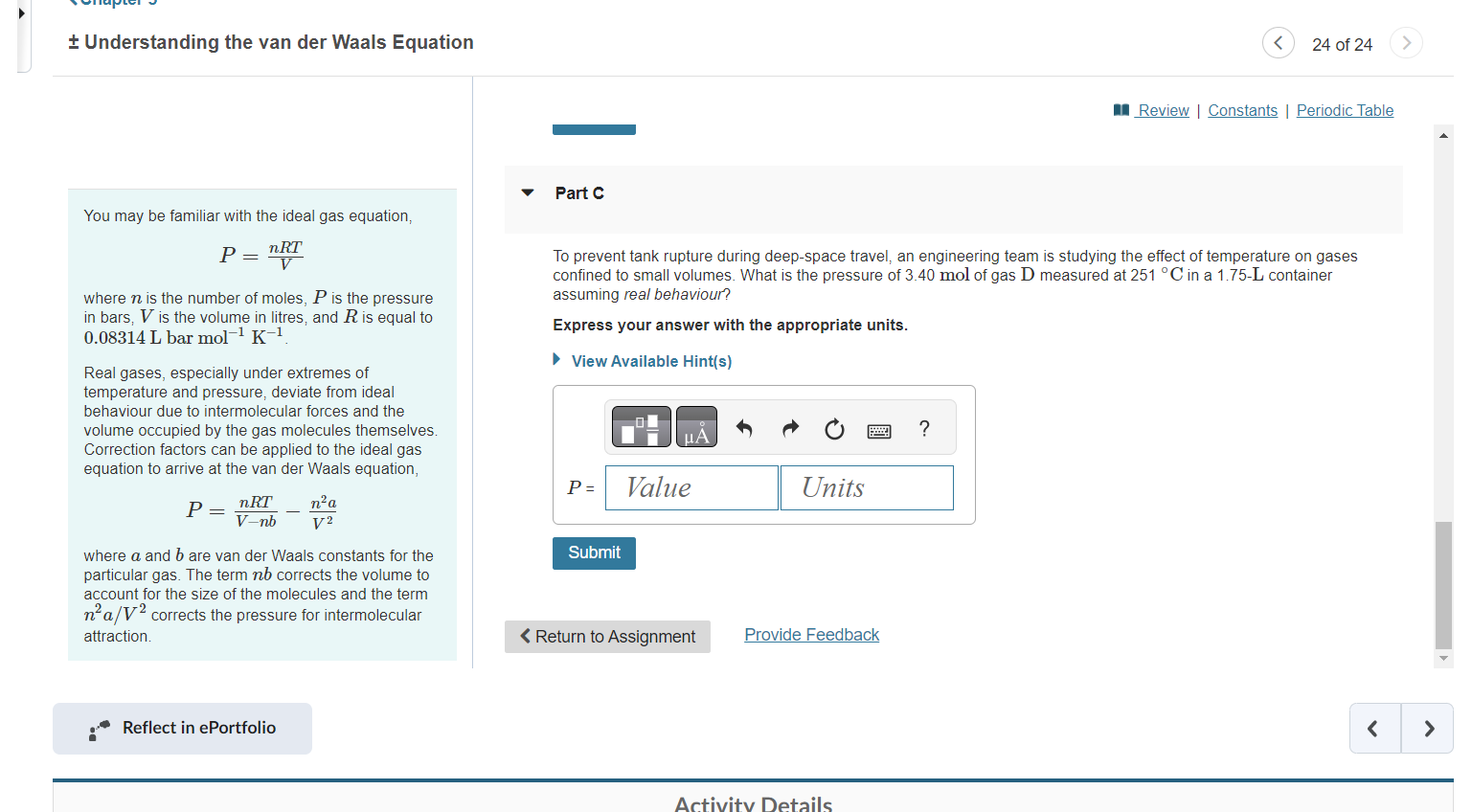
Understanding the van der Waals Equation 24 of 24 Part B You may be familiar with the ideal gas equation, P=VnRT To prevent tank rupture during deep-space travel, an engineering team is studying the effect of temperature on gases confined to small volumes. What is the pressure of 3.40mol of gas D measured at 251C in a 1.75 - L container where n is the number of moles, P is the pressure assuming ideal behaviour? in bars, V is the volume in litres, and R is equal to Express your answer with the appropriate units. 0.08314L bar mol1K1. Real gases, especially under extremes of temperature and pressure, deviate from ideal behaviour due to intermolecular forces and the volume occupied by the gas molecules themselves. Correction factors can be applied to the ideal gas equation to arrive at the van der Waals equation, P=VnbnRTV2n2a where a and b are van der Waals constants for the particular gas. The term nb corrects the volume to account for the size of the molecules and the term n2a/V2 corrects the pressure for intermolecular attraction. Part C Understanding the van der Waals Equation 24 of 24 Part C You may be familiar with the ideal gas equation, P=VnRT To prevent tank rupture during deep-space travel, an engineering team is studying the effect of temperature on gases confined to small volumes. What is the pressure of 3.40mol of gas D measured at 251C in a 1.75L container where n is the number of moles, P is the pressure assuming real behaviour? in bars, V is the volume in litres, and R is equal to 0.08314Lbarmol1K1. Express your answer with the appropriate units. Real gases, especially under extremes of temperature and pressure, deviate from ideal behaviour due to intermolecular forces and the volume occupied by the gas molecules themselves. Correction factors can be applied to the ideal gas equation to arrive at the van der Waals equation, P=VnbnRTV2n2a where a and b are van der Waals constants for the particular gas. The term nb corrects the volume to account for the size of the molecules and the term n2a/V2 corrects the pressure for intermolecular attraction








