Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
updated , ignore the first post, these are the questions Chegg Home Study tools My courses My books Career Life Sharp Company manufactures a product
updated , ignore the first post, these are the questions 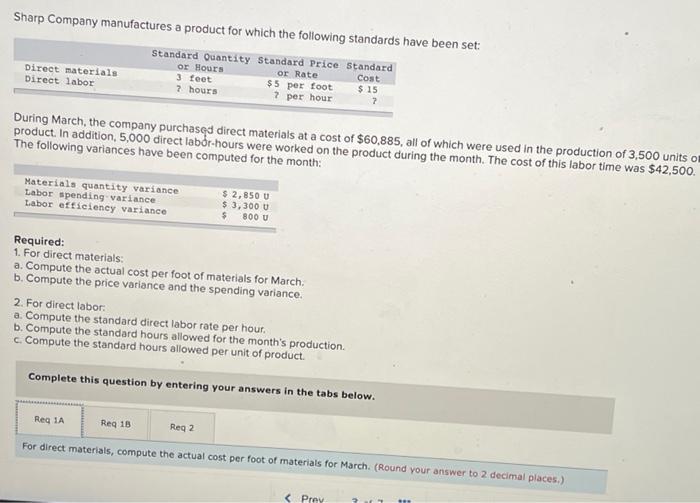
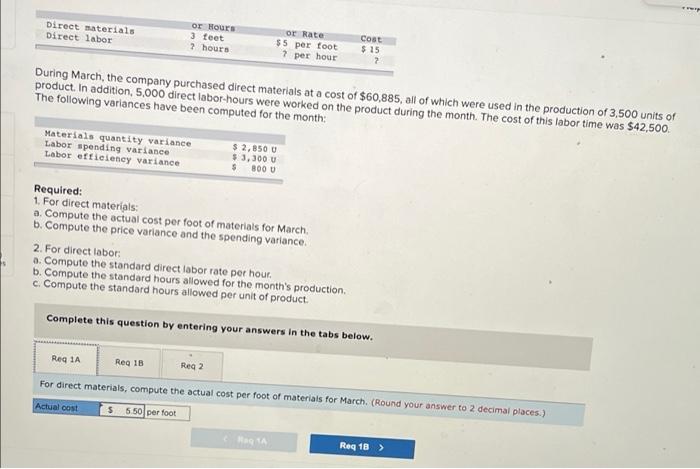
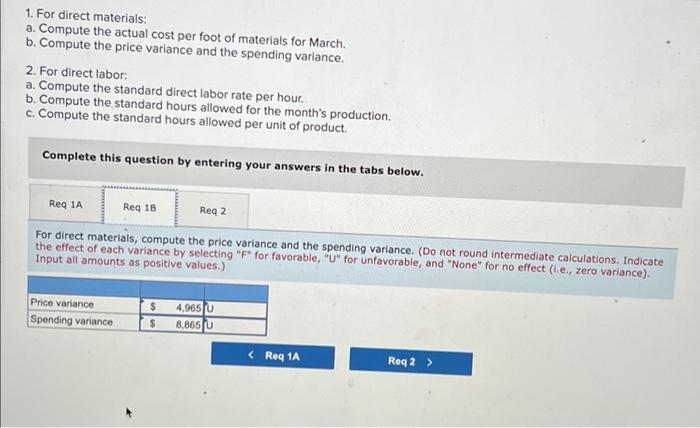
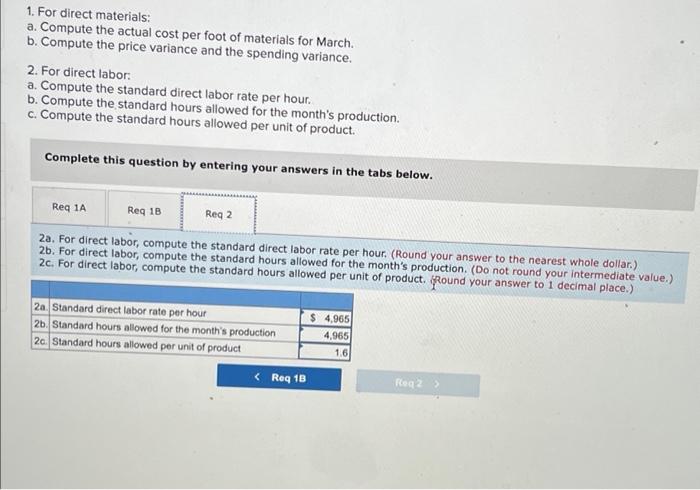
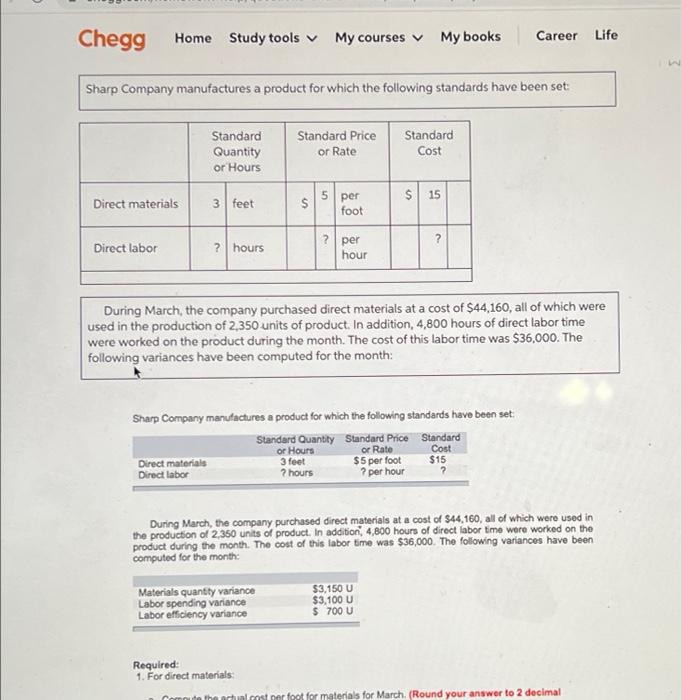
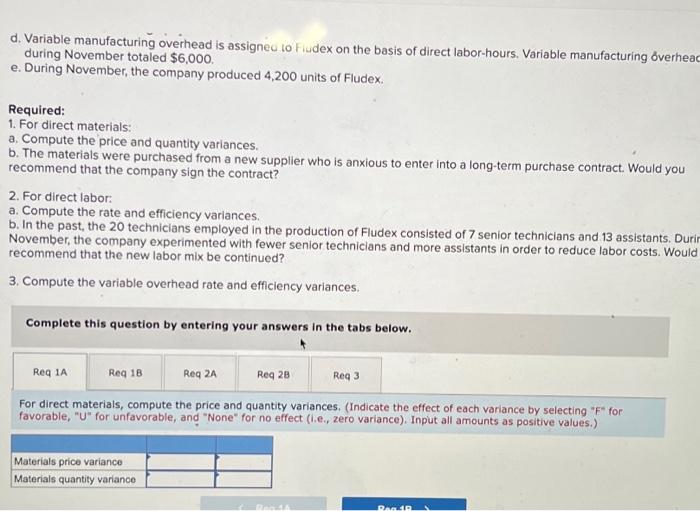
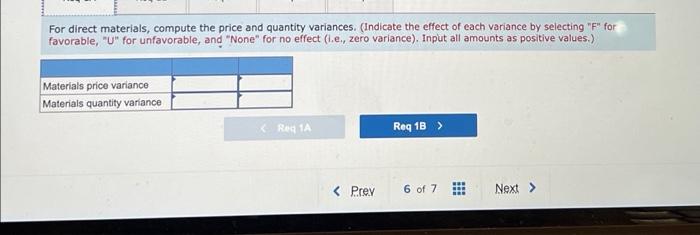
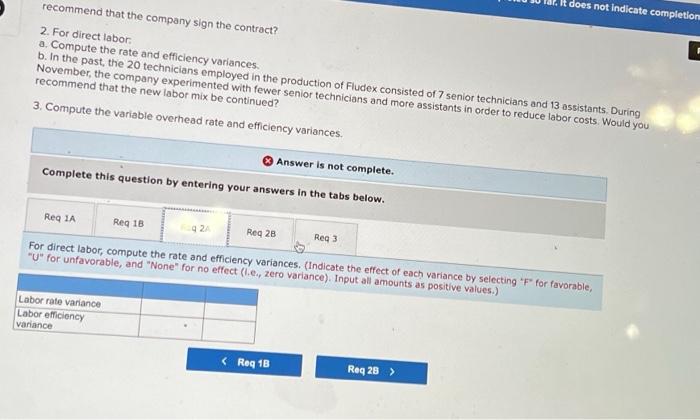
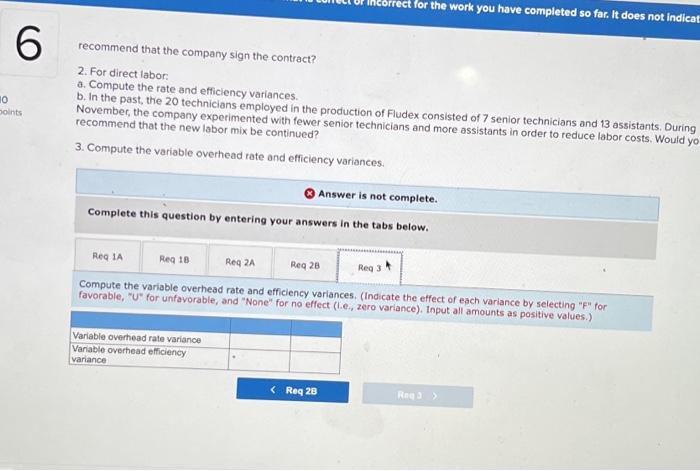
Chegg Home Study tools My courses My books Career Life Sharp Company manufactures a product for which the following standards have been set Standard Quantity or Hours Standard Price or Rate Standard Cost 5 per $ 15 Direct materials 3 feet $ foot ? per ? Direct labor ? hours hour During March, the company purchased direct materials at a cost of $44,160, all of which were used in the production of 2,350 units of product. In addition, 4,800 hours of direct labor time were worked on the product during the month. The cost of this labor time was $36,000. The following variances have been computed for the month: Sharp Company manufactures a product for which the following standards have been set Standard Quantity Standard Price Standard or Hours or Rate Cost Direct materials 3 feet $5 per foot $15 Direct labor ? hours ? per hour ? During March, the company purchased direct materials at a cost of $44,160, all of which were used in the production of 2,350 units of product. In addition 4,800 hours of direct labor time were worked on the product during the month. The cost of this labor time was $36,000. The following variances have been computed for the month: Materials quantity variance Labor spending variance Labor efficiency variance $3,150 U $3,100 U $ 700 U Required: 1. For direct materials: motor foot for materials for March (Round your answer to 2 decimal d. Variable manufacturing overhead is assigneo lo Fiudex on the basis of direct labor-hours. Variable manufacturing overhead during November totaled $6,000. e. During November, the company produced 4,200 units of Fludex. Required: 1. For direct materials: a. Compute the price and quantity variances. b. The materials were purchased from a new supplier who is anxious to enter into a long-term purchase contract. Would you recommend that the company sign the contract? 2. For direct labor: a. Compute the rate and efficiency variances. b. In the past, the 20 technicians employed in the production of Fludex consisted of 7 senior technicians and 13 assistants. Durir November, the company experimented with fewer senior technicians and more assistants in order to reduce labor costs. Would recommend that the new labor mix be continued? 3. Compute the variable overhead rate and efficiency variances Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Req 1A Reg 18 Reg 2A Reg 28 Req3 For direct materials, compute the price and quantity variances. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (le, zero variance). Input all amounts as positive values.) Materials price variance Materials quantity variance RIL For direct materials, compute the price and quantity variances. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (.e., zero variance). Input all amounts as positive values.) Materials price variance Materials quantity variance KRed 1A Reg 1B > recommend that the company sign the contract? It does not indicate completion 2. For direct labor a. Compute the rate and efficiency variances. b. In the past, the 20 technicians employed in the production of Fludex consisted of 7 senior technicians and 13 assistants. During November, the company experimented with fewer senior technicians and more assistants in order to reduce labor costs. Would you recommend that the new labor mix be continued? 3. Compute the variable overhead rate and efficiency variances. Answer is not complete Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Reg 1A Reg 18 Reg 28 Reg 3 For direct labor, compute the rate and efficiency variances. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (le, zero variance). Input all amounts as positive values.) Labor rate variance Labor efficiency variance for the work you have completed so far. It does not indicat 6 10 Joints recommend that the company sign the contract? 2. For direct labor a. Compute the rate and efficiency variances. b. In the past, the 20 technicians employed in the production of Fludex consisted of 7 senior technicians and 13 assistants. During November , the company experimented with fewer senior technicians and more assistants in order to reduce labor costs. Would yo recommend that the new labor mix be continued? 3. Compute the variable overhead rate and efficiency variances Answer is not complete. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Red IA Reg 18 Req ZA Reg 28 Reg Compute the variable overhead rate and efficiency variances. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (le, zero variance). Input all amounts as positive values.) Variable overhead rate variance Variable overhead efficiency variance 1. For direct materials: a. Compute the actual cost per foot of materials for March b. Compute the price variance and the spending variance. 2. For direct labor: a. Compute the standard direct labor rate per hour. b. Compute the standard hours allowed for the month's production. c. Compute the standard hours allowed per unit of product. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Reg 1A Reg 18 Reg 2 For direct materials, compute the price variance and the spending variance. (Do not round Intermediate calculations. Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F* for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (l.e., zero variance) Input all amounts as positive values.) Price variance Spending variance 4.965 U 8,865 U $ 1. For direct materials: a. Compute the actual cost per foot of materials for March. b. Compute the price variance and the spending variance. 2. For direct labor a. Compute the standard direct labor rate per hour b. Compute the standard hours allowed for the month's production. c. Compute the standard hours allowed per unit of product. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Req 1A Req 1B Reg 2 2a. For direct labor, compute the standard direct labor rate per hour. (Round your answer to the nearest whole dollar.) 2b. For direct labor, compute the standard hours allowed for the month's production. (Do not round your intermediate value.) 2c. For direct labor, compute the standard hours allowed per unit of product. Round your answer to 1 decimal place.) 2a. Standard direct labor rate per hour $ 4,965 2b. Standard hours allowed for the month's production 4,965 20 Standard hours allowed per unit of product 16 



Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


