
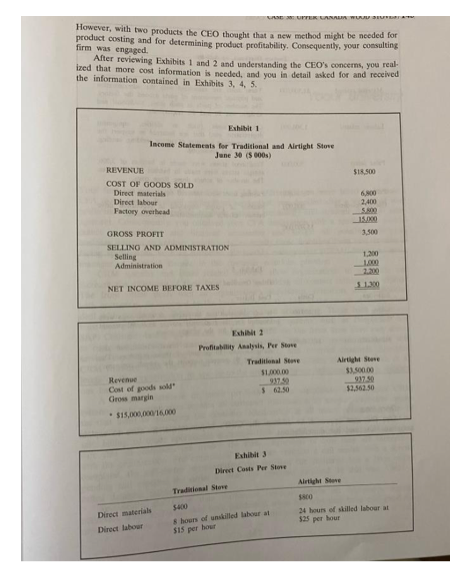
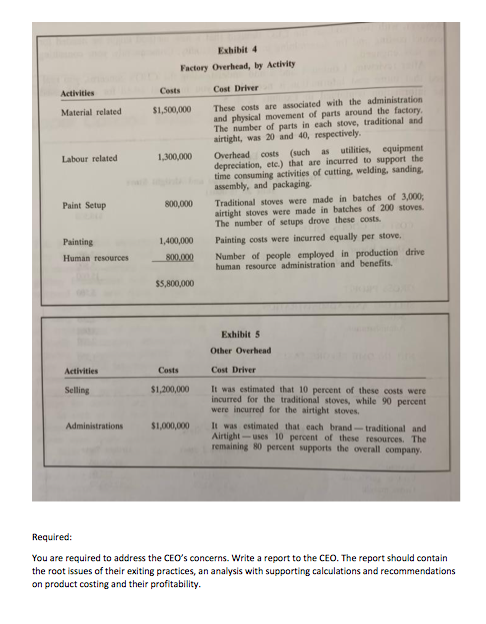
Upper Canada Wood Stoves This is your first assignment as a consultant with the prestigious McHenry Consulting firm. You want to do well. Three years ago you graduated with a business degree, and last month you earned your CPA designation. McHenry hired you last week; and after getting familiarized with McHenry's business model and practices, you have been assigned to a new client, Upper Canada Wood Stoves. Upper Canada Wood Stoves was established in 1810 as a family business. It was a booming business for its first century, but during the 20th century sales declined with the replacement of wood stoves with oil, natural gas, electricity, and central heating. Actually, the company nearly disappeared on more than one occasion. For the last two decades, the company produced only one model, called the Traditional Canadian wood stove. With this improvement in business, the owners saw an opportunity for a more contemporary model, called the Airtight Canadian. This new model is focused on cus- tomers using wood, at their cottages and country homes, as an alternative source of energy for cooking and heating In each of the first three years on the market, Airtight's sales met expectations. Company profits were, however, less than expected. It was unclear if the Airtight stoves were really profitable. Sales for the latest year, shown in Exhibit 1, were for 15,000 traditional stoves at $1,000 each and 1,000 airtight stoves at $3,500 each. The company had calcu. lated profitability in its normal method, as shown in Exhibit 2. The new airtight stoves were, accordingly, an outstanding success. On the other hand, profitability of the traditional stove had become dismal, which was difficult for the CEO to under- stand as it had been considered a successful stove up until the introduction of the airtight stove. The results, in Exhibit 2, were being questioned by the CEO. She recognized that profitability per stove had always been determined by gross profits per stove, i.e., by dividing the company's gross profits by the number of stoves sold. The CEO had considered raising the price of the traditional stove to improve profits, but had delayed that decision for two reasons. First, the traditional stove was already competitively priced in its market Market research had indicated that price increases would be met with even larger declines in units sold. Second, she wanted to get advice on product costing and product profitability. In the past, with one product, it was obvious that product profitability was synonymous with the company's profits. However, with two products the CEO thought that a new method might be needed for product costing and for determining product profitability. Consequently, your consulting firm was engaged After reviewing Exhibits 1 and 2 and understanding the CEO's concerns, you real ized that more cost information is needed, and you in detail asked for and received the information contained in Exhibits 3, 4, 5. Exhibit 1 Income Statements for Traditional and Airtight Store June 20 (000) REVENUE COST OF GOODS SOLD Direct materials Direct labour Factory Overhead $18.500 6.80 2.400 15.000 3,500 GROSS PROFIT SELLING AND ADMINISTRATION Selling Administration 1.200 2.200 NET INCOME BEFORE TAXES Exhibit 2 Profitability Analysis, Per Store Traditional See Alright Store 53.500.00 917 50 12.562.50 91750 Revenue Cost of goods sold Gros margin $15,000,000/16.000 Alright Store Direct Costs Per Stone Traditional Stone 5400 8 hours of filled labour $15 per hour Direct materials Direct labour 24 hours of skilled labour at 525 per hour Exhibit 4 Factory Overhead, by Activity Activities Costs Material related $1,500,000 Labour related 1,300,000 Cost Driver These costs are associated with the administration and physical movement of parts around the factory The number of parts in each stove, traditional and airtight, was 20 and 40, respectively. Overhead costs (such as utilities, equipment depreciation, etc.) that are incurred to support the time consuming activities of cutting, welding, sanding, assembly, and packaging. Traditional stoves were made in batches of 3,000, airtight stoves were made in batches of 200 stoves. The number of setups drove these costs. Painting costs were incurred equally per stove, Number of people employed in production drive human resource administration and benefits. Paint Setup 800,000 Painting Human resources 1,400,000 800.000 $5,800,000 Exhibit Other Overhead Activities Costs Cost Driver Selling $1,200,000 It was estimated that 10 percent of these costs were incurred for the traditional stoves, while 90 percent were incurred for the airtight stoves. It was estimated that each brand traditional and Airtight-uses 10 percent of these resources. The remaining 80 percent supports the overall company. Administrations $1,000,000 Required: You are required to address the CEO's concerns. Write a report to the CEO. The report should contain the root issues of their exiting practices, an analysis with supporting calculations and recommendations on product costing and their profitability









