Question
Use C++, chegg had the same question, but the answer was wrong. Design a class called DaysWorked . The class's purpose is to store a
Use C++, chegg had the same question, but the answer was wrong.
Design a class called DaysWorked. The class's purpose is to store a value mHours that could be evaluated in terms of days of work. For example:
8 hours are actually 1 day of work
12 hours are 1.5 days of work
18 hours are 2.25 days of work
The class should have a default constructor, and an overloaded constructor that accepts a number of hours. The class should also have the following overloaded operators:
+ The addition operator: When two DaysWorked objects are added together, this operator should return a new object that has mHours equal to the sum of the two objects mHours.
- The subtraction operator: When two DaysWorked objects are subtracted, this operator should return a new object that has mHours equal to the difference between the two objects mHours.
++ Prefix and postfix increment operators: These operators should increment the number of hours in the object. When incremented, the number of days of work should be recomputed.
-- Prefix and postfix decrement operators: These operators should decrease the number of hours in the object. When decremented, the number of days of work should be recomputed.
This operator should display to the screen all objects data in a clear fashion.
>> cin stream extraction operator: This operator should prompt the user to enter all the object's data in a clear fashion.
== equality comparison operator: This operator should return true if both objects have equal mHours member variables
[] subscript operator: This operator should return days if subscript is 0, hours if subscript is 1, and error out a message otherwise.
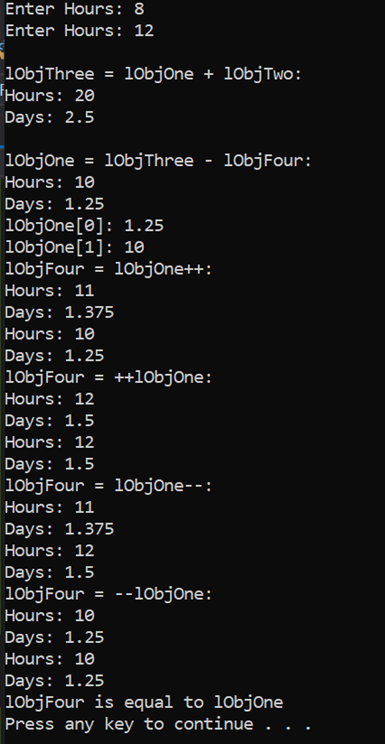
The below driver program should display the following output:
int main()
{
DaysWorked lObjOne;
DaysWorked lObjTwo;
cin >> lObjOne;
cin >> lObjTwo;
DaysWorked lObjThree = lObjOne + lObjTwo;
cout
cout
DaysWorked lObjFour(10);
lObjOne = lObjThree - lObjFour;
cout
cout
cout
cout
cout
lObjFour = lObjOne++;
cout
cout
cout
lObjFour = ++lObjOne;
cout
cout
cout
lObjFour = lObjOne--;
cout
cout
cout
lObjFour = --lObjOne;
cout
cout
if (lObjFour == lObjOne)
cout
else
cout
system("PAUSE");
return 0;
}
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


