Use Python for this assignment
Download the needed files from - http://www.cs.uni.edu/~fienup/cs1520s18/homework/hw3.zip
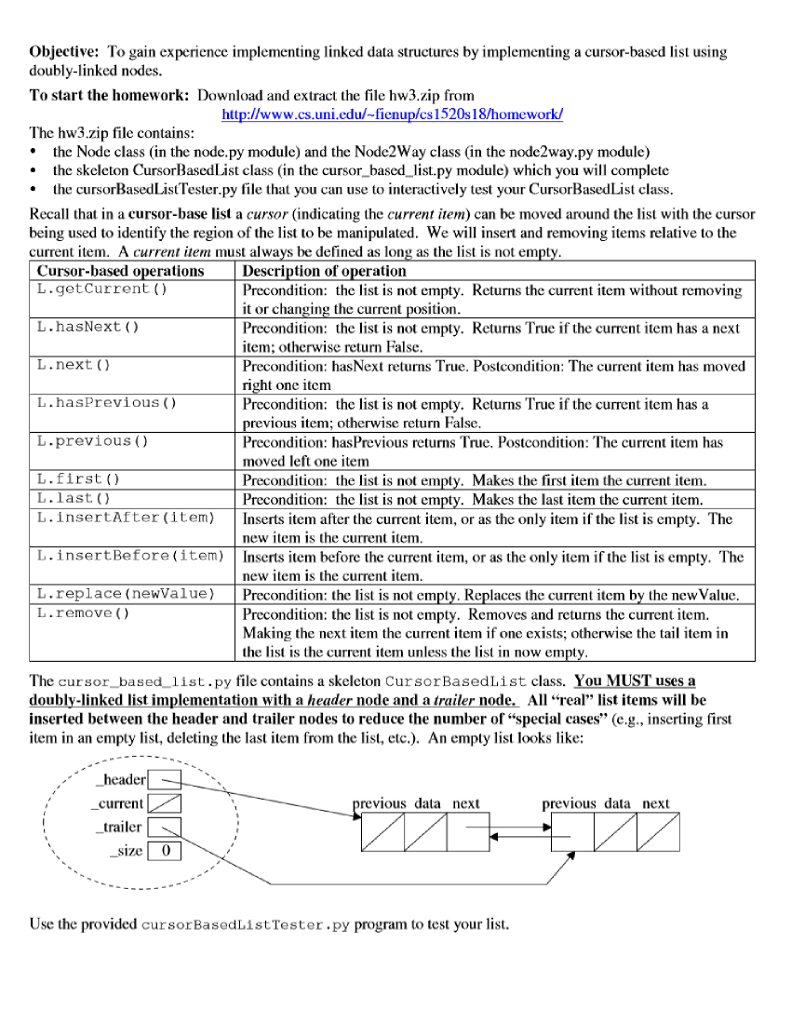
Objective: To gain experience implementing linked data structures by implementing a cursor-based list using doubly-linked nodes. To start the homework: Download and extract the file hw3.zip from http://www.cs.uni.edu/-fienup/cs1520s18/homework The hw3.zip file contains: the Node class (in the node.py module) and the Node2Way class (in the nodc2way.py module) the skeleton CursorBasedList class (in the cursor_based_list.py module) which you will complete the cursorBasedListTester.py file that you can use to interactively test your CursorBasedList class. Recall that in a cursor-base list a cursor (indicating the current item) can be moved around the list with the cursor being used to identify the region of the list to be manipulated. We will insert and removing items relative to the current item. A current item must always be defined as long as the list is not em Cursor-based oper ations Description of operation L.getcurrent () L.hasNext () L.next L.hasPrevious() Precondition: the list is not empty. Returns the current item without removing it or changing the current position Precondition: the list is not empty. Returns True if the current item has a next item; otherwise return False Precondition: hasNext returns True. Postcondition: The current item has moved ght one item Precondition: the list is not empty. Returns True if the current item has a revious item; otherwise return False Precondition: hasPrevious returns True. Postcondition: The current item has moved left one item Precondition: the list is not empty, Makes the first item the current item Precondition: the list is not empty. Makes the last item the current item L.previous () L.first () L. last L.insertafter (item) Inserts item after the current item, or as the only item if the list is empty. The new item is the current item L.insertBefore (item) Inserts item before the current item, or as the only item if the list is empty. The new item is the current item L.replace (newValue) Precondition: the list is not empty. Replaces the current item by the new Value L.remove () Precondition: the list is not empty. Removes and returns the current item. Making the next item the current item if one exists; otherwise the tail item in teis the current item unless the list in now em The cursor_based list.py file contains a skeleton CursorBasedList class. You MUST uses a doubly-linked list implementation with a header node and a trailer node. All "real" list items will be inserted between the header and trailer nodes to reduce the number of"special cases" (e.g., inserting first item in an empty list, deleting the last item from the list, etc). An empty list looks like: header current trailer revious data next previous data next size 0 Use the provided cursorBasedListTester.py program to test your list. Objective: To gain experience implementing linked data structures by implementing a cursor-based list using doubly-linked nodes. To start the homework: Download and extract the file hw3.zip from http://www.cs.uni.edu/-fienup/cs1520s18/homework The hw3.zip file contains: the Node class (in the node.py module) and the Node2Way class (in the nodc2way.py module) the skeleton CursorBasedList class (in the cursor_based_list.py module) which you will complete the cursorBasedListTester.py file that you can use to interactively test your CursorBasedList class. Recall that in a cursor-base list a cursor (indicating the current item) can be moved around the list with the cursor being used to identify the region of the list to be manipulated. We will insert and removing items relative to the current item. A current item must always be defined as long as the list is not em Cursor-based oper ations Description of operation L.getcurrent () L.hasNext () L.next L.hasPrevious() Precondition: the list is not empty. Returns the current item without removing it or changing the current position Precondition: the list is not empty. Returns True if the current item has a next item; otherwise return False Precondition: hasNext returns True. Postcondition: The current item has moved ght one item Precondition: the list is not empty. Returns True if the current item has a revious item; otherwise return False Precondition: hasPrevious returns True. Postcondition: The current item has moved left one item Precondition: the list is not empty, Makes the first item the current item Precondition: the list is not empty. Makes the last item the current item L.previous () L.first () L. last L.insertafter (item) Inserts item after the current item, or as the only item if the list is empty. The new item is the current item L.insertBefore (item) Inserts item before the current item, or as the only item if the list is empty. The new item is the current item L.replace (newValue) Precondition: the list is not empty. Replaces the current item by the new Value L.remove () Precondition: the list is not empty. Removes and returns the current item. Making the next item the current item if one exists; otherwise the tail item in teis the current item unless the list in now em The cursor_based list.py file contains a skeleton CursorBasedList class. You MUST uses a doubly-linked list implementation with a header node and a trailer node. All "real" list items will be inserted between the header and trailer nodes to reduce the number of"special cases" (e.g., inserting first item in an empty list, deleting the last item from the list, etc). An empty list looks like: header current trailer revious data next previous data next size 0 Use the provided cursorBasedListTester.py program to test your list







