Question
Use this link to answer questions 1-5: https://phet.colorado.edu/sims/html/density/latest/density_en.html If that link doesn't work, please try https://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulations/prototypes then click on Density. After the PhET simulation opens,
Use this link to answer questions 1-5:https://phet.colorado.edu/sims/html/density/latest/density_en.html
If that link doesn't work, please tryhttps://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulations/prototypesthen click on "Density". After the PhET simulation opens, double-click on "Compare".
1. You will do several exercises to find the density of blocks made of various materials. The masses are either given or can be measured with a mass scale (in kilograms). The volume can be determined bycompletely submergingeach block into a pool of water.
The volume of the water in the pool without any blocks is V(no_blocks)= [ Select ] ["100.00 L", "0", "113.75 L", "118.75 L", "None of the given choices are correct."] .
Some blocks will sink on their own and some will float. When a block iscompletely submergedin the water, the new volume of water, V(with_block), will [ Select ] ["increase", "decrease", "stay the same"] . The volume of the block, V, can be calculated from: [ Select ] ["C", "A", "B", "D"]
A) V = V(no_block)- V(with_block) B) V = V(with_block)
C) V = V(with_block)- V(no_block) D) V = V(no_block)
2. At the bottom of the screen, double-click on the "Mystery" box. Five blocks of different masses and volumes will appear (if Set 1 is selected). Click on and drag each block onto the mass scale to measure its mass. Record it in the table below.
| Block | Mass (kg) |
| Purple (1A) | [ Select ] ["19.30 kg", "2.80 kg", "0.40 kg", "5.00 kg", "105.50 kg", "None of the given choices are correct."] |
| Blue (1B) | [ Select ] ["0.40 kg", "4.0 kg", "19.30 kg", "1.0 kg", "None of the given choices are correct."] |
| Yellow (1C) | [ Select ] ["19.32 kg", "0.40 kg", "101 kg", "2.8", "None of the given choices are correct."] |
| Red (1D) | [ Select ] ["5.00 kg", "0.40 kg", "19.30 kg", "None of the given choices are correct."] |
| Green (1E) | [ Select ] ["2.80 kg", "19.30 kg", "0.40 kg", "7.00 kg", "None of the given choices are correct."] |
3. Next, submerge each block into the pool to measure its volume. Record it in the table below.
| Block | Volume (L) |
| Purple (1A) | [ Select ] ["5.50 L", "105.50 L", "19.30 L", "0.40 L", "None of the given choices are correct."] |
| Blue (1B) | [ Select ] ["1.00 L", "100.40 L", "0.40 L", "101.00 L", "None of the given choices are correct."] |
| Yellow (1C) | [ Select ] ["1.00 L", "101.00 L", "19.32 L", "6.50 L", "None of the given choices are correct."] |
| Red (1D) | [ Select ] ["5.00 L", "105.00 L", "100.00 L", "1.00 L", "None of the given choices are correct."] |
| Green (1E) | [ Select ] ["7.00 L", "2.80 L", "107.00 L", "102.80 L", "None of the given choices are correct."] |
4. (This is a continuation of the previousExercise 3 - Mystery.)
Calculate the density of each block. Record everything in the table below.
| Block | Density, (kg/L) |
| Purple (1A) | [ Select ] ["3.51", "0.285", "106.15", "0.183", "5.46", "None of the given choices are correct."] |
| Blue (1B) | [ Select ] ["0.4", "0.16", "2.70", "0.83", "None of the given choices are correct."] |
| Yellow (1C) | [ Select ] ["19.32", "11.34", "8.96", "3.51", "None of the given choices are correct."] |
| Red (1D) | [ Select ] ["1.00", "0.95", "0.83", "0.68", "None of the given choices are correct."] |
| Green (1E) | [ Select ] ["0.4", "2.5", "19.6", "0.83", "None of the given choices are correct."] |
5. Click on "Density Table" to expand it. Use the table to identify the material each block is made of and record it in the table below.
| Block | Material |
| Purple (1A) | [purple] |
| Blue (1B) | [blue] |
| Yellow (1C) | [yellow] |
| Red (1D) | [red] |
| Green (1E) | [green] |
Group of answer choices
purple: [diamond gasoline gold water apple titanium glass ice lead copper wood steel]
blue: [diamond gasoline gold water apple titanium glass ice lead copper wood steel]
yellow: [diamond gasoline gold water apple titanium glass ice lead copper wood steel]
red: [diamond gasoline gold water apple titanium glass ice lead copper wood steel]
green: [diamond gasoline gold water apple titanium glass ice lead copper wood steel]
6. Mass measures the amount of matter an object has; volume measures the amount of space an object occupies.Density, D, is defined as the ratio of the mass (M) and the volume (V) of an object:
D =
The base SI unit for density is kilogram per cubic meter (kg/m3). Densities are also commonly expressed in grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm3). Another common unit is kilogram per liter (kg/L), where 1 kg/L = 103kg/m3.
Different objects may have different masses and volumes. However, objects made of the same material have the same density. Therefore, the density can be used to identify an unknown material.
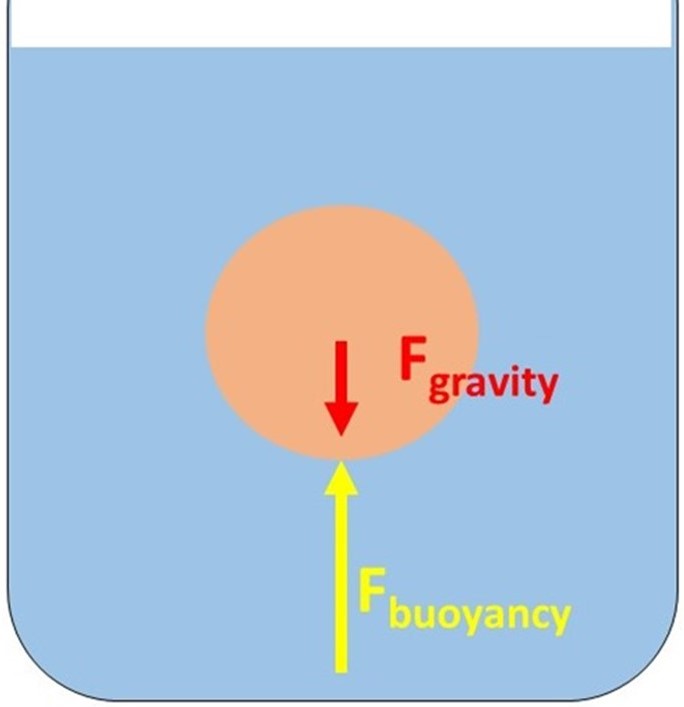
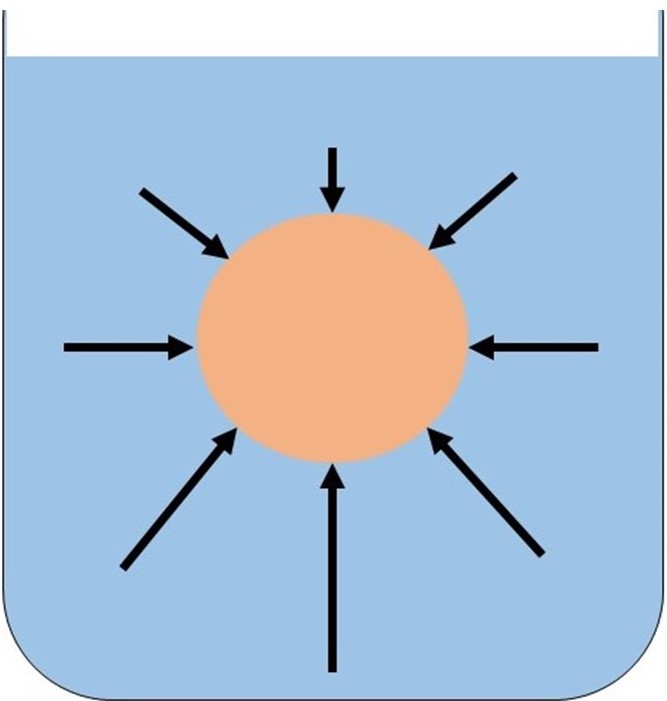
When an object is completely or partially submerged in a fluid, the pressure from the fluid is greater at the bottom of the object than higher up. This is shown in Fig. 1.
Figure 1:
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


