Question
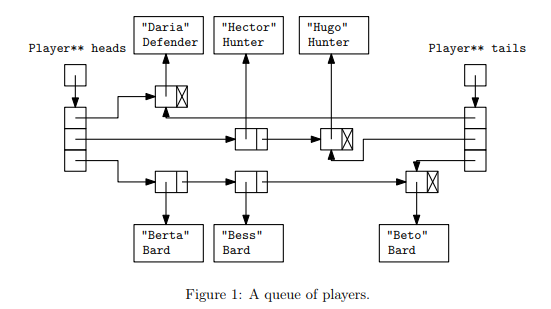
Use three linked-list-based queues, one for each player role and create a new C++ source file named lfgqueue.cpp that implements the LFGQueue class declared in
Use three linked-list-based queues, one for each player role and create a new C++ source file named lfgqueue.cpp that implements the LFGQueue class declared in lfgqueue.h such that provided files compile into a program that runs with no failed tests. Please use the files provided below and the final output after passing all the tests on main.cpp should output "Assignment complete."
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// (lfgqueue.h)
#ifndef LFGQUEUE_H #define LFGQUEUE_H #include "player.h" class LFGQueue { public: // All of the methods are the same // as in hwLFG1. LFGQueue(); int size(); void push_player(Player* p); Player* front_player(Player::Role r); void pop_player(Player::Role r); bool front_group(Player** group); void pop_group(); private: class Node { public: Player* p; Node* next; }; // You can index into these arrays using Player::Role values! // Check out player.h to see the int value of each Role. // // This lets you do things like: // "if (heads[p->role()] == nullptr)" and "++counts[p->role()]" Node* heads[3]; Node* tails[3]; int counts[3]; }; #endif
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// (player.h)
#ifndef PLAYER_H #define PLAYER_H #includeusing namespace std; class Player { public: // This works like a custom type with just three values. // Outside of Player methods, reference them like: // "if (p->role == Player::Defender)", etc. enum Role {Defender=0, Hunter=1, Bard=2}; // Initializes a player with the given name and role Player(string name, Role role); // Returns the name of the player string name(); // Returns the role of the player Role role(); private: string _name; Role _role; }; #endif
#include "player.h" Player :: Player(string name, Role role) { _name = name; _role = role; } string Player :: name() { return _name; } Player::Role Player :: role() { return _role; } #include#include #include #include "lfgqueue.h" using namespace std; inline void _test(const char* expression, const char* file, int line) { cerr name() == oss.str()); oss.str(""); oss name() == oss.str()); oss.str(""); oss name() == oss.str()); q.pop_group(); test(q.size() == 999 - 3 * (i+1)); } test(q.size() == 0); test(!q.front_group(group)); for (int i = 0; i (choice); string name; switch (role) { case Player::Defender: name = "Defender #?"; break; case Player::Hunter: name = "Hunter #?"; break; case Player::Bard: name = "Bard #?"; break; } q.push_player(new Player(name, role)); ++added[choice]; } test(q.size() == 1000000); // Remove as many complete groups as possible int complete_groups = added[0]; if (added[1]
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


