Question: 8- Nitrogen gas enters a turbine operating at steady state with a velocity of 60 m/s, a pressure of 0.345 MPa, and a temperature

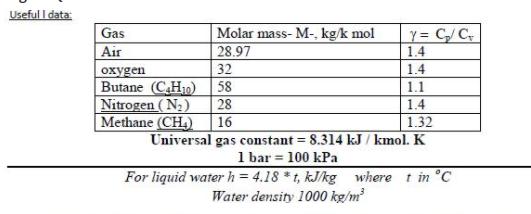
8- Nitrogen gas enters a turbine operating at steady state with a velocity of 60 m/s, a pressure of 0.345 MPa, and a temperature of 700 K. At the exit, the velocity is 0.6 m/s, the pressure is 0.14 MPa, and the temperature is 390 K. Heat transfer from the surface of the turbine to the surroundings occurs at a rate of 36 kJ per kg of nitrogen flowing. Neglecting potential energy effects and using the ideal gas model, determine the power developed by the turbine, in kJ/kg. Useful I data: Gas Molar mass- M-, kg/k mol 28.97 Y= C/C 1.4 Air 32 1.4 en Butane (C.H10) Nitrogen (N2) Methane (CH) 58 1.1 28 1.4 16 1.32 Universal gas constant = 8.314 kJ / kmol. K 1 bar = 100 kPa For liquid water h = 4.18 *t, kJ/kg where t in C Water density 1000 kg/m
Step by Step Solution
3.38 Rating (139 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
To find the power developed by the turbine we can apply the steadyflow energy equation First Law of ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


