Question
USING JAVA CODE THE FOLLOWING: PART 1: MODIFY EMPLOYEE.JAVA NOTE: The # symbol means the variable is protected as the access modifier. Also if it
USING JAVA CODE THE FOLLOWING:
PART 1: MODIFY EMPLOYEE.JAVA
NOTE: The # symbol means the variable is "protected" as the access modifier. Also if it is underlined, that means it is static.
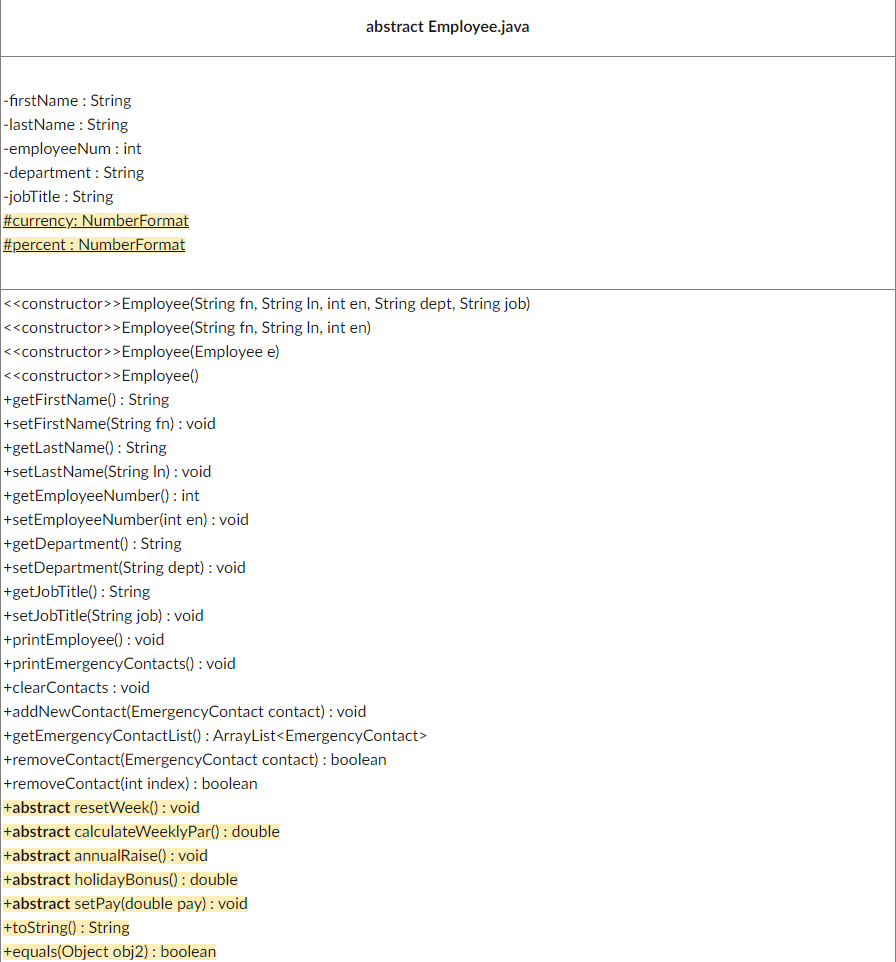
Note the following changes:
The class is now an abstract.
We have eliminated the following fields and their methods to get/set.
-hoursWorked
-payRate
Consequently we can't call the calculateWeeklyPay() or resetHours() method anymore as we don't have the variables, BUT we still need these methods in the sub classes. So to make sure they are there, we have them as abstract methods. NOTE: Since we are going to salary and commission employees those aren't "hourly" so resetHours() doesn't make sense for a method name, instead that is switched to "resetWeek()" Again though, you are not coding it here, just defining it as abstract. We also added annualRaise() and holidayBonus() as two other abstract methods.
Also note the first constructor, we don't have a payRate to send so we get rid of the "double pr" in the parameter list. Secondly, our other constructors hoursWorked and payRate to 0 each. You need to delete those in each of the constructors. Basically once you delete those fields in your class, you should see the errors for what you need to fix/delete.
Add in the following methods to @Override
-equals
-toString()
We have added 2 static protected variables that are NumberFormat objects. These will each be set to a default currency and percent NumberFormat object.
-currency
-percent
We now have can have our NumberFormat variables protected and static to help us in our sub classes. Make that change to the currency and ADD a percent formatter. These can then be used on the Hourly, Salary, and Commission employees as needed.
-protected static NumberFormat currency = NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance();
-protected static NumberFormat percent = NumberFormat.getPercentInstance();
We will have a problem with the percentage NumberFormat so setup the percent variable to have 3 decimal places. To do this you will need to add this in each constructor in the Employee class:
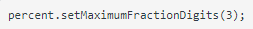
New Methods:
-equals(Object obj) - This method Overrides the Object equals(). It will, check that the object is an Employee type, convert it and then compare the employeeNum field to the current employeeNum. If they are the same, it will return true otherwise false.
-toString() - This method will return the same String contained in the printEmployee() method. You will want to refactor your code by making your print's saved into a single String with ' ' characters as needed.
Name: [firstName] [lastName] ID: [employeeNum] Department: [department] Title: [jobTitle]
EMPLOYEE.JAVA CODE TO MODIFY IS BELOW:
import java.text.NumberFormat; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.text.NumberFormat; import java.util.ArrayList; public class Employee { private String firstName; private String lastName; private int employeeNum; private String department; private String jobTitle; private double hoursWorked; private double payRate; private ArrayList emergencyContact; static NumberFormat currency = NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance(); Employee(String firstN, String lastN, int empNum) { hoursWorked = 0.0; firstName = firstN; lastName = lastN; employeeNum = empNum; department = ""; jobTitle = ""; payRate = 0.0; emergencyContact = new ArrayList(); } Employee(Employee emp) { hoursWorked = 0.0; firstName = emp.getFirstName(); lastName = emp.getLastName(); employeeNum = emp.getEmployeeNumber(); department = emp.getDepartment(); jobTitle = emp.getJobTitle(); payRate = emp.getPayRate(); emergencyContact = emp.getEmergencyContactList(); } Employee() { hoursWorked = 0.0; firstName = ""; lastName = ""; employeeNum = 0; department = ""; jobTitle = ""; payRate = 0.0; emergencyContact = new ArrayList(); } public String getFirstName() { return firstName; } public String getLastName() { return lastName; } public int getEmployeeNumber() { return employeeNum; } public String getDepartment() { return department; } public String getJobTitle() { return jobTitle; } public double getHoursWorked() { return hoursWorked; } public double getPayRate() { return payRate; } public void setFirstName(String firstN) { firstName = firstN; } public void setLastName(String lastN) { lastName = lastN; } public void setEmployeeNumber(int empNum) { employeeNum = empNum; } public void setDepartment(String depart) { department = depart; } public void setJobTitle(String jbTitle) { jobTitle = jbTitle; } public void setPayRate(double payRt) { payRate = payRt; } public void addHours() { hoursWorked += 1; } public void addHours(double h) { if(h > 0) hoursWorked +=h; } double calculateWeeklyPay(){ return payRate * hoursWorked; } public void resetHours() { hoursWorked = 0; } void printEmployee() { System.out.println("Name: " + firstName + " " + lastName); System.out.println("ID: " + employeeNum); System.out.println("Department: " + department); System.out.println("Title: " + jobTitle); System.out.println("Pay: " + currency.format(payRate)); System.out.println("Hours Worked: " + hoursWorked); } Employee(String firstN, String lastN, int empNum, String depart, String jbTitle, double payRt) { hoursWorked = 0.0; firstName = firstN; lastName = lastN; employeeNum = empNum; department = depart; jobTitle = jbTitle; payRate = payRt; emergencyContact = new ArrayList(); } public ArrayList getEmergencyContactList() { return emergencyContact; } public void clearContacts() { emergencyContact.clear(); } public void addNewContact(EmergencyContact contact) { emergencyContact.add(contact); } public boolean removeContact(EmergencyContact contact) { if (emergencyContact.contains(contact)) { emergencyContact.remove(contact); return true; } else { return false; } } public boolean removeContact(int index) { if (index >= 0 && index PART 2: CODE HOURLY EMPLOYEE:

Notes on Methods
Constructor - The constructor accepts all that an employee requires as well as a double for wage, and sets hoursWorked to 0.0.
toString - Overrides the Employee toString, but calls the super.toString and adding "Wage: " + wage and "Hours Worked: " + hoursWorked at the end each on their new line. (This is basically what we had setup for last iteration of the Employee class). Use the currency NumberFormat object on the wage variable.
Name: [firstName] [lastName] ID: [employeeNum] Department: [department] Title: [jobTitle] Wage: [wage] Hours Worked: [hoursWorked]
increaseHours() - This method adds 1 hour to hoursWorked variable
increaseHours(double h) - this method adds the value sent(h) to hoursWorked variable. Check so that we don't add negative hours to the employee.
resetWeek() - sets hoursWorked to 0.0
annualRaise() - give a wage increase of 5%
holidayBonus() return the amount of pay for working 40 hours (40 * wage)
calculateWeeklyPay() - Return amount earned in the week using wage and hoursWorked. However, any hours worked over 40 is considered overtime, so you need to calculate those extra hours as one and a half of the wage (1.5 * wage) * (hours - 40). You will probably need an if statement or do some math with modulus to calculate the hours over 40.
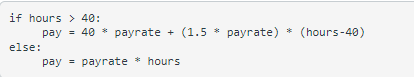
setPay(double pay) - should change the wage variable to the amount sent.
PART 3: CODE SALARY EMPLOYEE:
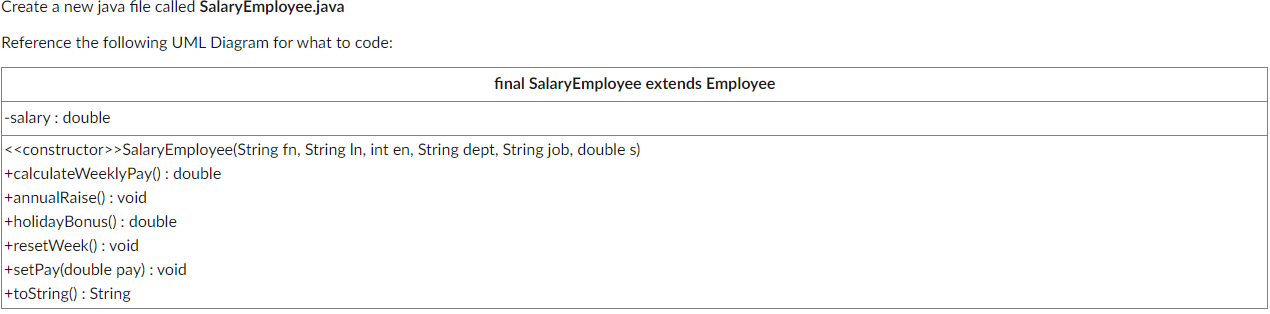
Notes on Methods:
Constructor - The constructor accepts all that an employee requires as well as a double for salary.
toString - Overrides the Employee toString, but calls the super.toString and adding "Salary: " + salary at the end of each on their own new line. Use the NumberFormat currency object on the salary variable.
Name: [firstName] [lastName] ID: [employeeNum] Department: [department] Title: [jobTitle] Salary: [salary]
calculateWeeklyPay() - returns weekly pay by taking the salary and dividing it by 52
annualRaise() - Salary increased by 6.25%
holidayBonus() - Returns 3.365% of salary
resetWeek() - Define this to leave it blank.
setPay(double pay) - should change the salary variable to the amount sent.
PART 4: CODE COMMISSION EMPLOYEE
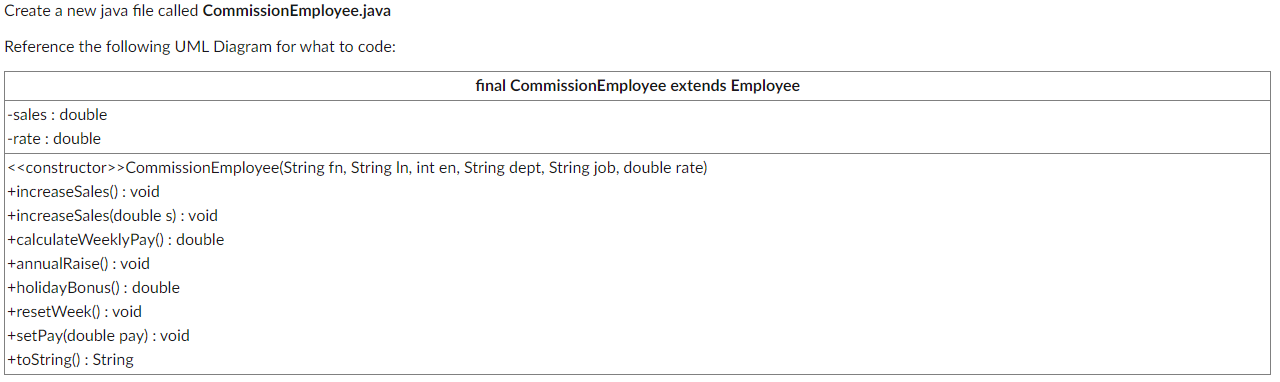
Notes on Methods:
Constructor - The constructor accepts all that an employee requires as well as a double for rate (in decimal form so 3.5% would be sent as .035). This also sets the sales to 0.0
toString - Overrides the Employee toString, but calls the super.toString, adding "Rate: " + rate and "Sales: " + sales each on a new line. Use the percent and currency NumberFormat objects on rate and sales respectively.
Name: [firstName] [lastName] ID: [employeeNum] Department: [department] Title: [jobTitle] Rate: [rate] Sales: [sales]
calculateWeeklyPay() - Returns the rate * sales
annualRaise() - Rate percentage increased by .002. example if rates is 3.5% it would be .035 + .002 so .037 or 3.7%
holidayBonus() - no bonus, return 0.
resetWeek() - reset sales to 0.0
increaseSales() - adds 100 to sales
increaseSales(double s) - adds the value sent (s) to sales. Again we shouldn't have negative sales add so make sure that the value sent is positive before adding.
setPay(double pay) - should change the rate variable to the amount sent.
abstract Employee.java -firstName : String -lastName : String -employeeNum : int -department : String -jobTitle : String \#currency: NumberFormat \#percent: NumberFormat > Employee(String fn, String In, int en, String dept, String job) > Employee(String fn, String In, int en) > Employee(Employee e ) > Employee() +getFirstName() : String +setFirstName(String fn) : void +getLastName() : String +setLastName(String In) : void +getEmployeeNumber() : int +setEmployeeNumber(int en) : void +getDepartment() : String +setDepartment(String dept) : void +getJobTitle() : String +setJobTitle(String job) : void +printEmployee() : void +printEmergencyContacts() : void +clearContacts : void +addNewContact(EmergencyContact contact) : void +getEmergencyContactList() : ArrayList +removeContact(EmergencyContact contact) : boolean +removeContact(int index) : boolean +abstract resetWeek() : void +abstract calculateWeeklyPar() : double +abstract annualRaise() : void +abstract holidayBonus() : double +abstract setPay(double pay) : void +toString(): String +equals(Object obj 2 ) : boolean percent.setMaximumFractionDigits(3); Create a new java file called HourlyEmployee.java Reference the following UML Diagram for what to code: final HourlyEmployee extends Employee -wage : double -hoursWorked : double > HourlyEmployee(String fn, String In, int en, String dept, String job, double w) +increaseHours() : void +increaseHours(double h) : void +calculateWeeklyPay() : double +annualRaise() : void +holidayBonus() : double +resetWeek() : void + setPay(double pay) : void +toString(): String ifhourspayelse:pay>40:=40payrate+(1.5payrate)(hours40)=payratehours Create a new java file called SalaryEmployee.java Reference the following UML Diagram for what to code: final SalaryEmployee extends Employee -salary : double > SalaryEmployee(String fn, String In, int en, String dept, String job, double s) +calculateWeeklyPay() : double +annualRaise() : void +holidayBonus() : double +resetWeek() : void +setPay(double pay) : void +toString(): String Create a new java file called CommissionEmployee.java Reference the following UML Diagram for what to code: final CommissionEmployee extends Employee -sales : double -rate : double > CommissionEmployee(String fn, String In, int en, String dept, String job, double rate) +increaseSales () : void +increaseSales(double s) : void +calculateWeeklyPay() : double +annualRaise() : void +holidayBonus() : double +resetWeek() : void +setPay(double pay) : void +toString(): String Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


