Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Using Recursion in Models and Decision Making: Relationships in Data IV.A Student Activity Sheet 2: Recursion and Linear Functions 1. Coen decides to take



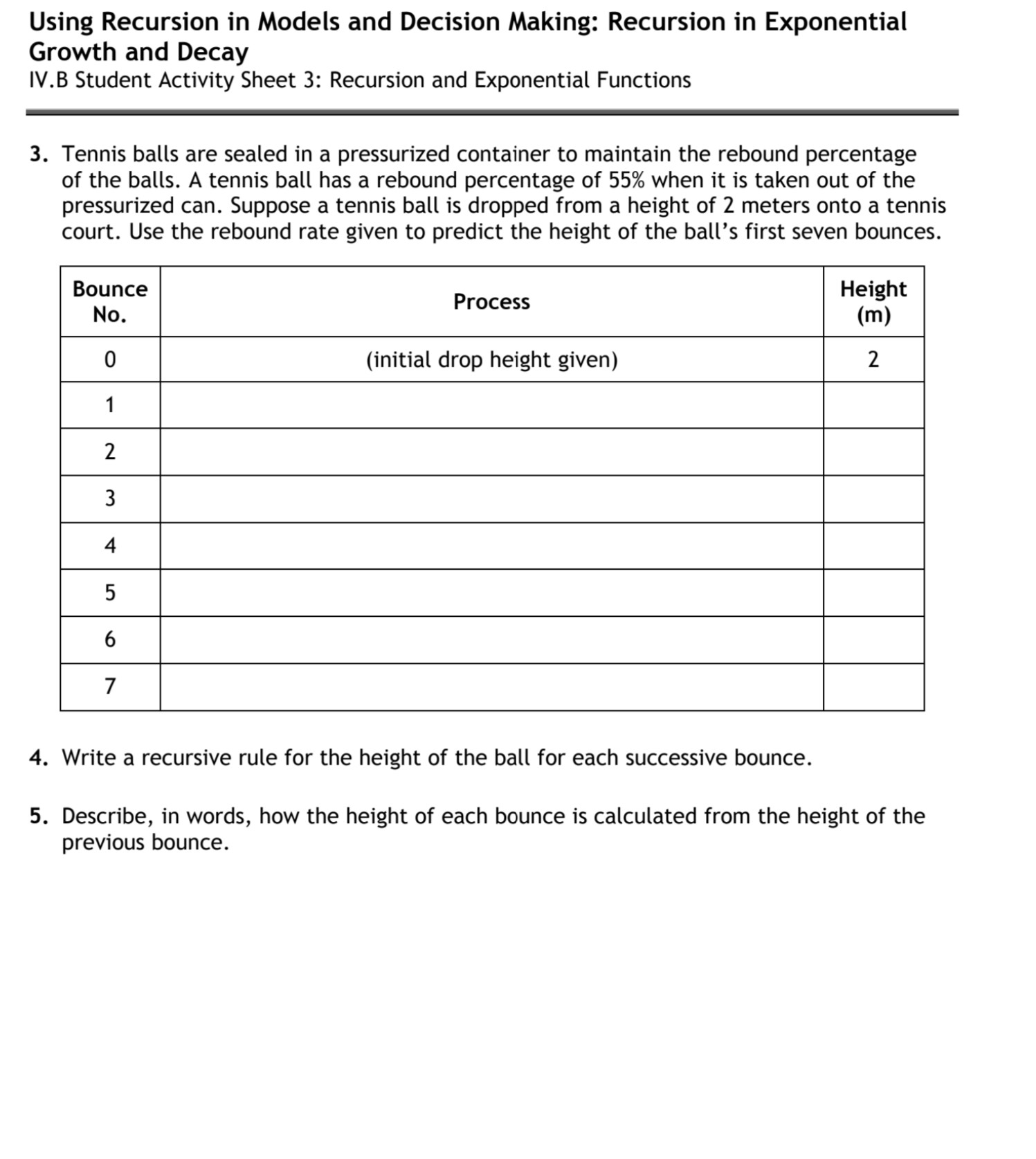
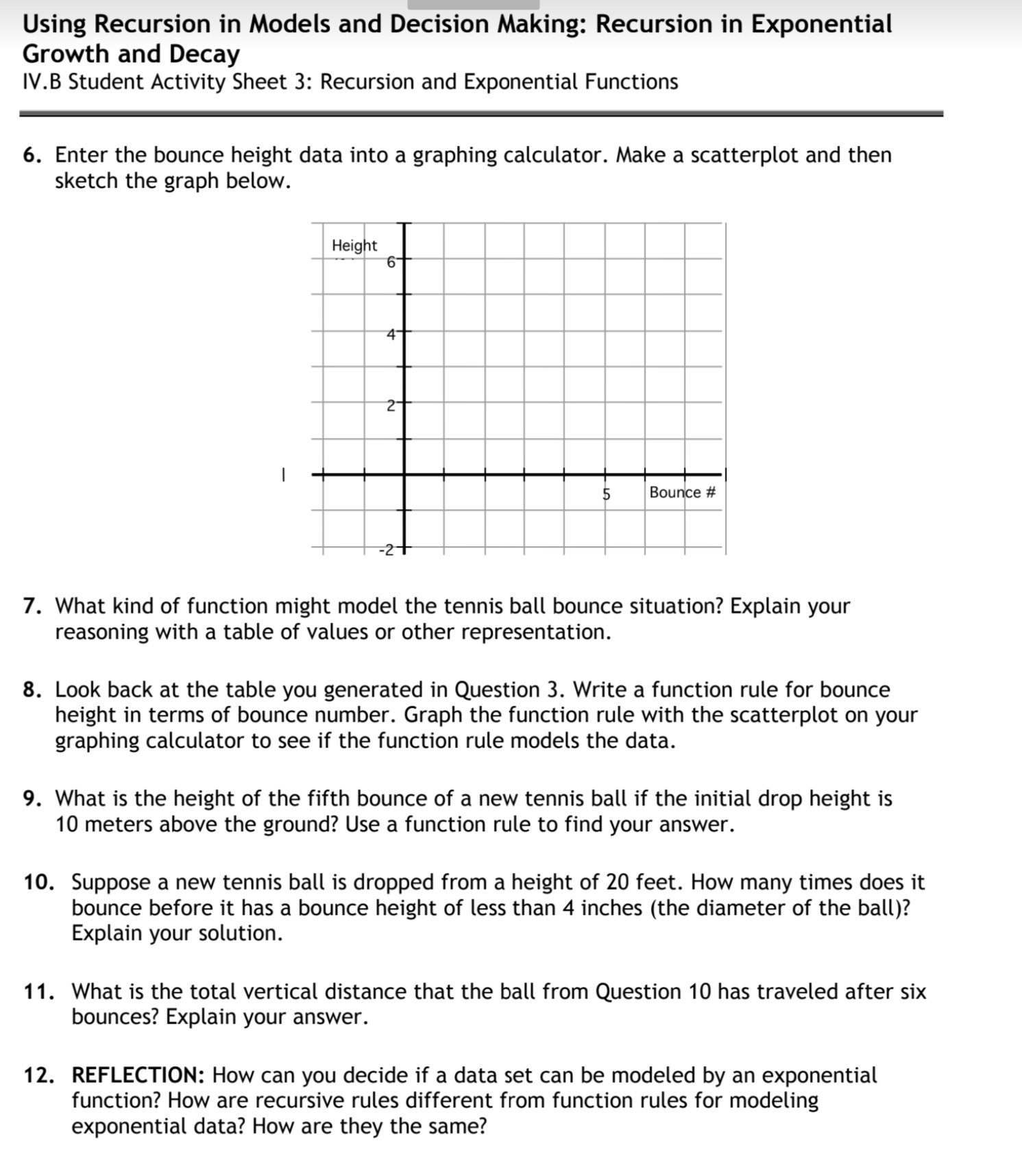
Using Recursion in Models and Decision Making: Relationships in Data IV.A Student Activity Sheet 2: Recursion and Linear Functions 1. Coen decides to take a job with a company that sells magazine subscriptions. He is paid $20 to start selling and then earns $1.50 for each subscription he sells. Fill in the following table, showing the amount of money (M) Coen earns for selling n subscriptions. Use the process column to note what is happening in each line. n 0 Process Mn Mo= M = M = M3 = M4= 2. Write a recursive rule for the amount of money Coen can earn selling magazine subscriptions. 3. REFLECTION: The rule in Question 2 defines a term (Mn + 1) with respect to the term that precedes it (Mn). Write a rule that defines a term (Mn) with respect to the term that precedes it (Mn - 1)? How is this rule similar to and different from the rule you wrote in Question 2? 4. Write an explicit function rule for the nth term in the sequence describing the amount of money Coen can earn. Describe any domain restrictions in your rule. How is this rule related to the rules you wrote in Question 2? Using Recursion in Models and Decision Making: Relationships in Data IV.A Student Activity Sheet 2: Recursion and Linear Functions 5. Use sequence notation to enter the data from your table in Question 1 in a graphing calculator, if your calculator has this capability. Limit your lists to 50 entries each. How do you expect the scatterplot of your data to look? Justify your reasoning. 6. How much does Coen earn if he sells 100 magazine subscriptions? Which rule did you use to answer this question? Why did you choose that rule? 7. Coen is trying to earn enough money to buy a new MP3 player. He needs $225 to cover the cost and tax on the MP3 player. How many magazine subscriptions does Coen need to sell to buy his new MP3 player? Justify your answer. Which rule did you use to answer this question? Why did you choose that rule? 8. Your phone service allows you to add international long distance to your phone. The cost is a $5 flat fee each month and 3 a minute for calls made. Write a recursive rule describing your monthly cost for international calls. Then write a function rule for the n minutes of calls made in a month. 9. REFLECTION How are recursive rules different from explicit function rules for modeling linear data? How are they the same? When are recursive rules more useful than function rules? When are function rules more useful? 10. EXTENSION: Think of a situation that can be described by a linear function. Model the situation using a recursive rule and a function rule. Write a question that is better answered using the recursive rule and give the solution. Using Recursion in Models and Decision Making: Recursion in Exponential Growth and Decay IV.B Student Activity Sheet 3: Recursion and Exponential Functions Different balls bounce at various heights depending on things like the type of ball, the pressure of air in the ball, and the surface on which it is bounced. The rebound percentage of a ball is found by determining the quotient of the rebound height (that is the height of each bounce) to the height of the ball before that bounce, converted to a percentage. 1. Collect data on a bouncing ball that show the maximum height of at least five bounces of the ball. Then make a scatterplot of the maximum height as a function of the bounce number. (Let Bounce 0 be the initial drop height of the ball.) Bounce No. Height 0 1 2 3 4 5 Height 41 2 5 Bounce 2. Find the average rebound percentage for your ball. Show your work. Bounce No. Height 0 1 2 3 4 5 Process Rebound Percentage Using Recursion in Models and Decision Making: Recursion in Exponential Growth and Decay IV.B Student Activity Sheet 3: Recursion and Exponential Functions 3. Tennis balls are sealed in a pressurized container to maintain the rebound percentage of the balls. A tennis ball has a rebound percentage of 55% when it is taken out of the pressurized can. Suppose a tennis ball is dropped from a height of 2 meters onto a tennis court. Use the rebound rate given to predict the height of the ball's first seven bounces. Bounce No. 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Process (initial drop height given) Height (m) 2 4. Write a recursive rule for the height of the ball for each successive bounce. 5. Describe, in words, how the height of each bounce is calculated from the height of the previous bounce. Using Recursion in Models and Decision Making: Recursion in Exponential Growth and Decay IV.B Student Activity Sheet 3: Recursion and Exponential Functions 6. Enter the bounce height data into a graphing calculator. Make a scatterplot and then sketch the graph below. Height 6 4 21 5 Bounce # 7. What kind of function might model the tennis ball bounce situation? Explain your reasoning with a table of values or other representation. 8. Look back at the table you generated in Question 3. Write a function rule for bounce height in terms of bounce number. Graph the function rule with the scatterplot on your graphing calculator to see if the function rule models the data. 9. What is the height of the fifth bounce of a new tennis ball if the initial drop height is 10 meters above the ground? Use a function rule to find your answer. 10. Suppose a new tennis ball is dropped from a height of 20 feet. How many times does it bounce before it has a bounce height of less than 4 inches (the diameter of the ball)? Explain your solution. 11. What is the total vertical distance that the ball from Question 10 has traveled after six bounces? Explain your answer. 12. REFLECTION: How can you decide if a data set can be modeled by an exponential function? How are recursive rules different from function rules for modeling exponential data? How are they the same?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


