Using Table 5.3 as your guide, what is your estimate of the expected annual HPR on the S&P 500 stock portfolio if the current risk-free interest rate is 5.3%? (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.)
Expected annual HPR %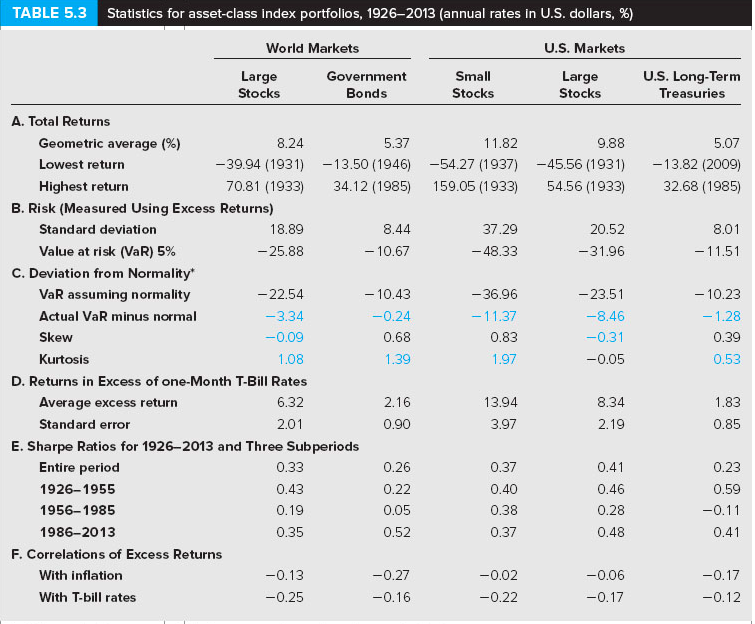
TABLE 5.3 Statistics for asset-class index portfolios, 1926-2013 (annual rates in U.S. dollars, %) World Markets U.S. Markets Government Bonds Small Stocks U.S. Long-Term Treasuries arge arge Stocks Stocks A. Total Returns Geometric average (%) Lowest return Highest return 5.07 -39.94 (1931) -13.50 (1946) -54.27 (1937) -45.56 (1931) -13.82 (2009) 70.81 (1933) 34.12 (1985) 159.05 (1933) 54.56 (1933) 32.68 (1985) 8.24 5.37 9.88 B. Risk (Measured Using Excess Returns) 37.29 -48.33 20.52 31.96 8.01 11.51 Standard deviation 18.89 8.44 Value at risk (VaR) 5% -25.88 -10.67 C. Deviation from Normality -22.54 3.34 0.09 1.08 D. Returns in Excess of one-Month T-Bill Rates 6.32 2.01 VaR assuming normality Actual VaR minus normal Skew Kurtosis 10.43 -0.24 0.68 1.39 -36.96 -11.37 0.83 1.97 23.51 8.46 0.31 -0.05 10.23 1.28 0.39 0.53 Average excess return Standard error 2.16 0.90 13.94 3.97 8.34 0.85 E. Sharpe Ratios for 1926-2013 and Three Subperiods Entire period 1926-1955 1956-1985 1986-2013 0.33 0.43 0.26 0.22 0.05 0.52 0.37 0.40 0.38 0.37 0.23 0.59 0.46 0.28 0.35 F. Correlations of Excess Returns -0.02 -0.22 With inflation 0.27 0.06 0.17 0.17 With T-bill rates 0.25 TABLE 5.3 Statistics for asset-class index portfolios, 1926-2013 (annual rates in U.S. dollars, %) World Markets U.S. Markets Government Bonds Small Stocks U.S. Long-Term Treasuries arge arge Stocks Stocks A. Total Returns Geometric average (%) Lowest return Highest return 5.07 -39.94 (1931) -13.50 (1946) -54.27 (1937) -45.56 (1931) -13.82 (2009) 70.81 (1933) 34.12 (1985) 159.05 (1933) 54.56 (1933) 32.68 (1985) 8.24 5.37 9.88 B. Risk (Measured Using Excess Returns) 37.29 -48.33 20.52 31.96 8.01 11.51 Standard deviation 18.89 8.44 Value at risk (VaR) 5% -25.88 -10.67 C. Deviation from Normality -22.54 3.34 0.09 1.08 D. Returns in Excess of one-Month T-Bill Rates 6.32 2.01 VaR assuming normality Actual VaR minus normal Skew Kurtosis 10.43 -0.24 0.68 1.39 -36.96 -11.37 0.83 1.97 23.51 8.46 0.31 -0.05 10.23 1.28 0.39 0.53 Average excess return Standard error 2.16 0.90 13.94 3.97 8.34 0.85 E. Sharpe Ratios for 1926-2013 and Three Subperiods Entire period 1926-1955 1956-1985 1986-2013 0.33 0.43 0.26 0.22 0.05 0.52 0.37 0.40 0.38 0.37 0.23 0.59 0.46 0.28 0.35 F. Correlations of Excess Returns -0.02 -0.22 With inflation 0.27 0.06 0.17 0.17 With T-bill rates 0.25







