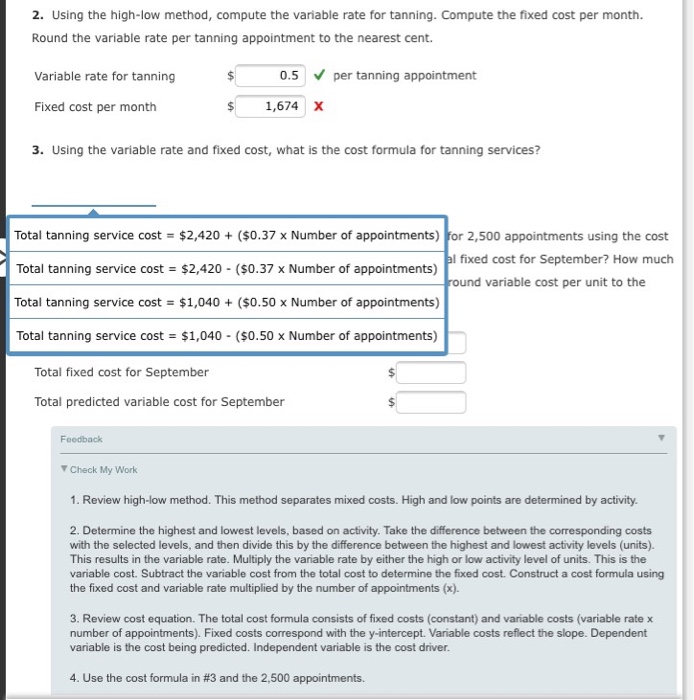
Using the high-low method, compute the variable rate for tanning. Compute the fixed cost per month. Round the variable rate per tanning appointment to the nearest cent. Variable rate for tanning $ 0.5 per tanning appointment Fixed cost per month $ 1, 674 Using the variable rate and fixed cost, what is the cost formula for tanning services? Total fixed cost for September $ Total predicted variable cost for September $ Review high-low method. This method separates mixed costs. High and low points are determined by activity. Determine the highest and lowest levels, based on activity. Take the difference between the corresponding costs with the selected levels, and then divide this by the difference between the highest and lowest activity levels (units). This results in the variable rate. Multiply the variable rate by either the high or low activity level of units. This is the variable cost. Subtract the variable cost from the total cost to determine the fixed cost. Construct a cost formula using the fixed cost and variable rate multiplied by the number of appointments (x). Review cost equation. The total cost formula consists of fixed costs (constant) and variable costs (variable rate x number of appointments). Fixed costs correspond with the y-intercept. Variable costs reflect the slope. Dependent variable is the cost being predicted. Independent variable is the cost driver. Use the cost formula in #3 and the 2.500 appointments. Using the high-low method, compute the variable rate for tanning. Compute the fixed cost per month. Round the variable rate per tanning appointment to the nearest cent. Variable rate for tanning $ 0.5 per tanning appointment Fixed cost per month $ 1, 674 Using the variable rate and fixed cost, what is the cost formula for tanning services? Total fixed cost for September $ Total predicted variable cost for September $ Review high-low method. This method separates mixed costs. High and low points are determined by activity. Determine the highest and lowest levels, based on activity. Take the difference between the corresponding costs with the selected levels, and then divide this by the difference between the highest and lowest activity levels (units). This results in the variable rate. Multiply the variable rate by either the high or low activity level of units. This is the variable cost. Subtract the variable cost from the total cost to determine the fixed cost. Construct a cost formula using the fixed cost and variable rate multiplied by the number of appointments (x). Review cost equation. The total cost formula consists of fixed costs (constant) and variable costs (variable rate x number of appointments). Fixed costs correspond with the y-intercept. Variable costs reflect the slope. Dependent variable is the cost being predicted. Independent variable is the cost driver. Use the cost formula in #3 and the 2.500 appointments