Question
Using the information below from your JetBlue IPO case for problems 1-3: 1- Using only the information provided in the table, you decide to value
Using the information below from your JetBlue IPO case for problems 1-3:
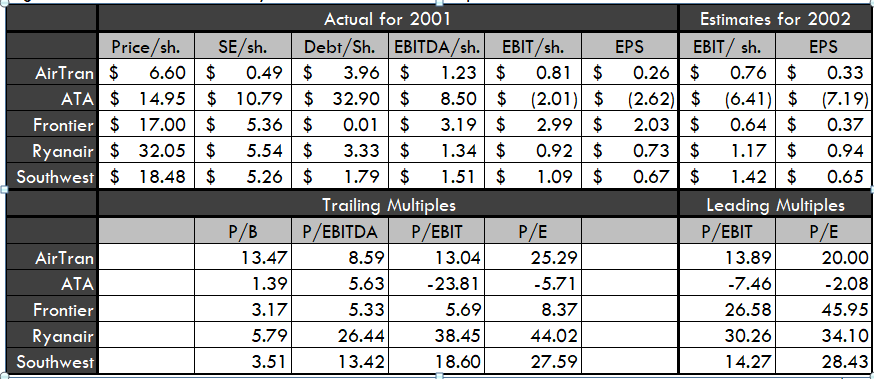
1- Using only the information provided in the table, you decide to value JetBlues IPO using either a P/EBIT or P/E multiple. Based on this decision, which comparable company would you be most likely exclude from your analysis?
A) AirTran, because it is valued at a discount to Frontier, Ryanair, and Southwest on a leading multiple basis
B) ATA, because it would produce anirrationalshare price for JetBlue
C) Frontier, because it is an airline major, not a low cost provider
D) Rynair, because it is bigger and more established than JetBlue
E) Southwest, because it is a low cost provider, not an airline major
2- Using the information provided in the table and the sales, fixed Assets, EBIT, and depreciation figures from the financial forecast provided to you in your student worksheet JetBlue IPO case file, you decide to value JetBlues IPO using either a P/EBIT or P/E multiple. Assume JetBlues IPO price was for $25.00 per share and there were 35 total units of common shares. To remove outliers, calculate the five company median for each multiple. You decide to compare the valuation you get for JetBlue using lagging P/EBIT and lagging P/E (weighed equally) tothe valuation you get for JetBlue using leading P/EBIT and leading P/E (weighted equally). Which of the following statement is most likely TRUE (2 points):
A) JetBlues IPO price was at a 38% discount to the value derived from leadingmultiple relative valuation
B) JetBlues IPO price was at a 47% discount to the value derived from leading multiple relative valuation
C) JetBlues IPO price was at a 62% discount to the value derived from lagging multiple relative valuation
D) JetBlues IPO price was at a 62% premium to the value derived from lagging multiple relative valuation
E) JetBlues IPO price was at a 87% premium to the value derived from leading multiple relative valuation
3- Using the sales, fixed Assets, EBIT, and depreciation figures from the financial forecast provided to you in your student worksheet JetBlue IPO case file. Calculate depreciation as a percentage of fixed assets. Compare the useful life of fixed assets in 2002 to the useful life of fixed assets in 2001. Which of the following statements is most likely TRUE:
A) In 2002, the useful life of fixed assets was 5.5 years shorter than the useful life of fixed assets in 2001
B) In 2002, the useful life of fixed assets was 2.2 years shorter than the useful life of fixed assets in 2001
C) In 2002, the useful life of fixed assets was 2.0 years longer than the useful life of fixed assets in 2001
D) In 2002, the useful life of fixed assets was 2.2 years longer than the useful life of fixed assets in 2001
E) In 2002, the useful life of fixed assets was 5.5 years longer than the useful life of fixed assets in 2001
Actual for 2001 Estimates for 2002 Price/sh.E/sh. Debt/Sh. EBITDA/sh. EBIT/sh. EPS EBIT sh. EPS $6.60$ 0.493.96$ 1.230.810.26$ 0.760.33 AirTran AlAS IA.9S $ 1tL/9 $ 32.90 $ 8iO $ (2.Ol ) $ (2.62) $ (Al) $ (.19) Frontier Ryanair Southwest $ 17.005.36$0.01$ 3.19 2.99$ 2.03 0.640.37 $ 32.055.543.33 $ 1.34 0.92$ 0.73 1.17 0.94 $ 18.48$ 5.26$1.79 $1.51$ 1.09 0.67 $1.42 $ 0.65 Trailing Multiples | P/EBITDA| 8.59 Leading Multiples /EBIT P/B P/EBIT 13.04 25.29 AirTran Frontier Ryanair Southwest 13.89 26.58 45.95 14.27 20.00 2.08 13.47 1.39 3.17 5.7926.4438.45 44.02 3.51 5.63-23.81 5.33 5.69 3026 34.10 18.60 28.43 13:42 9.0027.3Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


