Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Using these information of Characterization tests of alkanes and alkenes lab, please solve and fill the two tables (Table3, Table4) and write or show the
Using these information of Characterization tests of alkanes and alkenes lab, please solve and fill the two tables (Table3, Table4)
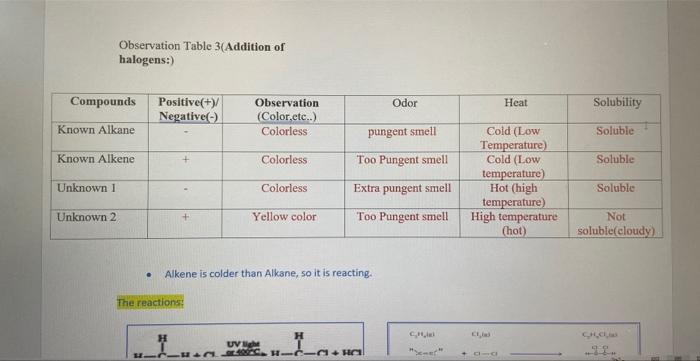
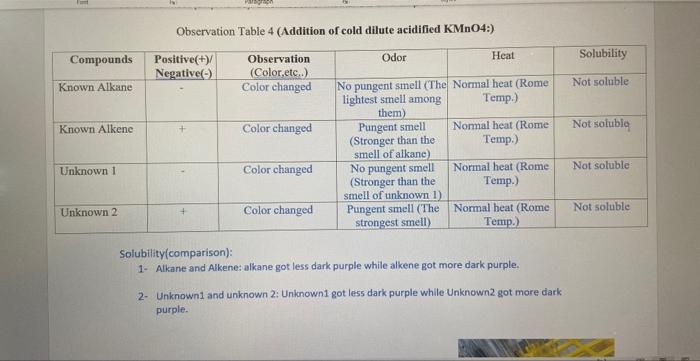
Characterization tests of Alkanes and Alkenes Organic chemistry A. Introduction Compounds known as hydrocarbons only contain the atoms of hydrogen ( H2 ) and carbon (C2). Additionally, they are primarily employed as fuels and solvents. Each family of hydrocarbons has a unique pattern of bonding (alkane, alkene, alkyne, aromatic). Alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes are simple hydrocarbon chains devoid of functional groups. The most fundamental organic compounds are alkanes. Alkanes that only have a single bond between the carbon atoms are known as saturated hydrocarbons. Alkenes include at least one carbon-carbon double bond. Pre -Laboratory Questions: 1. Explain Markovnikoff s rule and the formation of carbocation. The Markovnikov rule is closely related to the formation of carbocations, which are intermediate species formed during the addition of a hydrogen halide to an alkene. Pre -Laboratory Questions: 1. Explain Markovnikoff's rule and the formation of carbocation. The Markovnikov rule is closely related to the formation of carbocations, which are intermediate species formed during the addition of a hydrogen halide to an alkene. The rule states that in the addition of a hydrogen halide (HX) to an alkene, the hydrogen atom will bond to the carbon atom that already has the most hydrogen atoms bonded to it (the more substituted carbon), while the halide will bond to the carbon atom that has the least number of hydrogen atoms bonded to it (the less substituted carbon). This is because, in the addition process, the carbon atom that has the most hydrogens attached to it is more stable due to the inductive effect and this is called Markovnikov's rule. When the HX molecule adds to the alkene, the carbon atom that receives the hydrogen atom forms a carbocation. This carbocation is more stable if it has more alkyl groups attached to it, which is the basis of the Markovnikov rule. Thus, the rule predicts that the carbocation will form on the more substituted carbon of the alkene, which leads to the formation of the most stable carbocation. Give ONE (1) example in detail of an alkane and alkene commonly used. (You can include its physical and chemical properties, uses and any relevant information) Alkane molecule: Propane Propane is a three-carbon alkane hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C3H8. It is a colourless, odourless, and flammable gas that is commonly used as a fuel source for heating, cooking, and transportation. Physical Properties: - Propane is a gas at room temperature and atmospheric pressure, with a boiling point of 42C. - It has a density of 1.52g/L at room temperature and pressure. - It has a high-octane number and low specific gravity. - It is non-toxic and non-corrosive. - Propane has low ignition energy and a wide flammable range, making it a good fuel for combustion. Chemical Properties: - It is an alkane hydrocarbon, meaning it is composed of only carbon and hydrogen atoms. - Propane is a highly flammable substance, with a flash point of 104C, - It is relatively stable and does not react readily with other chemicals. - Propane is a widely used fuel source, particularly in rural and remote areas where natural gas pipelines are not available. - It is commonly used for heating homes and water, as well as for powering generators, stoves, and grills. - It is also used as fuel for vehicles, particularly for forklifts and other industrial equipment. - In the industry, propane is used as a raw material to produce various chemicals like acrylonitrile, propylene oxide, isopropyl alcohol, and propylene glycol. Propane is a hydrocarbon and thus, its combustion produces carbon dioxide and water vapor and also smail amounts of other pollutants like nitrogen oxides and particulate matter. Therefore, it is important to use it in an efficient and clean way. Test 3: Addition of halogens: - 20 liquid drops of liquid alkane were placed in one test tube, 20 liquid drops of liquid alkene were placed in another test tube, 20 drops of unknown compound number one was placed in a third test tube, and 20 drops of unknown compound number two was placed in a fourth test tube. -Each test tube contains 10 drops of bromine dissolved in chloroform, which is placed in a clean pipette. After shaking it, we wait five minutes before examining the results. Test 4: Addition of cold dilute acidified KMnO4: - 20 drops of liquid alkane were placed in one test tube, 20 drops of liquid alkene were placed in another test tube, 20 drops of unknownl compound was placed in a third test tube, and 20 drops of unknown compound number two was placed in a fourth test tube. Each test tube received 10 drops of diluted acidified (KMnO4) at room temperature from a clean pipette. After shaking it, we wait five minutes before examining the results. Moreover, we repeated everything then we brought a big beaker and put hot water in it, after that we brought the four tubes and put them inside the hot water bath, and we waited five minutes. For each test you need to: 1. Observations ( Color, odor, Heat Solubility etc) 2. The chemical reactions that occurs Observation Table 3(Addition of halogens:) - Alkene is colder than Alkane, so it is reacting. Observation Table 4 (Addition of cold dilute acidified KMnO4:) Solubility(comparison): 1- Alkane and Alkene: alkane got less dark purple while alkene got more dark purple. 2- Unknown1 and unknown 2: Unknown1 got less dark purple while Unknown2 got more dark purple. Characterization tests of Alkanes and Alkenes Organic chemistry A. Introduction Compounds known as hydrocarbons only contain the atoms of hydrogen ( H2 ) and carbon (C2). Additionally, they are primarily employed as fuels and solvents. Each family of hydrocarbons has a unique pattern of bonding (alkane, alkene, alkyne, aromatic). Alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes are simple hydrocarbon chains devoid of functional groups. The most fundamental organic compounds are alkanes. Alkanes that only have a single bond between the carbon atoms are known as saturated hydrocarbons. Alkenes include at least one carbon-carbon double bond. Pre -Laboratory Questions: 1. Explain Markovnikoff s rule and the formation of carbocation. The Markovnikov rule is closely related to the formation of carbocations, which are intermediate species formed during the addition of a hydrogen halide to an alkene. Pre -Laboratory Questions: 1. Explain Markovnikoff's rule and the formation of carbocation. The Markovnikov rule is closely related to the formation of carbocations, which are intermediate species formed during the addition of a hydrogen halide to an alkene. The rule states that in the addition of a hydrogen halide (HX) to an alkene, the hydrogen atom will bond to the carbon atom that already has the most hydrogen atoms bonded to it (the more substituted carbon), while the halide will bond to the carbon atom that has the least number of hydrogen atoms bonded to it (the less substituted carbon). This is because, in the addition process, the carbon atom that has the most hydrogens attached to it is more stable due to the inductive effect and this is called Markovnikov's rule. When the HX molecule adds to the alkene, the carbon atom that receives the hydrogen atom forms a carbocation. This carbocation is more stable if it has more alkyl groups attached to it, which is the basis of the Markovnikov rule. Thus, the rule predicts that the carbocation will form on the more substituted carbon of the alkene, which leads to the formation of the most stable carbocation. Give ONE (1) example in detail of an alkane and alkene commonly used. (You can include its physical and chemical properties, uses and any relevant information) Alkane molecule: Propane Propane is a three-carbon alkane hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C3H8. It is a colourless, odourless, and flammable gas that is commonly used as a fuel source for heating, cooking, and transportation. Physical Properties: - Propane is a gas at room temperature and atmospheric pressure, with a boiling point of 42C. - It has a density of 1.52g/L at room temperature and pressure. - It has a high-octane number and low specific gravity. - It is non-toxic and non-corrosive. - Propane has low ignition energy and a wide flammable range, making it a good fuel for combustion. Chemical Properties: - It is an alkane hydrocarbon, meaning it is composed of only carbon and hydrogen atoms. - Propane is a highly flammable substance, with a flash point of 104C, - It is relatively stable and does not react readily with other chemicals. - Propane is a widely used fuel source, particularly in rural and remote areas where natural gas pipelines are not available. - It is commonly used for heating homes and water, as well as for powering generators, stoves, and grills. - It is also used as fuel for vehicles, particularly for forklifts and other industrial equipment. - In the industry, propane is used as a raw material to produce various chemicals like acrylonitrile, propylene oxide, isopropyl alcohol, and propylene glycol. Propane is a hydrocarbon and thus, its combustion produces carbon dioxide and water vapor and also smail amounts of other pollutants like nitrogen oxides and particulate matter. Therefore, it is important to use it in an efficient and clean way. Test 3: Addition of halogens: - 20 liquid drops of liquid alkane were placed in one test tube, 20 liquid drops of liquid alkene were placed in another test tube, 20 drops of unknown compound number one was placed in a third test tube, and 20 drops of unknown compound number two was placed in a fourth test tube. -Each test tube contains 10 drops of bromine dissolved in chloroform, which is placed in a clean pipette. After shaking it, we wait five minutes before examining the results. Test 4: Addition of cold dilute acidified KMnO4: - 20 drops of liquid alkane were placed in one test tube, 20 drops of liquid alkene were placed in another test tube, 20 drops of unknownl compound was placed in a third test tube, and 20 drops of unknown compound number two was placed in a fourth test tube. Each test tube received 10 drops of diluted acidified (KMnO4) at room temperature from a clean pipette. After shaking it, we wait five minutes before examining the results. Moreover, we repeated everything then we brought a big beaker and put hot water in it, after that we brought the four tubes and put them inside the hot water bath, and we waited five minutes. For each test you need to: 1. Observations ( Color, odor, Heat Solubility etc) 2. The chemical reactions that occurs Observation Table 3(Addition of halogens:) - Alkene is colder than Alkane, so it is reacting. Observation Table 4 (Addition of cold dilute acidified KMnO4:) Solubility(comparison): 1- Alkane and Alkene: alkane got less dark purple while alkene got more dark purple. 2- Unknown1 and unknown 2: Unknown1 got less dark purple while Unknown2 got more dark purple and write or show the reactions that accurs for each, (Please as fast as possible) 















Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


