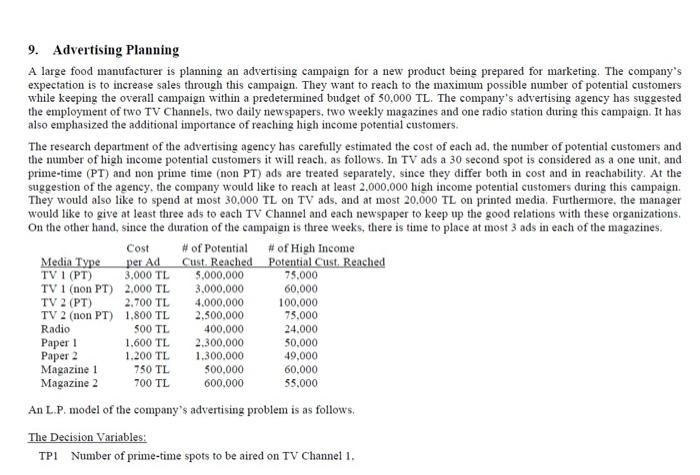
V. The Advertising Planning Problem 5. How would the L.P. model related to this problem and the optimal value be effected, after the following alterations/additions? Regarding possible changes in the optimal solution and/or the optimal value, just state whether a change is expected or not and the direction of the change if it is expected. 1) The company insists on having some radio commercials within the framework of this advertising campaign. ii) The value of which variable or parameter in the optimal primal or dual solution would give you information regarding the potential benefit or loss to the company in terms of the number of potential customers reached) regarding the additional condition stated in (i)? iii) The value of which variable or parameter in the optimal primal or dual solution would give you information regarding the potential benefit or loss to the company in terms of the number of potential customers reached) of insisting on at least 3 ads per newspaper? iv) The value of which variable or parameter in the optimal primal or dual solution would give you information regarding the potential benefit or loss to the company in terms of the number of potential customers reached) on insisting to reach high income group potential customers (assuming that the budget and other conditions remain the same) T2 Number of non prime-time spots to be aired on TV Channel 1, TP2 Number of prime-time spots to be aired on TV Channel 2. Number of non prime-time spots to be aired on TV Channel 2. R1 Number of spots to be aired on the radio channel, G1 Number of ads to be placed in Newspaper 1. G2 Number of ads to be placed in Newspaper 2. MI Number of ads to be placed in Magazine 1, M2 Number of ads to be placed in Magazine 2. The objective (in units of 1000 persons): Max 5000 TP1+3000 T1+ 4000 TP2+ 2500 T2+ 400 R1+2300 GI+ 1300 G2+ 500 Ml+ 600 M2 The Constraints: 3.0 TP1+ 2.0 TI+2.7 TP2+ 1.8 T2+0.5 R1+ 1.6 G1+ 1.2 G2+0.75M1+0.7 M2 530 75 TP1+60 TI+ 100 TP2+ 75 T2+ 24R1+ 50 GI+ 49 G2+ 60 MI+ 55 M2 22000 3.0 TP1+2.0 TI+2.7 TP2+ 1.8 T2 1.6G1+1.2 G2+0.75 M1+0.7 M2 TP1+ TI 23 TP2+ T2 S30 5 20 23 G2 23 MI 53 M2 53 TPI, TI, TP2, T2, R1. MI, M2 20 Such models may be employed in similar problems faced in marketing and advertising activities in various sectors. However, it should be noted that the constructed objective function (ie, total number of potential customers reached through the campaign) is again at most a "proxy" for the real objective the managers have in mind, which is to increase sales and and/or profits through such a campaign. 9. Advertising Planning A large food manufacturer is planning an advertising campaign for a new product being prepared for marketing. The company's expectation is to increase sales through this campaign. They want to reach to the maximum possible number of potential customers while keeping the overall campaign within a predetermined budget of 50,000 TL. The company's advertising agency has suggested the employment of two TV Channels, two daily newspapers, two weekly magazines and one radio station during this campaign. It has also emphasized the additional importance of reaching high income potential customers. The research department of the advertising agency has carefully estimated the cost of each ad, the number of potential customers and the number of high income potential customers it will reach, as follows. In TV ads a 30 second spot is considered as a one unit, and prime-time (PT) and non prime time (non PT) ads are treated separately, since they differ both in cost and in reachability. At the suggestion of the agency, the company would like to reach at least 2.000.000 high income potential customers during this campaign. They would also like to spend at most 30.000 TL on TV ads, and at most 20.000 TL on printed media. Furthermore, the manager would like to give at least three ads to each TV Channel and each newspaper to keep up the good relations with these organizations. On the other hand, since the duration of the campaign is three weeks, there is time to place at most 3 ads in each of the magazines. Cost # of Potential of High Income Media Type per Ad Cust. Reached Potential Cust. Reached TV I (PT) 3.000 TL 5,000,000 75.000 TV 1 (non PT) 2.000 TL 3.000.000 60,000 TV 2 (PT) 2.700 TL 4.000.000 100,000 TV 2 (non PT) 1,800 TL 2,500,000 75.000 Radio 500 TL 400.000 24.000 Paper 1 1,600 TL 2,300,000 50.000 Paper 2 1.200 TL 1,300,000 49,000 Magazine 1 750 TL 500.000 60.000 Magazine 2 700 TL 600.000 55.000 An L.P. model of the company's advertising problem is as follows. The Decision Variables: TPI Number of prime-time spots to be aired on TV Channel I. V. The Advertising Planning Problem 5. How would the L.P. model related to this problem and the optimal value be effected, after the following alterations/additions? Regarding possible changes in the optimal solution and/or the optimal value, just state whether a change is expected or not and the direction of the change if it is expected. 1) The company insists on having some radio commercials within the framework of this advertising campaign. ii) The value of which variable or parameter in the optimal primal or dual solution would give you information regarding the potential benefit or loss to the company in terms of the number of potential customers reached) regarding the additional condition stated in (i)? iii) The value of which variable or parameter in the optimal primal or dual solution would give you information regarding the potential benefit or loss to the company in terms of the number of potential customers reached) of insisting on at least 3 ads per newspaper? iv) The value of which variable or parameter in the optimal primal or dual solution would give you information regarding the potential benefit or loss to the company in terms of the number of potential customers reached) on insisting to reach high income group potential customers (assuming that the budget and other conditions remain the same) T2 Number of non prime-time spots to be aired on TV Channel 1, TP2 Number of prime-time spots to be aired on TV Channel 2. Number of non prime-time spots to be aired on TV Channel 2. R1 Number of spots to be aired on the radio channel, G1 Number of ads to be placed in Newspaper 1. G2 Number of ads to be placed in Newspaper 2. MI Number of ads to be placed in Magazine 1, M2 Number of ads to be placed in Magazine 2. The objective (in units of 1000 persons): Max 5000 TP1+3000 T1+ 4000 TP2+ 2500 T2+ 400 R1+2300 GI+ 1300 G2+ 500 Ml+ 600 M2 The Constraints: 3.0 TP1+ 2.0 TI+2.7 TP2+ 1.8 T2+0.5 R1+ 1.6 G1+ 1.2 G2+0.75M1+0.7 M2 530 75 TP1+60 TI+ 100 TP2+ 75 T2+ 24R1+ 50 GI+ 49 G2+ 60 MI+ 55 M2 22000 3.0 TP1+2.0 TI+2.7 TP2+ 1.8 T2 1.6G1+1.2 G2+0.75 M1+0.7 M2 TP1+ TI 23 TP2+ T2 S30 5 20 23 G2 23 MI 53 M2 53 TPI, TI, TP2, T2, R1. MI, M2 20 Such models may be employed in similar problems faced in marketing and advertising activities in various sectors. However, it should be noted that the constructed objective function (ie, total number of potential customers reached through the campaign) is again at most a "proxy" for the real objective the managers have in mind, which is to increase sales and and/or profits through such a campaign. 9. Advertising Planning A large food manufacturer is planning an advertising campaign for a new product being prepared for marketing. The company's expectation is to increase sales through this campaign. They want to reach to the maximum possible number of potential customers while keeping the overall campaign within a predetermined budget of 50,000 TL. The company's advertising agency has suggested the employment of two TV Channels, two daily newspapers, two weekly magazines and one radio station during this campaign. It has also emphasized the additional importance of reaching high income potential customers. The research department of the advertising agency has carefully estimated the cost of each ad, the number of potential customers and the number of high income potential customers it will reach, as follows. In TV ads a 30 second spot is considered as a one unit, and prime-time (PT) and non prime time (non PT) ads are treated separately, since they differ both in cost and in reachability. At the suggestion of the agency, the company would like to reach at least 2.000.000 high income potential customers during this campaign. They would also like to spend at most 30.000 TL on TV ads, and at most 20.000 TL on printed media. Furthermore, the manager would like to give at least three ads to each TV Channel and each newspaper to keep up the good relations with these organizations. On the other hand, since the duration of the campaign is three weeks, there is time to place at most 3 ads in each of the magazines. Cost # of Potential of High Income Media Type per Ad Cust. Reached Potential Cust. Reached TV I (PT) 3.000 TL 5,000,000 75.000 TV 1 (non PT) 2.000 TL 3.000.000 60,000 TV 2 (PT) 2.700 TL 4.000.000 100,000 TV 2 (non PT) 1,800 TL 2,500,000 75.000 Radio 500 TL 400.000 24.000 Paper 1 1,600 TL 2,300,000 50.000 Paper 2 1.200 TL 1,300,000 49,000 Magazine 1 750 TL 500.000 60.000 Magazine 2 700 TL 600.000 55.000 An L.P. model of the company's advertising problem is as follows. The Decision Variables: TPI Number of prime-time spots to be aired on TV Channel