Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Value-Stream Costing Objective During the week of June 12, Harrison Manufacturing produced and shipped 16,000 units of its aluminum wheels: 3,800 units of Model
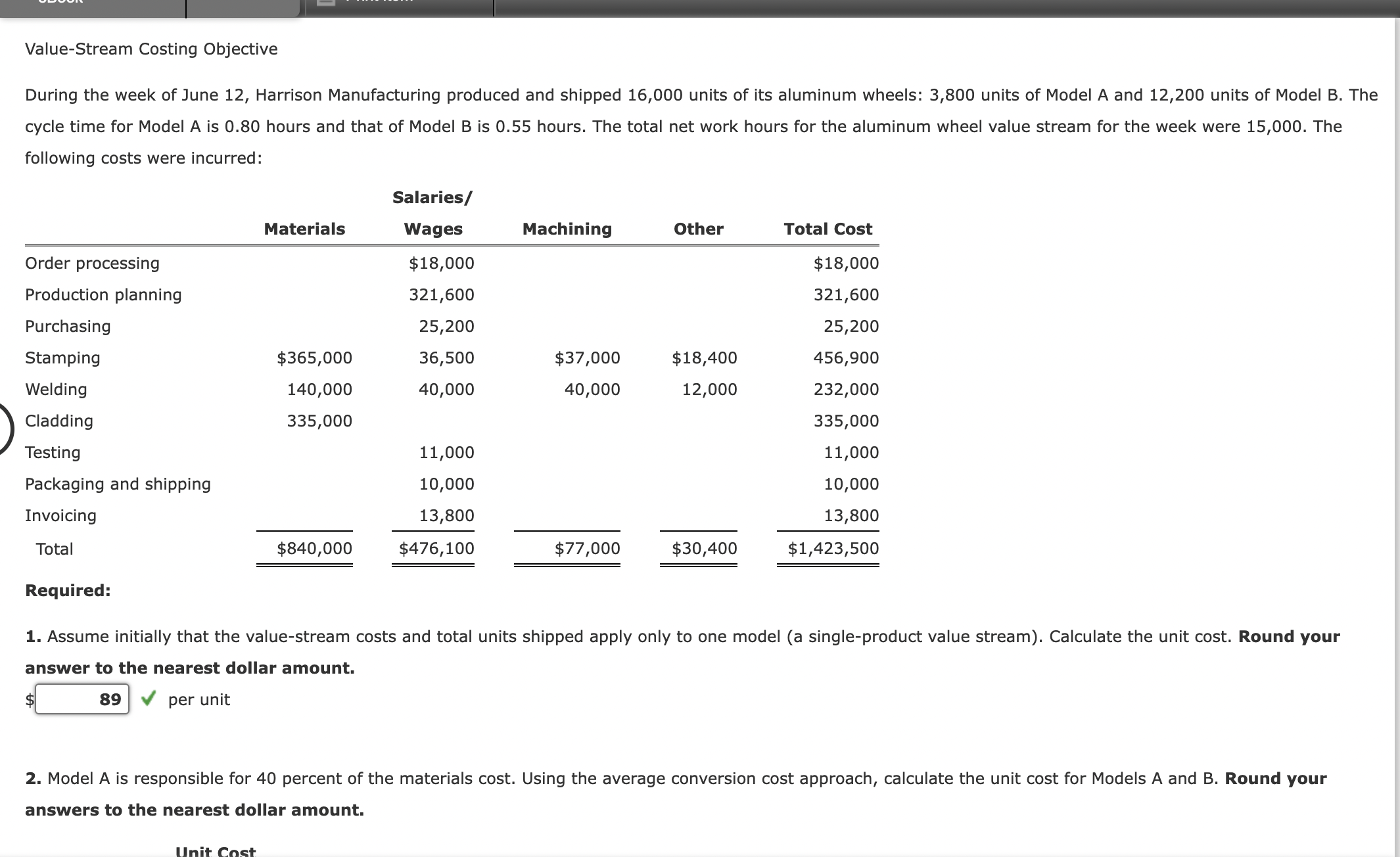
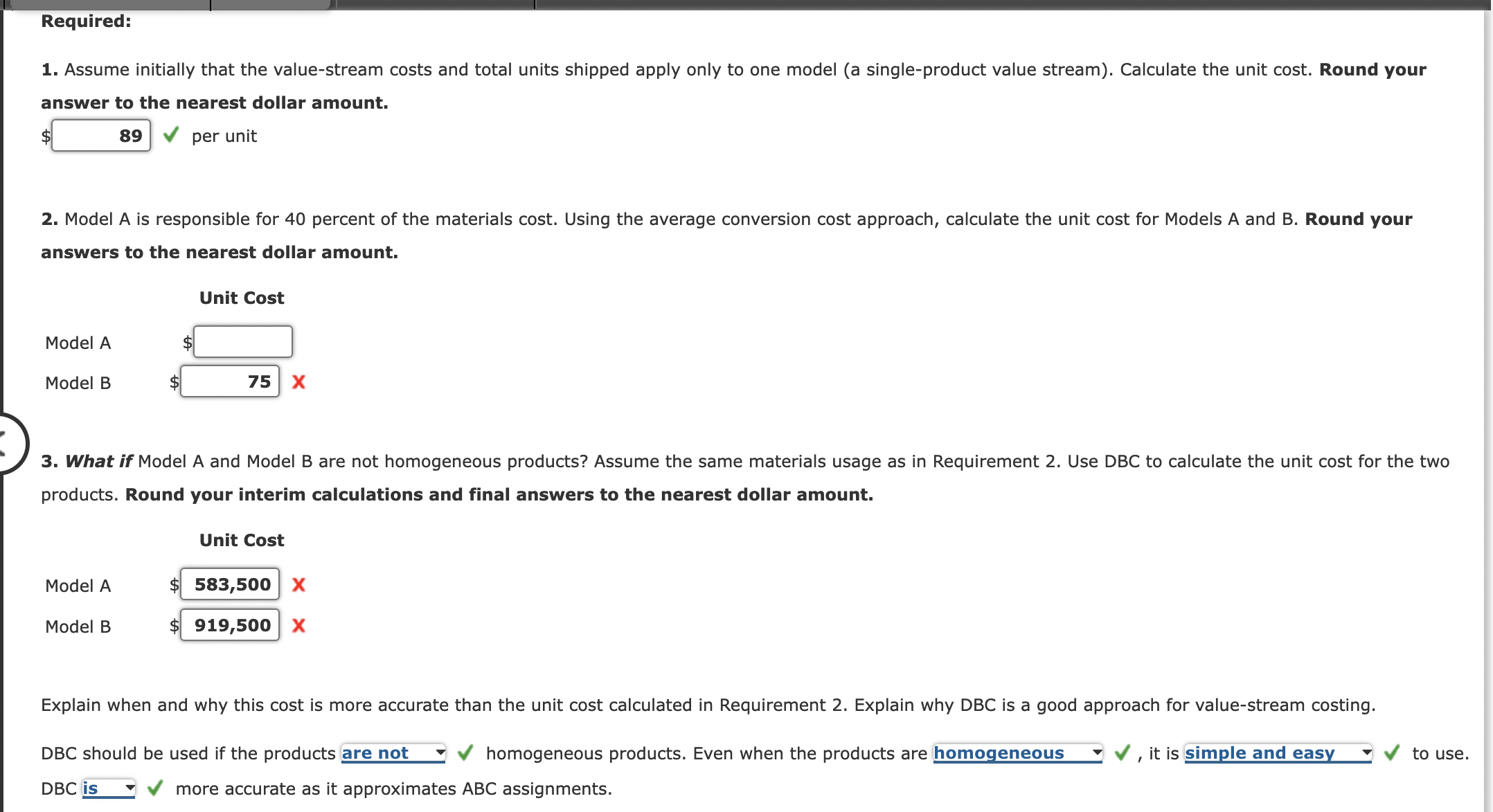
Value-Stream Costing Objective During the week of June 12, Harrison Manufacturing produced and shipped 16,000 units of its aluminum wheels: 3,800 units of Model A and 12,200 units of Model B. The cycle time for Model A is 0.80 hours and that of Model B is 0.55 hours. The total net work hours for the aluminum wheel value stream for the week were 15,000. The following costs were incurred: Order processing Production planning Purchasing Stamping Welding Salaries/ Materials Wages $365,000 $18,000 321,600 25,200 36,500 Machining $37,000 40,000 Other Total Cost $18,000 321,600 25,200 $18,400 456,900 12,000 232,000 335,000 11,000 11,000 10,000 10,000 13,800 13,800 $840,000 $476,100 $77,000 $30,400 $1,423,500 140,000 40,000 09 Cladding Testing Packaging and shipping Invoicing Total Required: 335,000 1. Assume initially that the value-stream costs and total units shipped apply only to one model (a single-product value stream). Calculate the unit cost. Round your answer to the nearest dollar amount. $ 89 per unit 2. Model A is responsible for 40 percent of the materials cost. Using the average conversion cost approach, calculate the unit cost for Models A and B. Round your answers to the nearest dollar amount. Unit Cost Required: 1. Assume initially that the value-stream costs and total units shipped apply only to one model (a single-product value stream). Calculate the unit cost. Round your answer to the nearest dollar amount. $ 89 per unit 2. Model A is responsible for 40 percent of the materials cost. Using the average conversion cost approach, calculate the unit cost for Models A and B. Round your answers to the nearest dollar amount. Unit Cost Model A Model B $ 75 X 3. What if Model A and Model B are not homogeneous products? Assume the same materials usage as in Requirement 2. Use DBC to calculate the unit cost for the two products. Round your interim calculations and final answers to the nearest dollar amount. Unit Cost Model A $ 583,500 X Model B $ 919,500 X DBC should be used if the products are not Explain when and why this cost is more accurate than the unit cost calculated in Requirement 2. Explain why DBC is a good approach for value-stream costing. homogeneous products. Even when the products are homogeneous it is simple and easy to use. DBC is more accurate as it approximates ABC assignments.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


