Question
Video transcript: Adamson Corporation is considering four average-risk projects with the following costs and expected rates of return. Given the information about different sources of
Video transcript: Adamson Corporation is considering four average-risk projects with the following costs and expected rates of return. Given the information about different sources of capital, we have been asked to calculate the cost of each of the capital components, then calculate the weighted-average cost of capital, and then we will choose which projects will be accepted. And the decision-making criterion is any project with an expected return that is greater than the weighted-average cost of capital. So let's start with the calculation of the weighted-average cost of capital. The weighted-average cost of capital is equal to weight of debt times cost of debt times 1 minus the tax rate plus the weight of preferred times the cost of preferred plus the weight of common times the cost of common. The company estimates that it can issue debt at a rate of 10% and its tax rate is 25%. Cost of debt is 10%. Given a tax rate of 25%, the after-tax cost of debt is 10% times 1 minus .25. So that would be 10% times .75 or 7.5%. That is the after-tax cost of debt. It can issue preferred stock that pays a constant dividend of $5.00 per year at $50.00 per share. The cost of preferred is equal to dividend divided by price. Dividend is $5.00 a share, price is $50.00 a share. That gives us a cost of preferred equal to 10%. Its common stock currently sells for $38.00 per share. The next expected dividend is 4.25. The dividend is expected to grow at a constant rate of 5% per year. So we can use the discounted cash flow model to calculate the cost of common equity as D1 divided by price plus g. D1 is 4.25. Price is 38. Add to that a growth rate of 5%. This is equal to 0.1118 plus .05. That is 0.1618 or 16.18%. That is the cost of common equity. Now, for the capital structure, we're using the target capital structure, which is 75% common stock. So weight of common, .75; 15% debt, weight of debt .15. And the rest, 10% in preferred stock. Weight of preferred, .10. Weight of debt times after-tax cost of debt, .15 times 7.5 gives us 1.125%. Weight of preferred times cost of preferred, .1 times 10% is equal to 1%. Then, the weight of equity, .75, times the cost of equity, 16.18%. That is equal to 12.135%. So the largest contribution to the weighted-average cost of capital is due to the cost of common equity, which makes sense. It is the most expensive source of capital and it is the greatest weight in your target capital structure. So the weighted-average cost of capital is 1.125% plus 1% plus 12.135%, which is equal to 14.26%. Now, given a weighted-average cost of capital of 14.26%, which projects will be accepted? So let's check. Is the expected return greater than the weighted-average cost of capital? That was our decision-making criterion, that the expected return has to exceed the weighted-average cost of capital, the weighted-average cost of capital, being 14.26%. Project 1: Return is greater than cost of capital. Project 2: Return is greater than cost of capital. Project 3: Return is not greater than cost of capital. Project 4: Return is not greater than cost of capital. So we will accept projects 1 and 2 only.


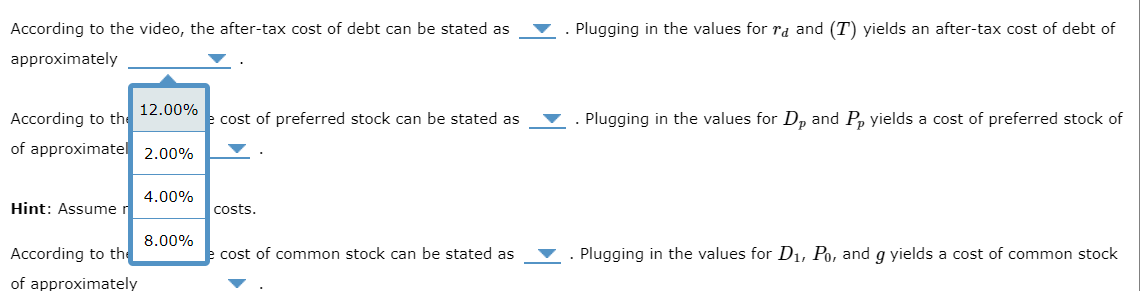
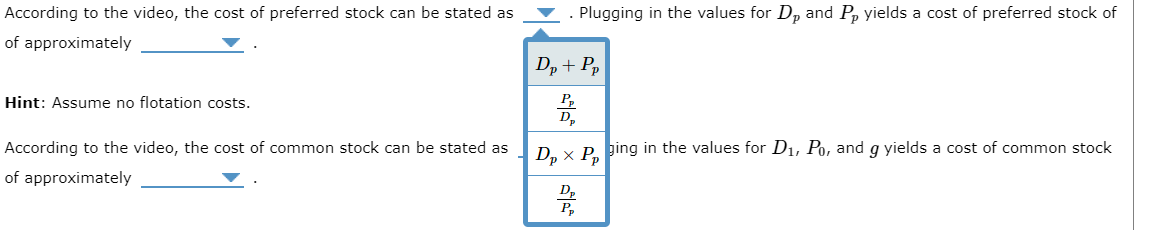

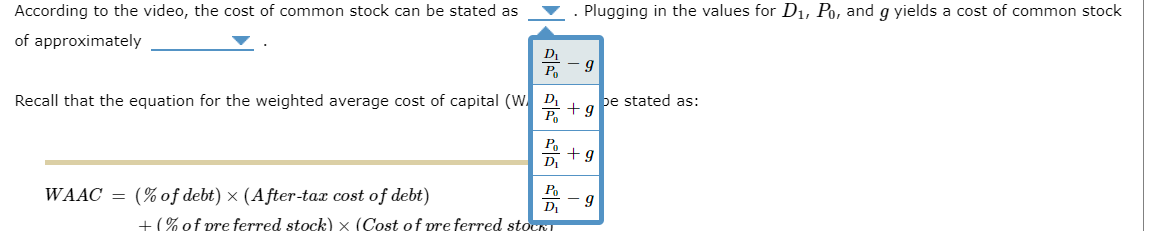
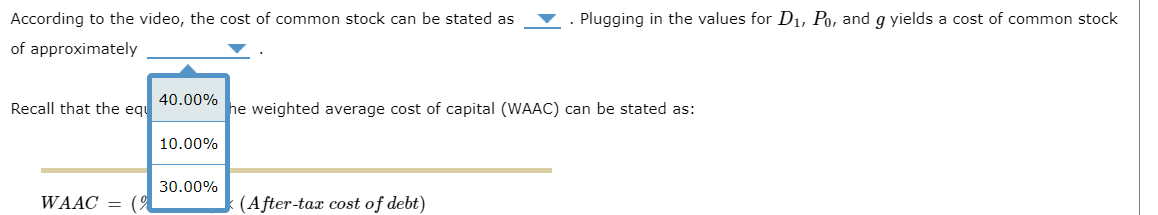

 According to the video, the cost of common stock can be stated as . Plugging in the values for D1,P0, and g yields a cost of common stock of approximately Recall that the equation for the weighted average cost of capital (WAAC) can be stated as: WAAC=(%ofdebt)(After-taxcostofdebt)+(%ofpreferredstock)(Costofpreferredstock)+(%ofCommonequity)(Costofcommonequity) Plugging in the relevant values into the formula for WACC yields a WAAC of approximately Suppose that Mullens will only accept projects with an expected rate of return that exceeds the WAAC. Which of the following projects will Mullens accept? Check all that apply. Project 1 Project 2 Project 3 According to the video, the after-tax cost of debt can be stated as . Plugging in the values for rd and (T) yields an after-tax cost of debt of approximately rd(1+T) According to the video, the cost of preferred stock can be stated as rd(T)g in the values for Dp and Pp yields a cost of preferred stock of of approximately Hint: Assume no flotation costs. rd(1T)rd(LT) According to the video, the after-tax cost of debt can be stated as . Plugging in the values for rd and (T) yields an after-tax cost of debt of approximately According to the of approximatel Hint: Assume r According to the 12.00% cost of preferred stock can be stated as 2.00% 4.00% 8.00% costs. cost of common stock can be stated as . Plugging in the values for D1,P0, and g yields a cost of common stock Plugging in the values for Dp and Pp yields a cost of preferred stock of Pluging in the values for D1,P0, and g yields a cost of common stock According to the video, the cost of preferred stock can be stated as . Plugging in the values for Dp and Pp yields a cost of preferred stock of of approximately Hint: Assume no flotation costs. According to the video, the cost of common stock can be stated as of approximately Plugging in the relevant values into the formula for WACC yields a WAAC of approximately Suppose that Mullens will only accept projects with an expected rate of return that exceeds Which of the following projects will Mullens accept? Check all that apply. Project 1 Project 2 Project 3 According to the video, the cost of common stock can be stated as . Plugging in the values for D1,P0, and g yields a cost of common stock of approximately Recall that the equation for the weighted average cost of capital (W, P0D1g P0D1+g pe stated as: WAAC=(% of debt )( After-tax cost of debt ) D1P0gD1P0+g Suppose Mullens Corporation is considering three average-risk projects with the following costs and rates of return: Mullens estimates that it can issue debt at a rate of rd=10.00% and a tax rate of T=20.00%. It can issue preferred stock that pays a constant dividend of Dp=$15.00 per year and at Pp=$75.00 per share. Also, its common stock currently sells for P0=$17.00 per share. The expected dividend payment of the common stock is D1=$4.25 and the dividend is expected to grow at a constant annual rate of g=5.00% per year. Mullens' target capital structure consists of ws=80.00% common stock, wd=10.00% debt, and wp=10.00% preferred stock. According to the video, the after-tax cost of debt can be stated as approximately According to the video, the cost of preferred stock can be stated as of approximately Hint: Assume no flotation costs. According to the video, the cost of common stock can be stated as of approximately . Plugging in the values for rd and (T) yields an after-tax cost of debt of . Plugging in the values for Dp and Pp yields a cost of preferred stock of . Plugging in the values for D1,P0, and g yields a cost of common stock According to the video, the cost of preferred stock can be stated as of approximately Hint: Assume no According to the of approximately . Plugging in the values for Dp and Pp yields a cost of preferred stock of i. : of common stock can be stated as . Plugging in the values for D1,P0, and g yields a cost of common stock
According to the video, the cost of common stock can be stated as . Plugging in the values for D1,P0, and g yields a cost of common stock of approximately Recall that the equation for the weighted average cost of capital (WAAC) can be stated as: WAAC=(%ofdebt)(After-taxcostofdebt)+(%ofpreferredstock)(Costofpreferredstock)+(%ofCommonequity)(Costofcommonequity) Plugging in the relevant values into the formula for WACC yields a WAAC of approximately Suppose that Mullens will only accept projects with an expected rate of return that exceeds the WAAC. Which of the following projects will Mullens accept? Check all that apply. Project 1 Project 2 Project 3 According to the video, the after-tax cost of debt can be stated as . Plugging in the values for rd and (T) yields an after-tax cost of debt of approximately rd(1+T) According to the video, the cost of preferred stock can be stated as rd(T)g in the values for Dp and Pp yields a cost of preferred stock of of approximately Hint: Assume no flotation costs. rd(1T)rd(LT) According to the video, the after-tax cost of debt can be stated as . Plugging in the values for rd and (T) yields an after-tax cost of debt of approximately According to the of approximatel Hint: Assume r According to the 12.00% cost of preferred stock can be stated as 2.00% 4.00% 8.00% costs. cost of common stock can be stated as . Plugging in the values for D1,P0, and g yields a cost of common stock Plugging in the values for Dp and Pp yields a cost of preferred stock of Pluging in the values for D1,P0, and g yields a cost of common stock According to the video, the cost of preferred stock can be stated as . Plugging in the values for Dp and Pp yields a cost of preferred stock of of approximately Hint: Assume no flotation costs. According to the video, the cost of common stock can be stated as of approximately Plugging in the relevant values into the formula for WACC yields a WAAC of approximately Suppose that Mullens will only accept projects with an expected rate of return that exceeds Which of the following projects will Mullens accept? Check all that apply. Project 1 Project 2 Project 3 According to the video, the cost of common stock can be stated as . Plugging in the values for D1,P0, and g yields a cost of common stock of approximately Recall that the equation for the weighted average cost of capital (W, P0D1g P0D1+g pe stated as: WAAC=(% of debt )( After-tax cost of debt ) D1P0gD1P0+g Suppose Mullens Corporation is considering three average-risk projects with the following costs and rates of return: Mullens estimates that it can issue debt at a rate of rd=10.00% and a tax rate of T=20.00%. It can issue preferred stock that pays a constant dividend of Dp=$15.00 per year and at Pp=$75.00 per share. Also, its common stock currently sells for P0=$17.00 per share. The expected dividend payment of the common stock is D1=$4.25 and the dividend is expected to grow at a constant annual rate of g=5.00% per year. Mullens' target capital structure consists of ws=80.00% common stock, wd=10.00% debt, and wp=10.00% preferred stock. According to the video, the after-tax cost of debt can be stated as approximately According to the video, the cost of preferred stock can be stated as of approximately Hint: Assume no flotation costs. According to the video, the cost of common stock can be stated as of approximately . Plugging in the values for rd and (T) yields an after-tax cost of debt of . Plugging in the values for Dp and Pp yields a cost of preferred stock of . Plugging in the values for D1,P0, and g yields a cost of common stock According to the video, the cost of preferred stock can be stated as of approximately Hint: Assume no According to the of approximately . Plugging in the values for Dp and Pp yields a cost of preferred stock of i. : of common stock can be stated as . Plugging in the values for D1,P0, and g yields a cost of common stock Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


