
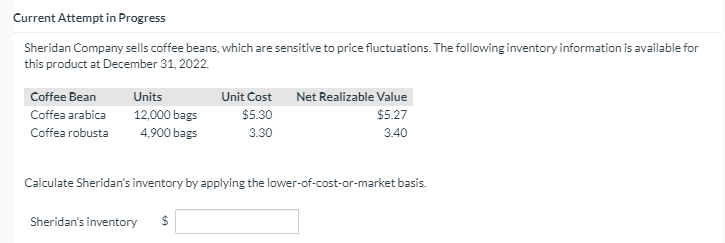
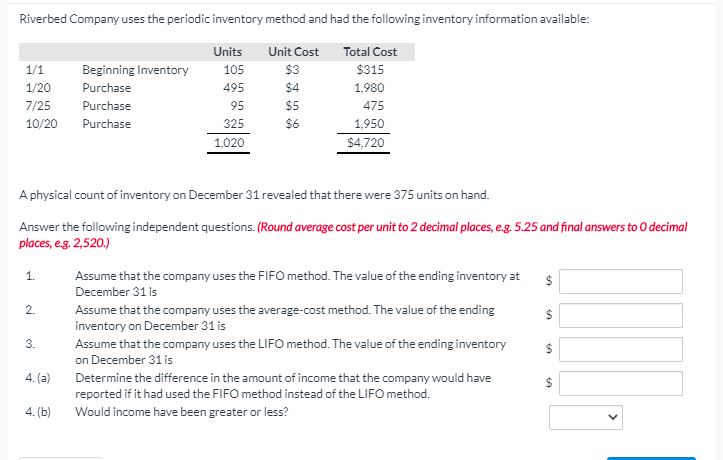
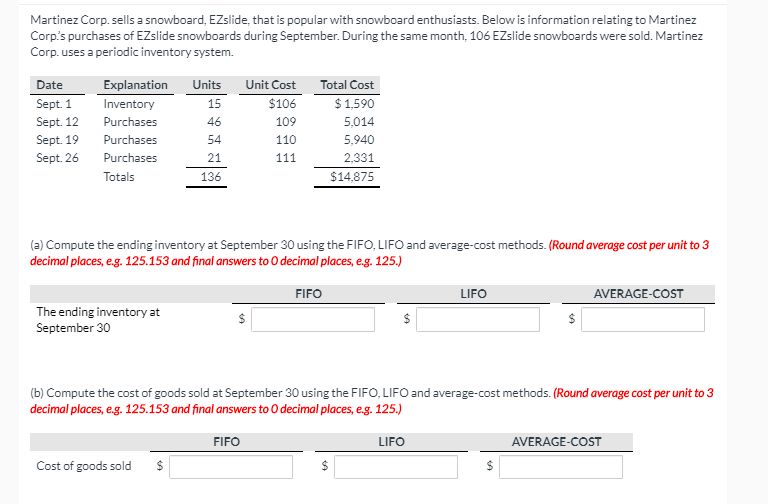
View Policies Current Attempt in Progress Flounder Company was undergoing an end of year audit of its financial records. The auditors were in the process of reviewing Flounder's inventory for year-end, December 31, 2022. They completed an end of year inventory. The value of the ending inventory prior to any adjustments was $181,000, but before finishing up they had a few questions. Discussion with Flounder's accountant revealed the following: Flounder sold goods costing $61.200 to Patricia Company FOB shipping point on December 28. The goods are not expected to reach Patricia until January 12. The goods were not included in the physical inventory because they were not in the warehouse (b) The physical count of the inventory did not include goods costing $94.000 that were shipped to Flounder FOB destination on December 27 and were still in transit at year-end. Flounder received goods costing $24.800 on January 2. The goods were shipped FOB shipping point on December 26 by Splish Brothers Company. The goods were not included in the physical count. (d) Flounder sold goods costing $39,400 to Sunland Company FOB destination on December 30. The goods were received by Sunland Company on January 8. Because the goods had been shipped, they were excluded from the physical inventory count. (e) Flounder received goods costing $42,800 on January 2 that were shipped FOB destination on December 29. The shipment was a rush order that was supposed to have arrived on December 31. This purchase was included in the ending inventory of $182,500. (f) Flounder Company, as the consignee, had goods on consignment that cost $2,700. Because these goods were on hand as of December 31, they were included in the physical inventory count. c) Analyze the above information and calculate a corrected amount for the ending inventory. Corrected inventory $ Current Attempt in Progress Sheridan Company sells coffee beans, which are sensitive to price fluctuations. The following inventory information is available for this product at December 31, 2022. Coffee Bean Coffea arabica Coffea robusta Units 12,000 bags 4,900 bags Unit Cost $5.30 3.30 Net Realizable Value $5.27 3.40 Calculate Sheridan's inventory by applying the lower-of-cost-or-market basis. Sheridan's inventory $ Riverbed Company uses the periodic inventory method and had the following inventory information available: Units Unit Cost Total Cost 1/1 Beginning Inventory 105 $3 $315 1/20 Purchase 495 1,980 7/25 Purchase 95 $5 475 10/20 Purchase 325 $6 1,950 1,020 $4,720 A physical count of inventory on December 31 revealed that there were 375 units on hand. Answer the following independent questions. (Round average cost per unit to 2 decimal places, e.g. 5.25 and final answers to decimal places, e.g. 2,520.) 1. $ 2. $ 3. Assume that the company uses the FIFO method. The value of the ending inventory at December 31 is Assume that the company uses the average-cost method. The value of the ending inventory on December 31 is Assume that the company uses the LIFO method. The value of the ending inventory on December 31 is Determine the difference in the amount of income that the company would have reported if it had used the FIFO method instead of the LIFO method. Would income have been greater or less? $ 4.(a) $ 4. (b) Martinez Corp. sells a snowboard, EZslide, that is popular with snowboard enthusiasts. Below is information relating to Martinez Corp's purchases of EZslide snowboards during September. During the same month, 106 EZslide snowboards were sold. Martinez Corp. uses a periodic inventory system. Date Sept 1 Sept. 12 Sept 19 Sept. 26 Explanation Inventory Purchases Purchases Purchases Totals Units 15 46 54 Unit Cost $106 109 110 Total Cost $ 1,590 5,014 5,940 2,331 $14,875 21 111 136 (a) Compute the ending inventory at September 30 using the FIFO, LIFO and average cost methods. (Round average cost per unit to 3 decimal places, eg. 125.153 and final answers to decimal places, e.g. 125.) FIFO LIFO AVERAGE-COST The ending inventory at September 30 $ (b) Compute the cost of goods sold at September 30 using the FIFO, LIFO and average-cost methods. (Round average cost per unit to 3 decimal places, e.g. 125.153 and final answers to decimal places, e.g. 125.) FIFO LIFO AVERAGE-COST Cost of goods sold $ $










