Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Warnerwoods Company uses a periodic inventory system. It entered into the following purchases and sales transactions for March. Date March 1 March 5 Activities
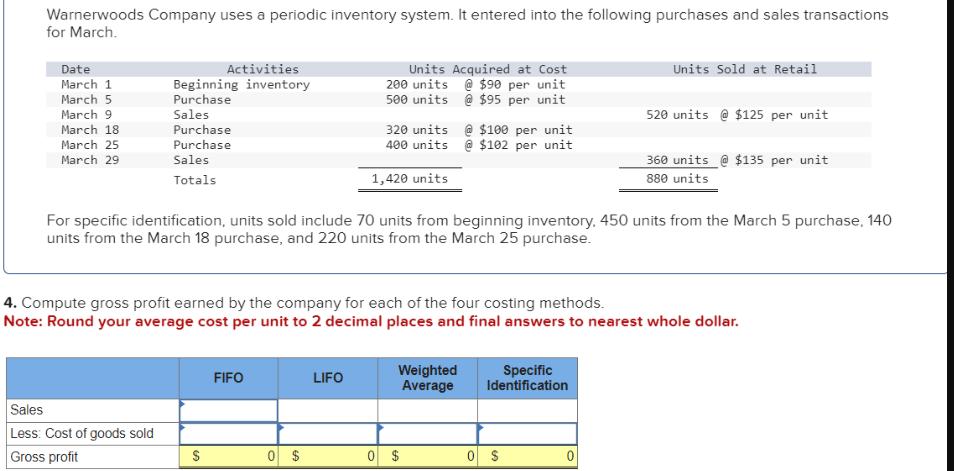

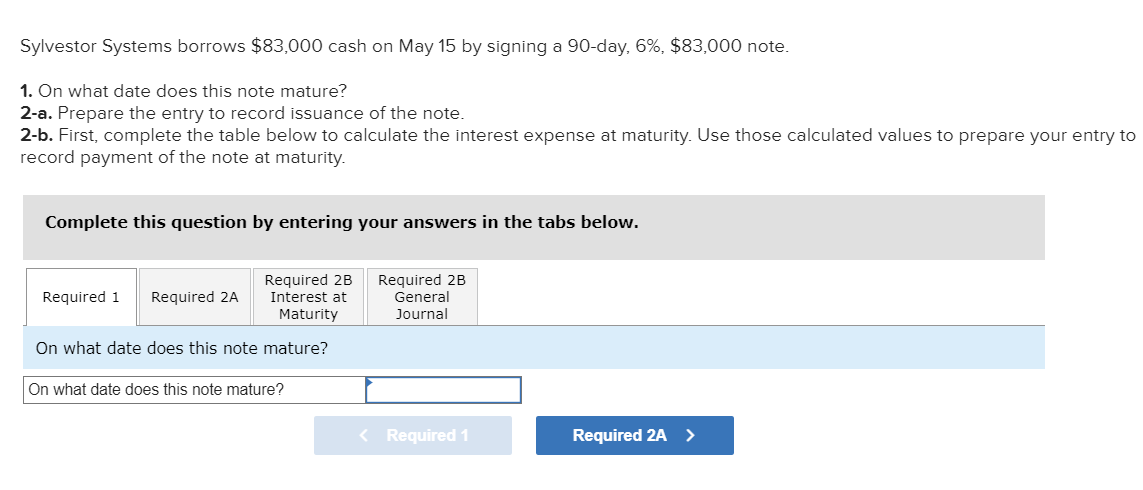
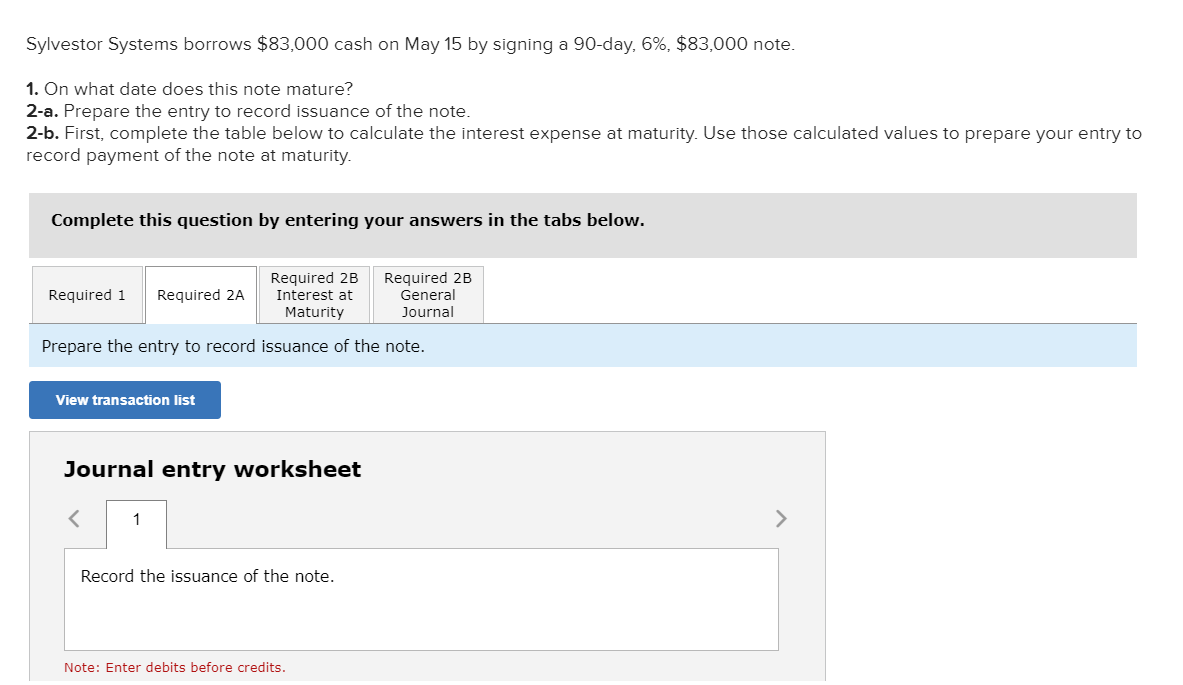
Warnerwoods Company uses a periodic inventory system. It entered into the following purchases and sales transactions for March. Date March 1 March 5 Activities Beginning inventory Purchase Units Acquired at Cost 200 units @ $90 per unit 500 units @ $95 per unit Units Sold at Retail March 9 Sales 520 units @ $125 per unit March 18 Purchase March 25 Purchase March 29 Sales Totals 320 units @ $100 per unit 400 units @ $102 per unit 1,420 units 360 units @ $135 per unit 880 units For specific identification, units sold include 70 units from beginning inventory, 450 units from the March 5 purchase, 140 units from the March 18 purchase, and 220 units from the March 25 purchase. 4. Compute gross profit earned by the company for each of the four costing methods. Note: Round your average cost per unit to 2 decimal places and final answers to nearest whole dollar. FIFO LIFO Weighted Average Specific Identification Sales Less: Cost of goods sold Gross profit $ 0 $ 0 $ 0 $ 0 Required information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] At December 31, Hawke Company reports the following results for its calendar year. Cash sales $ 480,000 Credit sales $ 1,200,000 In addition, its unadjusted trial balance includes the following items. Accounts receivable Allowance for doubtful accounts $ 648,000 debit $ 6,500 debit Required: 1. Prepare the adjusting entry to record bad debts under each separate assumption. a. Bad debts are estimated to be 3% of credit sales. b. Bad debts are estimated to be 2% of total sales. c. An aging analysis estimates that 5% of year-end accounts receivable are uncollectible. Adjusting entries (all dated December 31). Sylvestor Systems borrows $83,000 cash on May 15 by signing a 90-day, 6%, $83,000 note. 1. On what date does this note mature? 2-a. Prepare the entry to record issuance of the note. 2-b. First, complete the table below to calculate the interest expense at maturity. Use those calculated values to prepare your entry to record payment of the note at maturity. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required 2B Interest at Maturity Required 1 Required 2A On what date does this note mature? On what date does this note mature? Required 2B General Journal < Required 1 Required 2A > Sylvestor Systems borrows $83,000 cash on May 15 by signing a 90-day, 6%, $83,000 note. 1. On what date does this note mature? 2-a. Prepare the entry to record issuance of the note. 2-b. First, complete the table below to calculate the interest expense at maturity. Use those calculated values to prepare your entry to record payment of the note at maturity. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required 2B Required 2B Required 1 Required 2A Interest at General Maturity Journal Prepare the entry to record issuance of the note. View transaction list Journal entry worksheet < 1 Record the issuance of the note. Note: Enter debits before credits. >
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Lets address each of your questions one by one starting with the gross profit calculations for different inventory costing methods 1 Compute Gross Pro...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


