Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Water is discharged from a reservoir A through a pipe that rises to its highest point at B, 2.2 m above the free surface
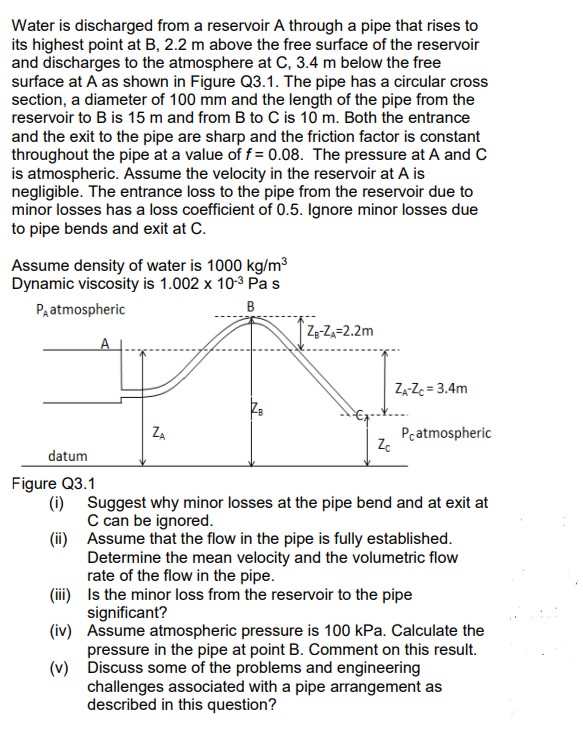
Water is discharged from a reservoir A through a pipe that rises to its highest point at B, 2.2 m above the free surface of the reservoir and discharges to the atmosphere at C, 3.4 m below the free surface at A as shown in Figure Q3.1. The pipe has a circular cross section, a diameter of 100 mm and the length of the pipe from the reservoir to B is 15 m and from B to C is 10 m. Both the entrance and the exit to the pipe are sharp and the friction factor is constant throughout the pipe at a value of f = 0.08. The pressure at A and C is atmospheric. Assume the velocity in the reservoir at A is negligible. The entrance loss to the pipe from the reservoir due to minor losses has a loss coefficient of 0.5. Ignore minor losses due to pipe bends and exit at C. Assume density of water is 1000 kg/m Dynamic viscosity is 1.002 x 10-3 Pa s PA atmospheric B ZA datum ZB-ZA-2.2m ZA-ZC=3.4m Pcatmospheric Zc Figure Q3.1 (i) Suggest why minor losses at the pipe bend and at exit at C can be ignored. (ii) Assume that the flow in the pipe is fully established. Determine the mean velocity and the volumetric flow rate of the flow in the pipe. (iii) Is the minor loss from the reservoir to the pipe significant? (iv) Assume atmospheric pressure is 100 kPa. Calculate the pressure in the pipe at point B. Comment on this result. (v) Discuss some of the problems and engineering challenges associated with a pipe arrangement as described in this question?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


