Question
we consider a parallelepiped junction, of surface S, polarized in direct (voltage V) and we place ourselves in the region of type n. In this
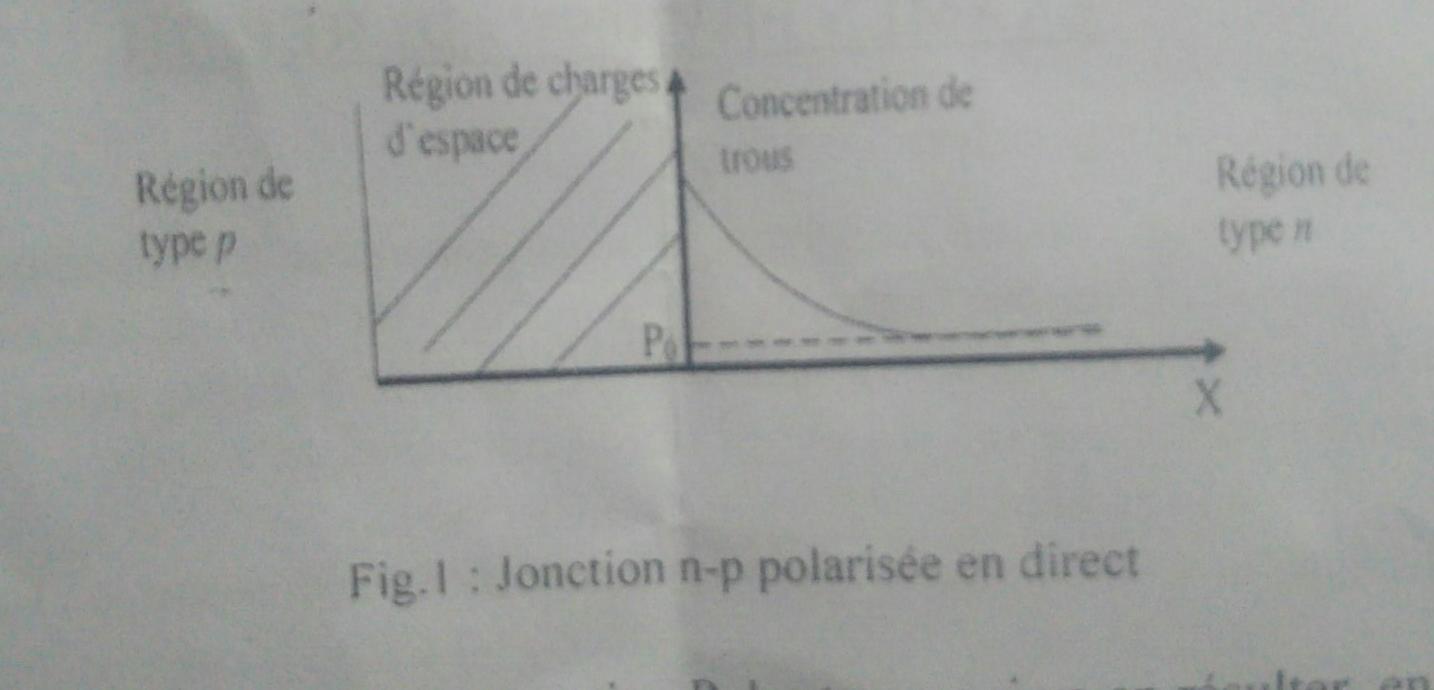
we consider a parallelepiped junction, of surface S, polarized in direct (voltage V) and we place ourselves in the region of type n. In this region, a hole diffusion current can flow. 1) What is the equation which governs the concentration p of the holes which will result from it, taking into account the fact that these holes are in the minority in the region of type n and that there may be disappearance of the holes by recombination or appearance of holes per generation depending on whether their concentration is greater or less than the equilibrium concentration P0. Write for the case of electrons, the equation in the p-type region. 2) Neglecting the component due to the electric field in the current density of holes, calculate P in steady state and then deduce jp (X = 0) Boundary conditions X = 0, P = P0exp (qv / KT); X tends towards more Infinite, P = P0. 3) Deduce the equation for the concentration of electrons in the p-type zone. Deduce the equation for the concentration of electrons in the p-type zone. Deduce Jn (X = 0) and the current density which crosses the junction.
please sir help with this exercise
Rgion de charges d'espace Concentration de trous Rgion de type p Rgion de typen P X Fig. 1 : Jonction n-p polarise en direct Rgion de charges d'espace Concentration de trous Rgion de type p Rgion de typen P X Fig. 1 : Jonction n-p polarise en directStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


