Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
We consider the symmetric graph G with 16 vertices. Reflexive edges are not dis- played explicitly, i.e. each vertex is connected to himself. 1.

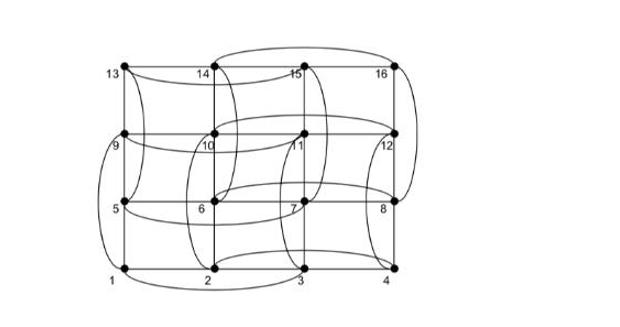
We consider the symmetric graph G with 16 vertices. Reflexive edges are not dis- played explicitly, i.e. each vertex is connected to himself. 1. Find an optimal colouring of G with minimum number of colours, i.e. no vertex of one colour is connected to any other vertex with the same colour. (2 credits) 2. We consider the graph G as a graph related to a sparse symmetric 16 16 matrix A. Describe the sparsity pattern of A. (2 credits) 3. The colouring from 1 leads to a permutation P and a reordering of A. Describe the sparsity pattern after reordering rows and columns of A. (3 credits) 4. Describe the advantage of this reordering for the Gauss-Seidel iteration. Typ- ically, any colouring with k colours splits up the Gauss-Seidel iteration into k phases. Split up the matrix from problem 3 into blocks and give formulas for these different phases. 13 14 16 10 12 2
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


