Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
We want to design an asynchronous process Split that is the dual of Merge (Textbook Fig. 4.3, page 129). The process Split has one input
We want to design an asynchronous process Split that is the dual of Merge (Textbook Fig. 4.3, page 129). The process Split has one input channel in and two output channels out1 and out2. The messages received on the input channel should be routed to one of the output channels in a nondeterministic manner so that all possible splittings of the input stream are feasible executions. Describe all the components of the desired process Split.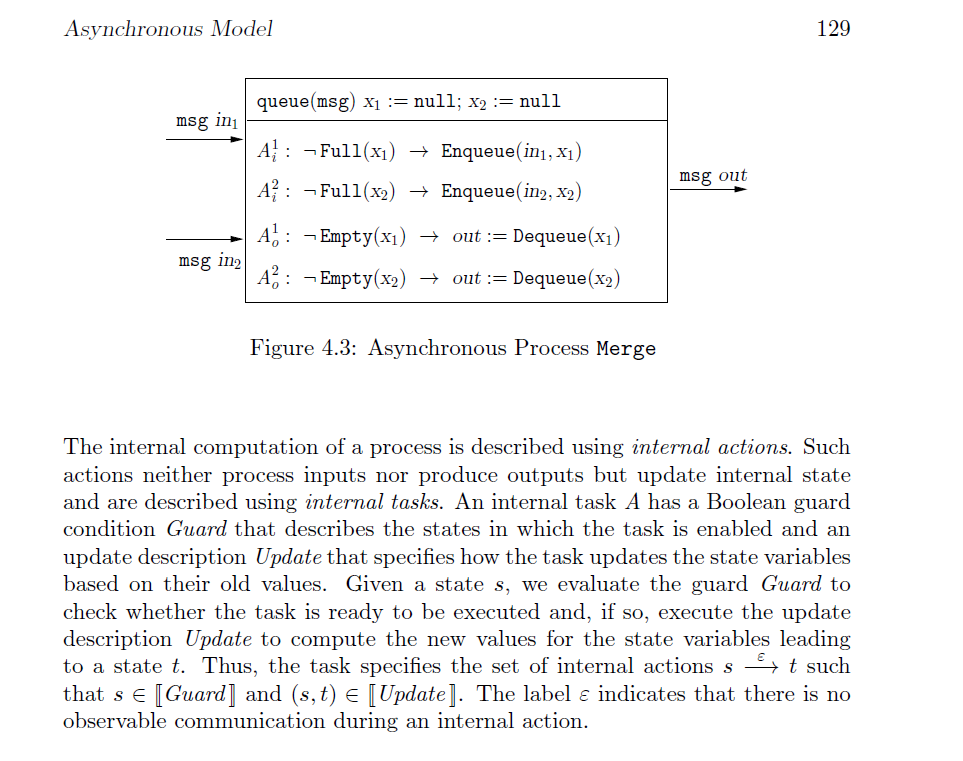
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


