Question: We will have two classes: a Board class to represent the chessboard and a Queen class to represent a single Queen. A Board object could
We will have two classes: a "Board" class to represent the chessboard and a "Queen" class to represent a single Queen.
A Board object could be represented in a number of ways. The most intuitive representation might be a two-dimensional array; however, such an array wastes space because only eight squares out of 64 are used. Instead we will use an STL vector that contains the 8 Queens. Each Queen will be stored in the position of the vector that corresponds to the Queen's column (i.e., the Queen in column 0 will be stored in position 0 of the vector, the Queen in column 1 will be stored in position 1 of the vector, and so on). Since each Queen will know its own location on the board, this vector will fully specify the state of the board.
Here is the pseudocode that I highly recommend. I have modified it from the pseudocode given in the text after a lot of experimentation with different approaches to determine the simplest approach.
pre: rowYou must use the following code as a starting point. Do not add anything to the class declarations. Your only task is to complete the definitions of the member functions for the "Queen" and "Board" classes.
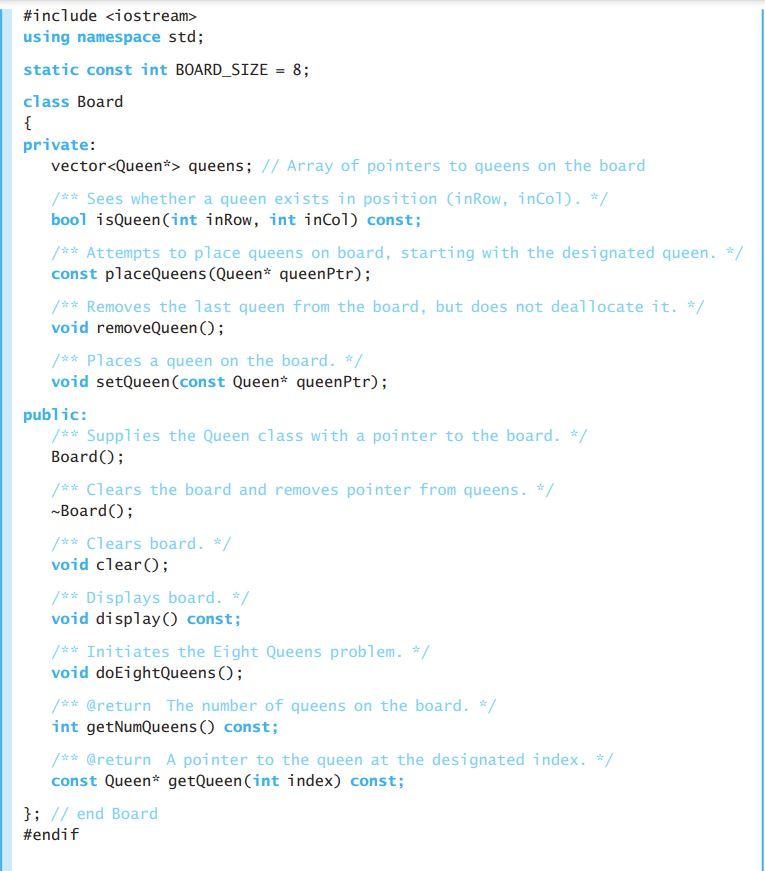
#include#include using namespace std; class Queen { public: void setRow(int inRow); int getRow() const; private: int row; }; int Queen::getRow() const { } void Queen::setRow(int inRow) { } class Board { public: static const int BOARD_SIZE = 8; Board(); void doQueens(); void display() const; private: bool placeQueens(int row, int col); bool findNextSafeSquare(int& row, int col); bool isUnderAttack(int row, int col); vector queens; }; Board::Board() { queens.resize(BOARD_SIZE); } void Board::doQueens() { if (placeQueens(0, 0)) { display(); } else { cout Text to go off of:
A chessboard contains 64 squares that form eight rows and eight columns. The most powerful piece in the game of chess is the queen, because it can attack any other piece within its row, within its column, or along its diagonal. The Eight Queens problem asks you to place eight queens on the chessboard so that no queen can attack any other queen. One strategy is to guess at a solution. However, according to Section 2.6.3of Chapter 2 , there are g (64, 8) = 4,426,165,368 ways to arrange eight queens on a chessboard of 64 squaresso many that it would be exhausting to check all of them for a solution to this problem. Nevertheless, a simple observation eliminates many arrangements from consideration: No queen can reside in a row or a column that contains another queen. Alternatively, each row and column can contain exactly one queen. Thus, attacks along rows or columns are eliminated, leaving only 8! = 40,320 arrangements of queens to be checked for attacks along diagonals. A solution now appears more feasible.
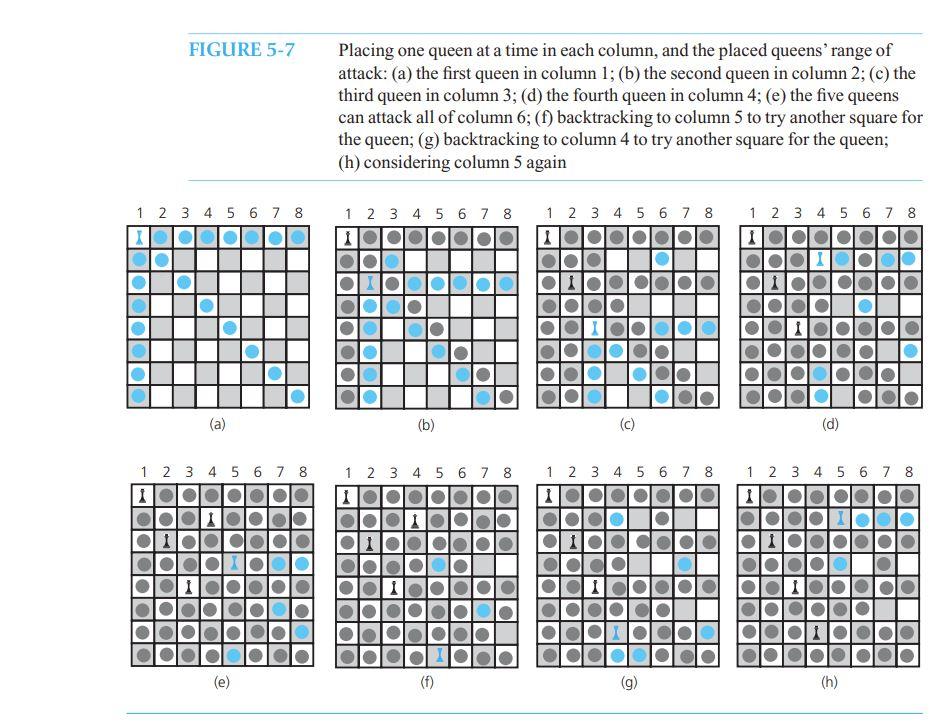
Suppose that you provide some organization for the guessing strategy by placing one queen per column, beginning with the fi rst square of column 1. Figure 5-7 a shows this queen and its range of attack. When you consider column 2, you eliminate its fi rst square because row 1 contains a queen, you eliminate its second square because of a diagonal attack, and you fi nally place a queen in the third square of column 2, as Figure 5-7 b illustrates. The black dots in the fi gure indicate squares that are rejected because a queen in that square is subject to attack by another queen in an earlier column. The blue dots indicate the additional squares that the new queen can attack. We continue to place queens in this manner until we get to column 6, as Figure 5-7 e shows. Although the fi ve placed queens cannot attack each other, they can attack any square in column 6, and therefore, you cannot place a queen in column 6. You must back up to column 5 and move its queen to the next possible square in column 5, which is in the last row, as Figure 5-7 f indicates. When you consider column 6 once again, there are still no choices for a queen in that column. Because you have exhausted the possibilities in column 5, you must back up to column 4. As Figure 5-7 g shows, the next possible square in column 4 is in row 7. You then consider column 5 again and place a queen in row 2 ( Figure 5-7 h). How can you use recursion in the process that was just described? Consider an algorithm that places a queen in a column, given that you have placed queens correctly in the preceding columns.
First, if there are no more columns to consider, you are fi nished; this is the base case. Otherwise, after you successfully place a queen in the current column, you need to consider the next column. That is, you need to solve the same problem with one fewer column; this is the recursive step. Thus, you begin with eight columns, consider smaller problems that decrease in size by one column at each recursive step, and reach the base case when you have a problem with no columns. This solution appears to satisfy the criteria for a recursive solution. However, you do not know whether you can successfully place a queen in the current column. If you can, you recursively consider the next column. If you cannot place a queen in the current column, you need to backtrack, as has already been described. The Eight Queens problem can be solved in a variety of ways. The solution in this chapter uses two classes: a Board class to represent the chessboard and a Queen class to represent a queen on the board. A Queen object keeps track of its row and column placement and contains a static pointer to the Board. It also has operations to move to the next row and to see whether it is subject to attack. A Board object keeps track of the Queen objects currently on the board and contains operationssuch as placeQueens to perform the Eight Queens problem and display the solution. The following pseudocode describes the algorithm for placing queens in columns, given that the previous columns contain queens that cannot attack one another:
Question 7 Consider a Four Queens problem, which has the same rules as the Eight Queens problem but uses a 4 4 board. Find all solutions to this new problem by applying backtracking by hand.
Implementing eight queens using the STL class vector. The Board class in the solution described thus far may be represented in a number of ways. The simplest representation would be a two-dimensional array; however, such an array wastes space because only eight squares out of 64 are used. Another approach would be to use a one-dimensional array of only the squares that contain a queen. Because the algorithm uses backtracking, a dynamic array is the optimal choice. The vector container in the STL is often used in place of an array type, because it allows the number of elements to vary dynamically and provides several built-in methods. Indexing is provided with array-type subscripting or with the at method, which provides range checking as well. As given in Listing 5-1, the class Board contains a vector of pointers to Queen objects, as well as several methods to manipulate the queens on the board. The class Queen appears in Listing 5-2.
FIGURE 5-7 Placing one queen at a time in each column, and the placed queens' range of attack: (a) the first queen in column 1; (b) the second queen in column 2; (c) the third queen in column 3; (d) the fourth queen in column 4; (e) the five queens can attack all of column 6; (f) backtracking to column 5 to try another square for the queen; (g) backtracking to column 4 to try another square for the queen; (h) considering column 5 again 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 NI 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 1 1 OLO OOOOO OOOOO OOOO O OOOOO OOOOOOON OOOOO 10 CON (a) (b) (d) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 O C 0 O O 0 0 O OO OO OH OOOH Ololololololo OOOO O CO OOO OOO IOIOIOIO l lololo OO OOOOO OOOO JIO OO OIOIO OOOO OOOO OOK OC O10 OOOO O10 DO 10 OOO OL 10 10 (e) (f) (h) // Places queens in eight columns placeQueens (queen: Queen): void if (queen's column is greater than the last column) The problem is solved else { while (unconsidered squares exist in queen's column and the problem is unsolved) { Find the next square in queen's column that is not under attack by a queen in an earlier column if (such a square exists) { Place a queen in the square // Try next column placeQueens (new Queen (firstrow, queen's column + 1)) if (no queen is possible in the next column) { Delete the new queen Remove the last queen placed on the board and consider the next square in that column } 3 } } The Eight Queens problem is initiated by the method doEightQueens, which calls placeQueens with a new queen in the upper-left corner of the board: doEightQueens() { placeQueens (new Queen (firstrow, firstcolumn)) } After doEightQueens has completed, the board may display the solution, if one was found. FIGURE 5-8 A solution to the Eight Queens problem 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Figure 5-8 indicates the solution that the previous algorithm finds. By modifying the arguments to placeQueens, you can discover other solutions to the Eight Queens problem. The Programming Problems at the end of this chapter ask you to consider other solutions to this algorithm, as well as additional modifications. ? Question 7 Consider a Four Queens problem, which has the same rules as the Eight Queens problem but uses a 4 X 4 board. Find all solutions to this new problem by applying backtracking by hand. CHECK POINT LISTING 5-1 The header file for the class Board /** Qfile Board.h */ #ifndef _BOARD #define BOARD #include "Queen.h" #include
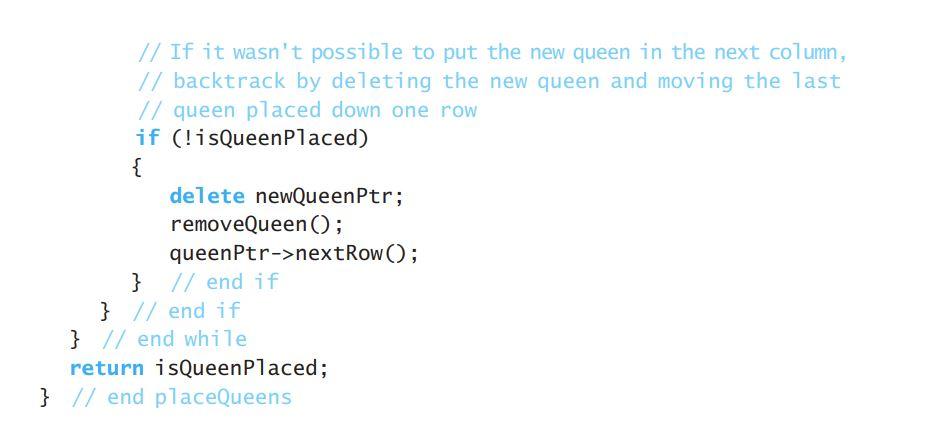
#include #include using namespace std; static const int BOARD_SIZE = 8; class Board { private: vector queens; // Array of pointers to queens on the board ** Sees whether a queen exists in position (inRow, incol). */ bool isQueen(int inRow, int incol) const; /** Attempts to place queens on board, starting with the designated queen. */ const placeQueens (Queen* queenPtr); /** Removes the last queen from the board, but does not deallocate it. */ void removeQueen(); *** Places a queen on the board. */ void setQueen(const Queen* queenptr); public: *** Supplies the Queen class with a pointer to the board. */ Board(); ** Clears the board and removes pointer from queens. */ -Board(); *** Clears board. */ void clear(); ** Displays board. */ void display() const; 1** Initiates the Eight Queens problem. */ void doEightQueens (); ** @return The number of queens on the board. */ int getNumQueens() const; *** @return A pointer to the queen at the designated index. */ const Queen* getQueen (int index) const; }; // end Board #endif LISTING 5-2 The class Queen class Board; // Forward declaration of Board class /** The Queen class. */ class Queen { public: *** Places a queen in upper-left corner of board. */ Queen(); (continues) /** Places a queen in supplied location. */ Queen(int inRow, int incol); /** @return Column number. */ int getCol() const; /** @return Row number. */ int getRow() const; /** Moves queen to next row. */ void nextRow(); /** Sees whether the queen is under attack by another queen. @return True if another queen is in the same row or the same diagonal; otherwise, returns false. */ bool isUnderAttack() const; /** Saves a pointer to the board for all queens. */ static void setBoard(const Board* bPtr); private: int row; // Row Cor prospective row) of queen if it is on the board int col; // Column (or prospective column) of queen if it is on // the board // All queens share the same board static const Board* boardPtr; }; // end Queen /** Places a queen in supplied location. */ Queen(int inRow, int incol); /** @return Column number. */ int getCol() const; /** @return Row number. */ int getRow() const; /** Moves queen to next row. */ void nextRow(); /** Sees whether the queen is under attack by another queen. @return True if another queen is in the same row or the same diagonal; otherwise, returns false. */ bool isUnderAttack() const; /** Saves a pointer to the board for all queens. */ static void setBoard(const Board* bPtr); private: int row; // Row Cor prospective row) of queen if it is on the board int col; // Column (or prospective column) of queen if it is on // the board // All queens share the same board static const Board* boardPtr; }; // end Queen An implementation of placeQueens follows: bool Board: :placeQueens (Queen* queenPtr) { // Base case: Try to place a queen in a nonexistent column. if (queenPtr->getCol() >= BOARD_SIZE) { delete queenPtr; return true; } // end if bool isQueen Placed = false; while (!isQueenPlaced && queenPtr->getRow() isUnderAttack()) queenPtr->nextRow(); else { // Put this queen on the board and try putting a // new queen in the first row of the next column setQueen(queenPtr); Queen* newQueenPtr = new Queen(0, queenPtr->getCol() + 1); isQueenPlaced = placeQueens (newQueenPtr); // If it wasn't possible to put the new queen in the next column, // backtrack by deleting the new queen and moving the last // queen placed down one row if (!isQueenPlaced) { delete newQueenPtr; removeQueen(); queenPtr->nextRow(); } // end if } // end if } // end while return isQueenplaced; } // end placeQueens FIGURE 5-7 Placing one queen at a time in each column, and the placed queens' range of attack: (a) the first queen in column 1; (b) the second queen in column 2; (c) the third queen in column 3; (d) the fourth queen in column 4; (e) the five queens can attack all of column 6; (f) backtracking to column 5 to try another square for the queen; (g) backtracking to column 4 to try another square for the queen; (h) considering column 5 again 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 NI 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 1 1 OLO OOOOO OOOOO OOOO O OOOOO OOOOOOON OOOOO 10 CON (a) (b) (d) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 O C 0 O O 0 0 O OO OO OH OOOH Ololololololo OOOO O CO OOO OOO IOIOIOIO l lololo OO OOOOO OOOO JIO OO OIOIO OOOO OOOO OOK OC O10 OOOO O10 DO 10 OOO OL 10 10 (e) (f) (h) // Places queens in eight columns placeQueens (queen: Queen): void if (queen's column is greater than the last column) The problem is solved else { while (unconsidered squares exist in queen's column and the problem is unsolved) { Find the next square in queen's column that is not under attack by a queen in an earlier column if (such a square exists) { Place a queen in the square // Try next column placeQueens (new Queen (firstrow, queen's column + 1)) if (no queen is possible in the next column) { Delete the new queen Remove the last queen placed on the board and consider the next square in that column } 3 } } The Eight Queens problem is initiated by the method doEightQueens, which calls placeQueens with a new queen in the upper-left corner of the board: doEightQueens() { placeQueens (new Queen (firstrow, firstcolumn)) } After doEightQueens has completed, the board may display the solution, if one was found. FIGURE 5-8 A solution to the Eight Queens problem 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Figure 5-8 indicates the solution that the previous algorithm finds. By modifying the arguments to placeQueens, you can discover other solutions to the Eight Queens problem. The Programming Problems at the end of this chapter ask you to consider other solutions to this algorithm, as well as additional modifications. ? Question 7 Consider a Four Queens problem, which has the same rules as the Eight Queens problem but uses a 4 X 4 board. Find all solutions to this new problem by applying backtracking by hand. CHECK POINT LISTING 5-1 The header file for the class Board /** Qfile Board.h */ #ifndef _BOARD #define BOARD #include "Queen.h" #include #include #include using namespace std; static const int BOARD_SIZE = 8; class Board { private: vector queens; // Array of pointers to queens on the board ** Sees whether a queen exists in position (inRow, incol). */ bool isQueen(int inRow, int incol) const; /** Attempts to place queens on board, starting with the designated queen. */ const placeQueens (Queen* queenPtr); /** Removes the last queen from the board, but does not deallocate it. */ void removeQueen(); *** Places a queen on the board. */ void setQueen(const Queen* queenptr); public: *** Supplies the Queen class with a pointer to the board. */ Board(); ** Clears the board and removes pointer from queens. */ -Board(); *** Clears board. */ void clear(); ** Displays board. */ void display() const; 1** Initiates the Eight Queens problem. */ void doEightQueens (); ** @return The number of queens on the board. */ int getNumQueens() const; *** @return A pointer to the queen at the designated index. */ const Queen* getQueen (int index) const; }; // end Board #endif LISTING 5-2 The class Queen class Board; // Forward declaration of Board class /** The Queen class. */ class Queen { public: *** Places a queen in upper-left corner of board. */ Queen(); (continues) /** Places a queen in supplied location. */ Queen(int inRow, int incol); /** @return Column number. */ int getCol() const; /** @return Row number. */ int getRow() const; /** Moves queen to next row. */ void nextRow(); /** Sees whether the queen is under attack by another queen. @return True if another queen is in the same row or the same diagonal; otherwise, returns false. */ bool isUnderAttack() const; /** Saves a pointer to the board for all queens. */ static void setBoard(const Board* bPtr); private: int row; // Row Cor prospective row) of queen if it is on the board int col; // Column (or prospective column) of queen if it is on // the board // All queens share the same board static const Board* boardPtr; }; // end Queen /** Places a queen in supplied location. */ Queen(int inRow, int incol); /** @return Column number. */ int getCol() const; /** @return Row number. */ int getRow() const; /** Moves queen to next row. */ void nextRow(); /** Sees whether the queen is under attack by another queen. @return True if another queen is in the same row or the same diagonal; otherwise, returns false. */ bool isUnderAttack() const; /** Saves a pointer to the board for all queens. */ static void setBoard(const Board* bPtr); private: int row; // Row Cor prospective row) of queen if it is on the board int col; // Column (or prospective column) of queen if it is on // the board // All queens share the same board static const Board* boardPtr; }; // end Queen An implementation of placeQueens follows: bool Board: :placeQueens (Queen* queenPtr) { // Base case: Try to place a queen in a nonexistent column. if (queenPtr->getCol() >= BOARD_SIZE) { delete queenPtr; return true; } // end if bool isQueen Placed = false; while (!isQueenPlaced && queenPtr->getRow() isUnderAttack()) queenPtr->nextRow(); else { // Put this queen on the board and try putting a // new queen in the first row of the next column setQueen(queenPtr); Queen* newQueenPtr = new Queen(0, queenPtr->getCol() + 1); isQueenPlaced = placeQueens (newQueenPtr); // If it wasn't possible to put the new queen in the next column, // backtrack by deleting the new queen and moving the last // queen placed down one row if (!isQueenPlaced) { delete newQueenPtr; removeQueen(); queenPtr->nextRow(); } // end if } // end if } // end while return isQueenplaced; } // end placeQueens
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts