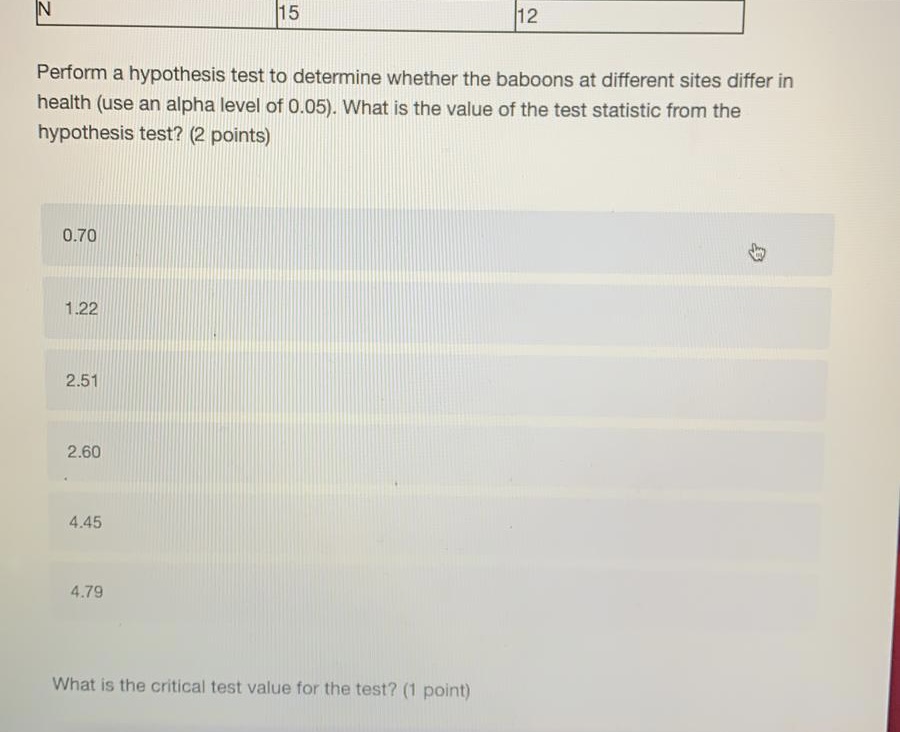
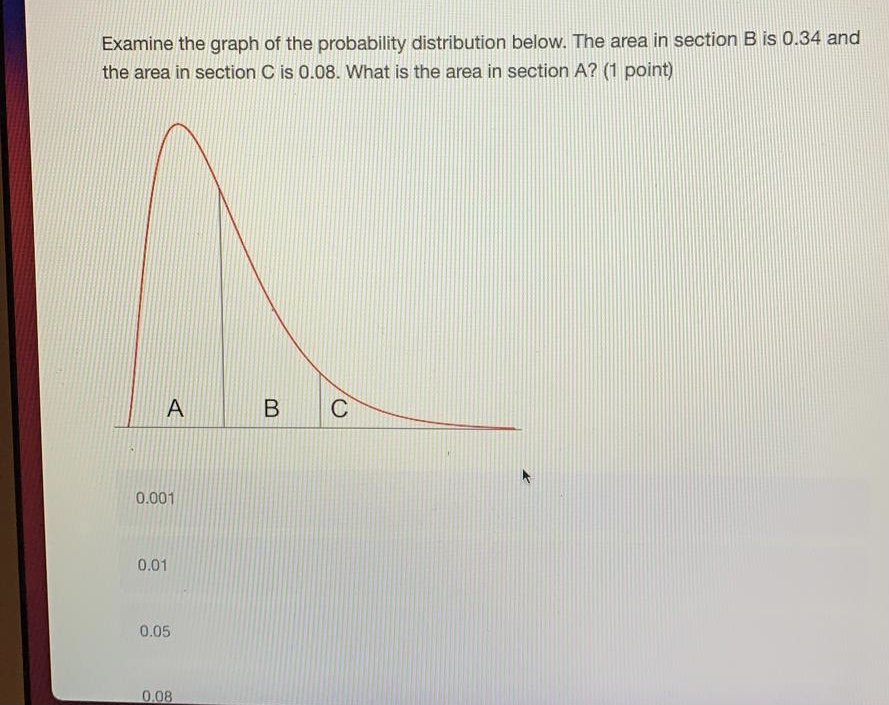
What alpha level do I use to obtain 95% confidence in my estimates? (1 point) 0.01 0.02 0.05 0.10 0.98 0.99 Next ->\fMarcus wants to know what proportion of Canadians exercise regularly. He collects a random sample of 750 Canadians and calculates that only 0.18 of his sample exercises regularly. Calculate a 95% confidence interval for this estimate. Report the lower and upper bounds of the confidence interval below. lower bound upper bound3.18 What conclusion can you draw based on the data? (2 points) You cannot say with 95% confidence that the health of baboons differs between site 1 an site 2 You can say with 95% confidence that baboons at site 1 are healthier than baboons at site 2 You can say with 95% confidence that baboons at site 2 are healthier than baboons at site 1 You can say with 95% confidence that baboon health at both sites is approximately the same You cannot draw any firm conclusions; more data are needed4.79 What is the critical test value for the test? (1 point) 1.64 1.71 1.96 2.06 2.22 3.18 What conclusion can you draw based on the data? (2 points) You cannot say with 95% confidence that the health of baboons differs between site 1 and site 2The mayor of Grenich wants to know if the poverty rate of households in the city is less than 5%. She gives a city employee named Meta the job of finding out. Meta decides to perform a hypothesis test to answer this question. What is Meta's null hypothesis? (1 point) the proportion of households who are in poverty is 0 the proportion of households who are in poverty is less than 0.05 the proportion of households who are in poverty is 0.05 the proportion of households who are in poverty is greater than 0.05Meta examines income records from 200 randomly selected households and finds that 4% of those households are in poverty. She uses this information to perform her hypothesis test (with an alpha level of 0.05). What is the value of her test statistic? (2 points) -2.33 -0.65 0.96 1.85 1.96 2.1115 12 Perform a hypothesis test to determine whether the baboons at different sites differ in health (use an alpha level of 0.05). What is the value of the test statistic from the hypothesis test? (2 points) 0.70 1.22 2.51 2.60 4.45 4.79 What is the critical test value for the test? (1 point)Like any good zoologist, you are interested in monitoring the health of wild animals. In particular, you want to know if exposure to humans alters animal health in any way. To answer this question, you capture 15 baboons from a site close to a large city, and for comparison another 12 baboons from a more remote site. You measure the overall health of each baboon on a scale of 1 to 20. Descriptive statistics on the baboons captured at each site are given in the table below. Site 1 - close to city Site 2 - remote average health 11.4 13.3 standard deviation of 2.2 1.6 health 15 12 Perform a hypothesis test to determine whether the baboons at different sites differ in health (use an alpha level of 0.05). What is the value of the test statistic from the hypothesis test? (2 points) 0.70 1.22You interested in whether a new city-wide job-training program is effective at reducing poverty. Four years after the program begins, you calculate the city's poverty rate from a random sample of city residents. You find that the poverty rate has dropped, and that the difference from the previous poverty rate is statistically significant. However, in reality the poverty rate has stayed the same. How could you describe this result? (2 points) none of the above a confirmation of the null hypothesis a type I error a standard error a type ll errorWhat conclusion can Meta draw based on her data? (2 points) She can say with 95% confidence that exactly 5% of the city's households are in poverty She cannot say with 95% confidence that less than 5% of the city's households are in poverty She can say with 95% confidence that less than 5% of the city's households are in poverty She can say with 95% confidence that more than 5% of the city's households are in povertyWhat can a p-value tell us? (2 points) a) whether there is a real pattern in our data (i.e., a real result, not due to chance) b) how important our result is c) how large our result is (i.e., smaller p-values mean a bigger result) d) the probability that we would get a result as far away from the null hypothesis value as we did (or farther) purely by chance if the null hypothesis were true both a and d both a and c both b and cYou calculate that the mean number of toy cars in children's toyboxes is 2345, with a 99% confidence interval of (1589, 3101). Can we be at least 95% confident that the true mean number of toy cars is greater than 1500? (1 point) no yes cannot be determinedWhich value lies at the center of the sampling distribution of the mean? (2 points) the mean in your sample the value 0 the standard error of the mean the mean in the population Examine the graph of the probability distribution below. The area in section B is 0.34 and the area in section C is 0.08. What is the area in section A? (1 point) A B C 0.001 0.01 0.05 0.08Which of the following best describes the central limit theorem? (2 points) a) as the sample size increases, the sampling distribution of any sample statistic becomes approximately normal b) as the sample size increases, the sampling distribution of the sample mean becomes approximately normal c) as the number of samples increases, the sampling distribution of the mean approaches a t- distribution with 1 degrees of freedom all of the above both a and b both a and c both b and cA new bill will pass if more than half of the legislature is in favor of it. You collect a random sample of members of the legislature and ask them if they are in favor of the bill, or opposed to it. Which type of test will you need to perform to predict whether the bill will pass? (2 points) a one sample, one sided hypothesis test a one sample, two sided hypothesis test a two sample, one sided hypothesis test `a two sample, two sided hypothesis testWhich value lies at the center of the sampling distribution of the mean? (2 points) the mean in your sample the value 0 the standard error of the mean the mean in the populationWhat conclusion can Meta draw based on her data? (2 points) She can say with 95% confidence that exactly 5% of the city's households are in poverty She cannot say with 95% confidence that less than 5% of the city's households are in poverty She can say with 95% confidence that less than 5% of the city's households are in poverty She can say with 95% confidence that more than 5% of the city's households are in poverty