Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
What are the main climatic influences for this station (air pressure, air mass sources, degree of conti-mentality, temperature of ocean currents)? 77777 SECTION 2 Earth's
What are the main climatic influences for this station (air pressure, air mass sources, degree of conti-mentality, temperature of ocean currents)?


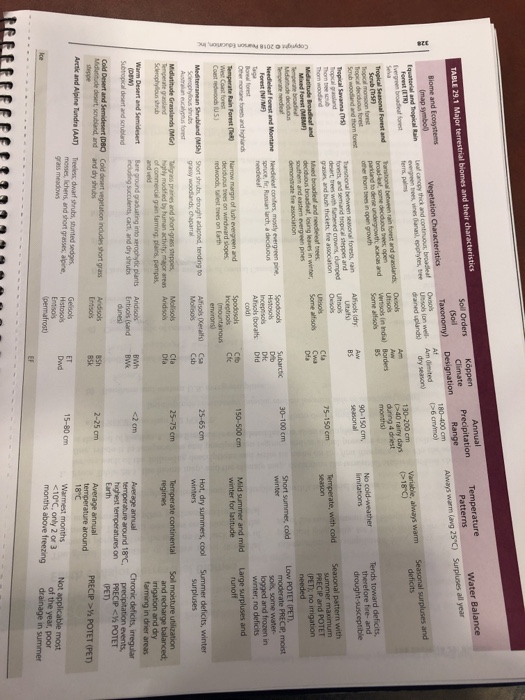
77777 SECTION 2 Earth's Major Terrestrial Biomes The global distribution of Earth's major terrestrial biomes is portrayed on the map on the back cover of this manual. Table 29.1 describes each biome on the map and summarizes other pertinent environmental Questions and completion items about this sample of Earth's terrestrial biomes. c) Mollisols and aridisols: 1. From Table 29.1, the biome map, and the climate map, determine the terrestrial biome that best charac terizes each of the following descriptions and write its name on the first line provided. On the second line, relate it to temperature and precipitation regimes and/or global pressure and wind belts outlined at the end of Section 1. The first one is completed for you as an example. a) PRECIP less than 1/2 POTET: [Warm desert and semidesert Imidlatitude continental interior and on leeward side of mountain rangel b) Southern and eastern U.S. evergreen pines: d) Characteristic of central Australia: e) Selva: f) Characteristic of the majority of central Canada: g) Transitional between rain forest and tropical steppes: h) Tallest trees on Earth: i) Sedges, mosses, and lichens: information-a compilation from many aspects of physical geography, for Earth's biomes are a synthe- sis of the environment and biosphere. i) Characteristic of Zambia (south-central Africa): k) Four biome types that occur in Chile: Lab Exercise 29: Biomes 1) Precipitation of 150-500 cm/year, outside the tropics: m) Characteristic of central Greenland: 322 n) Characteristic of Iran (northeast of the Persian Gulf o) Major area of commercial grain farming p) Seasonal precipitation of 90 to 150 cm/year ql Cla and Dfa climate types: r) Spodosols and permafrost, short summers: s) Southern Spain, Italy, and Greece, central California: t) Characteristic of Ireland and Wales: u) Just west of the 98th meridian in the United States: v) Just east of the 98th meridian in the United States: w) Bare ground and xerophytic plants: x) East coast of Madagascar: y) West coast of Madagascar: z) Characteristic of northern Mexico: Place name: Finally, from the GEOGRAPHY L. D. that you completed in the Preface of this lab manual, complete the following for your hometown or college campus location: Lab Exercise 29: Biome Kppen classification: 2. What are the main climatic influences for this station (air pressure, air mass sources, degree of conti- nentality, temperature of ocean currents)? Terrestrial biome characteristics: Copyright 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. 329 Copyright 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. TABLE 29.1 Major terrestrial biomes and their characteristics Biome and Ecosystems (map symbol) Equatorial and Tropical Rain Forest (ETR) Evergreen broadleaf forest Tropical Seasonal Forest and Scrub (TSF) Tropical monsoon forest Tropical deciduous forest Scrub woodland and the forest Ice Tropical Savanna (Tr) Tropical grassland Thon tree scrub Thom woodland Midatitude Broadleaf and Mixed Forest (MBM) Temperate broade Midantude deciduous Temperate needleaf Needleleaf Forest and Montane Forest (NMF) Taga Boreal forest Other montane forests and highlands Temperate Rain Forest (Te) West Coast forest Coast redwoods (US) Mediterranean Shrubland (MSH) Sclerophylous shrubs Australian eucalyptus forest Midlatitude Grasslands (MG) Temperate grassland Sclerophylous shrub Warm Desert and Semidesert (DBW) Subtropical desert and scrubland Cold Desert and Semidesert (DBC) Midlatitude desert, scrubland, and steppe Arctic and Alpine Tundra (AAT) Vegetation Characteristics Leal canopy thick and continuous; broadleaf evergreen trees, vines (anas), epiphytes, tree ferns, palms Transitional between rain forest and grasslands broad-leaf, some deciduous trees, open parkland to dense undergrowth; acacias and other thom trees in open growth Tansitional between seasonal forests, rain forests and semiarid tropical steppes and desert trees with flattened crowns, clumped grasses, and bush thickets, fire association Mixed broadleaf and needleleaf trees deciduous broadleat, losing leaves in winter, southern and eastern evergreen pines demonstrate fire association Needeleaf conifers, mostly evergreen pine, spruce, fic Russian larch, a deciduous reedelea Narrow margin of lush evergreen and deciduous trees on windward slopes redwoods, tallest trees on Earth Short shrubs, drought adapted, tending to grassy woodlands, chaparral Talligrass prairies and short-grass steppes, highly modified by human activity; major areas of commercial grain farming, plains, pampas, and veld Bare ground graduating into xerophytic plants including succulents, cact, and dry shrubs Cold desert vegetation includes short grass and dry shrubs Treeless dwarf shrubs, stunted sedges mosses, lichens, and short grasses; alpine, grass meadows Soll Orders (Soil Taxonomy) Osos Ultisols (on well- drained upland) Oxols Ultisols Vertisols (in India) Some alfisols Alisols (dry Utals) Utols Osos Utols Some alisols Spodosols Histosols Inceptisols Afisols (borals cold) Spodosols Inceptisols (mountainous environs) Alfisols (Xerals) Mollisos Mollisols Aridisols Aridisols Entisols (sand dunes) Aridisols Entisols Gelisols Histosols Entsols (permafrost) Kppen Climate Designation Af Am dimited dry season) Am Borders 85 Aw BS Cla Cwa Dia Subarctic Dib Dic Did Cfb Cic Csa Csb Cla Dfa BWh BWk BSh 85k ET Dwd EF Annual Precipitation Range 180-400 cm (>6 cm/mo) 130-200 cm 40 rainy days during 4 driest months) 90-150 cm, seasonal 75-150 cm 30-100 cm 150-500 cm 9 25-65 cm 25-75 cm 18'() No cold-weather limitations Temperate, with cold season Short summer, cold winter Mild summer and mild winter for latitude Hot, dry summers, cool winters Temperate continental regimes Average annual temperature around 18C Surpluses all year Water Balance Seasonal surpluses and deficits Tends toward deficits, therefore fire- and drought-susceptible Average annual temperature around 18C, highest temperatures on Earth Warmest months POTET (PET) Not applicable most of the year, poor drainage in summer
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.48 Rating (158 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


