Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
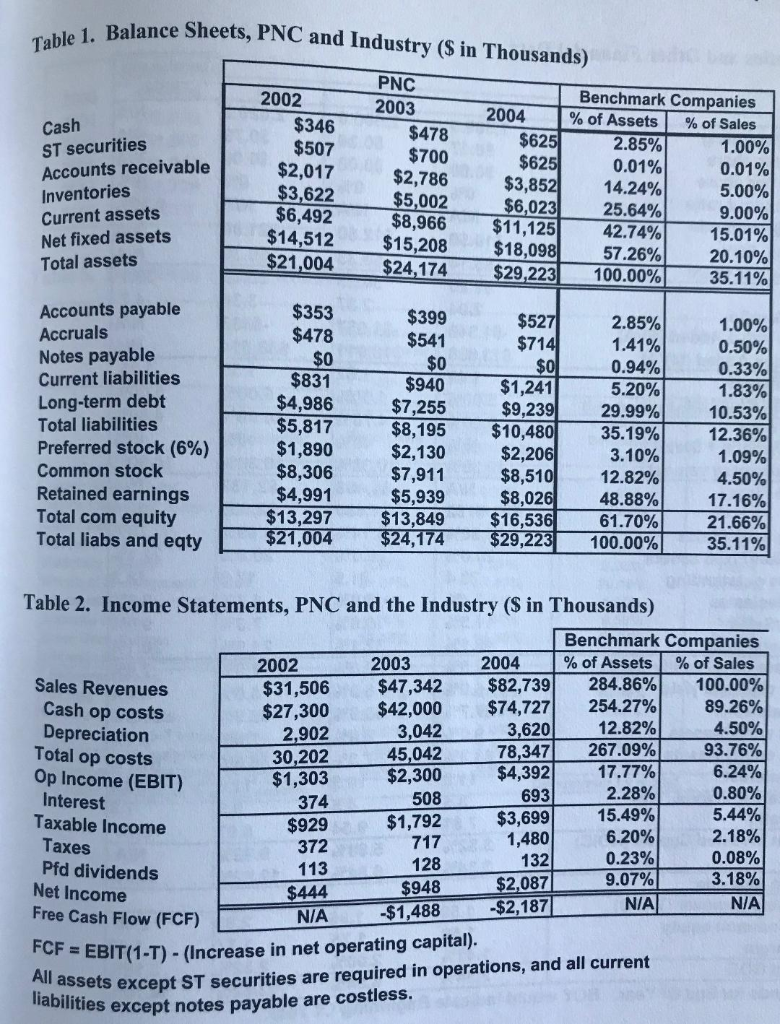
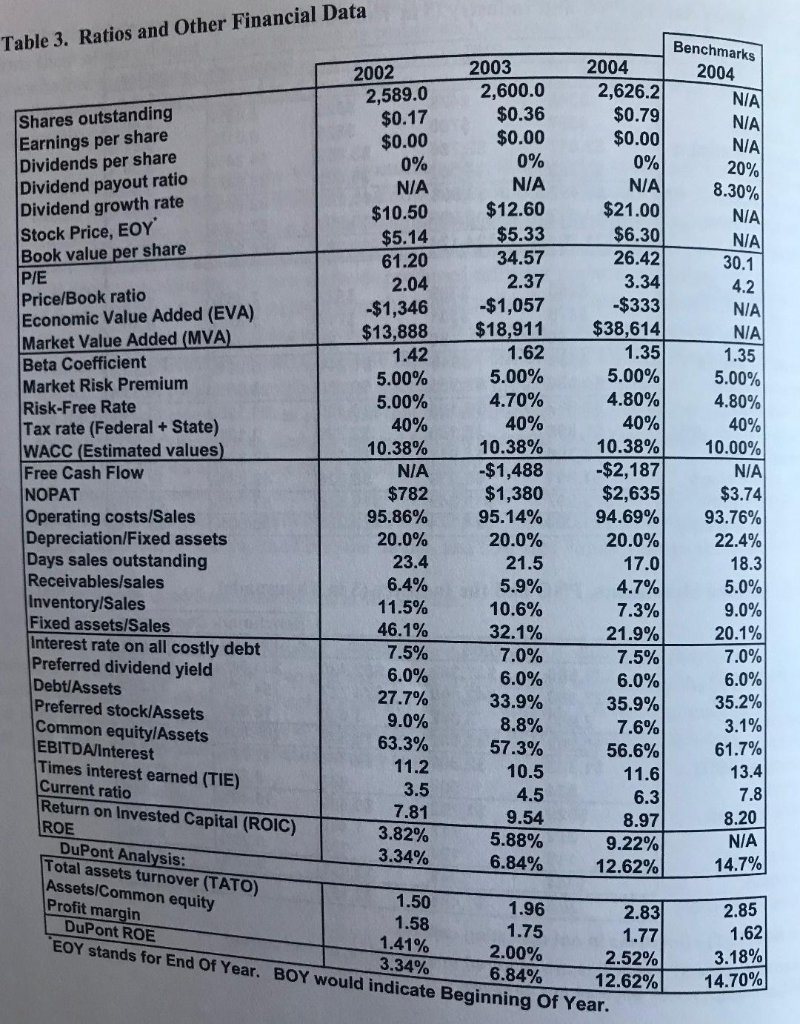
What are the relative valuation ratios. Table 3. Ratios and Other Financial Data Benchmarks 2004 2003 2004 2002 2,589.0 $0.17 $0.00 0% 2,626.2 $0.79 $0.00



What are the relative valuation ratios.
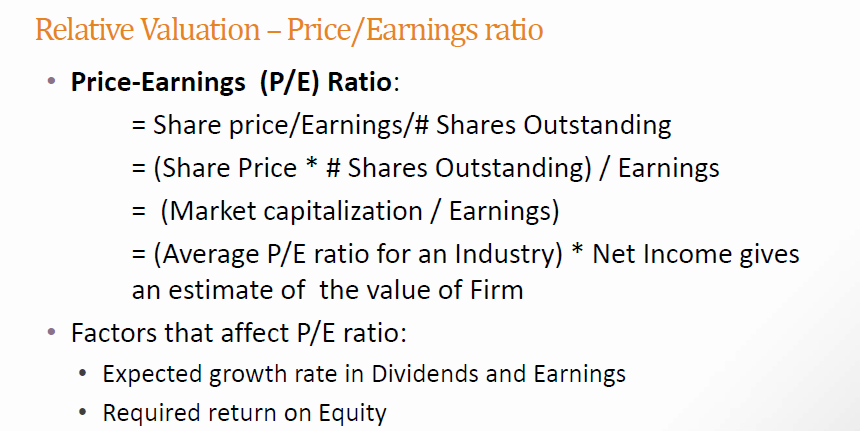
Table 3. Ratios and Other Financial Data Benchmarks 2004 2003 2004 2002 2,589.0 $0.17 $0.00 0% 2,626.2 $0.79 $0.00 0% N/A $21.00 $6.30 26.42 2,600.0 $0.36 $0.00 N/A N/A N/A 20% 8.30% Shares outstanding Earnings per share Dividends per share Dividend payout ratio Dividend growth rate Stock Price, EOY Book value per share P/E Price/Book ratio Economic Value Added (EVA) Market Value Added (MVA) Beta Coefficient Market Risk Premium Risk-Free Rate Tax rate (Federal + State) WACC (Estimated values) Free Cash Flow NOPAT Operating costs/Sales Depreciation/Fixed assets Days sales outstanding Receivables/sales Inventory/Sales Fixed assets/Sales Interest rate on all costly debt Preferred dividend yield Debt/Assets Preferred stock/Assets Common equity/Assets EBITDA/Interest Times interest earned (TIE) Current ratio Return on Invested Capital (ROIC) ROE DuPont Analysis: Total assets turnover (TATO) Assets/Common equity Profit margin DuPont ROE EOY stands for End Of Year. BOY would indicate Beginning Of Year. 0% N/A N/A $12.60 $5.33 $10.50 $5.14 N/A N/A 30.1 34.57 61.20 2.37 3.34 2.04 4.2 -$333 $38,614 -$1,057 -$1,346 $13,888 N/A $18,911 N/A 1.62 1.35 1.35 1.42 5.00% 5.00% 5.00% 5.00% 4.80% 4.70% 5.00% 40% 4.80% 40% 40% 40% 10.00% 10.38% 10.38% 10.38% -$2,187 $2,635 94.69% -$1,488 $1,380 95.14% N/A N/A $3.74 $782 95.86% 93.76% 20.0% 20.0% 20.0% 22.4% 23.4 21.5 17.0 18.3 6.4% 5.9% 4.7% 5.0% 11.5% 9.0% 20.1 % 10.6% 7.3% 46.1% 32.1% 21.9% 7.5% 7.0% 6.0% 7.5% 7.0% 6.0% 27.7% 6.0% 6.0% 33.9% 8.8% 57.3% 35.9% 7.6% 35.2% 9.0% 3.1% 63.3% 61.7% 13.4 56.6% 11.6 11.2 10.5 3.5 7.81 7.8 8.20 N/A 4.5 6.3 9.54 5.88% 6.84% 8.97 3.82% 9.22% 3.34% 14.7% 12.62% 1.50 1.58 1.41% 3.34% 1.96 2.83 2.85 1.75 2.00% 6.84% 1.62 1.77 3.18% 14.70% 2.52% 12.62% Relative Valuation DCF Valuation is problematic with negative Free Cash Flows (FCFs) Relative Valuation uses the rationale o standardizing value, using "Comparables" from the same industry as benchmarks Earnings Price/Earnings Value/EBIT Book Value Price/Book Value Revenue Price/Sales Comparable Multiples: Price/Earnings (P/E) ratio Determining Variables: Price/Book (P/BV) ratio Price/Sales ratio Relative Valuation - Price/Earnings ratio Price-Earnings (P/E) Ratio: = Share price/Earnings/#Shares Outstanding (Share Price* #Shares Outstanding) Earnings (Market capitalization Earnings) (Average P/E ratio for an Industry) * Net Income gives an estimate of the value of Firm Factors that affect P/E ratio: Expected growth rate in Dividends and Earnings Required return on Equity Relative Valuation - Price/Sales Ratio Price/sales ratio While, sales are less susceptible to manipulations, they are not necessarily correlated with profits or cash flows An additional requirement of similar operating margins on comparable businesses. Enterprise Value to EBITDA or EBIT EV/EBITDA or EV/EBIT multiples are popular being closer to cashflows Sample of Industry Average Comparables: Use Avg. P/E Multiple of 21.2 and multiply with earnings to get an estimate of firm value Use Avg. P/Rev. Multiple of 0.9 and multiply with sales to get an estimate of firm value Table 3. Ratios and Other Financial Data Benchmarks 2004 2003 2004 2002 2,589.0 $0.17 $0.00 0% 2,626.2 $0.79 $0.00 0% N/A $21.00 $6.30 26.42 2,600.0 $0.36 $0.00 N/A N/A N/A 20% 8.30% Shares outstanding Earnings per share Dividends per share Dividend payout ratio Dividend growth rate Stock Price, EOY Book value per share P/E Price/Book ratio Economic Value Added (EVA) Market Value Added (MVA) Beta Coefficient Market Risk Premium Risk-Free Rate Tax rate (Federal + State) WACC (Estimated values) Free Cash Flow NOPAT Operating costs/Sales Depreciation/Fixed assets Days sales outstanding Receivables/sales Inventory/Sales Fixed assets/Sales Interest rate on all costly debt Preferred dividend yield Debt/Assets Preferred stock/Assets Common equity/Assets EBITDA/Interest Times interest earned (TIE) Current ratio Return on Invested Capital (ROIC) ROE DuPont Analysis: Total assets turnover (TATO) Assets/Common equity Profit margin DuPont ROE EOY stands for End Of Year. BOY would indicate Beginning Of Year. 0% N/A N/A $12.60 $5.33 $10.50 $5.14 N/A N/A 30.1 34.57 61.20 2.37 3.34 2.04 4.2 -$333 $38,614 -$1,057 -$1,346 $13,888 N/A $18,911 N/A 1.62 1.35 1.35 1.42 5.00% 5.00% 5.00% 5.00% 4.80% 4.70% 5.00% 40% 4.80% 40% 40% 40% 10.00% 10.38% 10.38% 10.38% -$2,187 $2,635 94.69% -$1,488 $1,380 95.14% N/A N/A $3.74 $782 95.86% 93.76% 20.0% 20.0% 20.0% 22.4% 23.4 21.5 17.0 18.3 6.4% 5.9% 4.7% 5.0% 11.5% 9.0% 20.1 % 10.6% 7.3% 46.1% 32.1% 21.9% 7.5% 7.0% 6.0% 7.5% 7.0% 6.0% 27.7% 6.0% 6.0% 33.9% 8.8% 57.3% 35.9% 7.6% 35.2% 9.0% 3.1% 63.3% 61.7% 13.4 56.6% 11.6 11.2 10.5 3.5 7.81 7.8 8.20 N/A 4.5 6.3 9.54 5.88% 6.84% 8.97 3.82% 9.22% 3.34% 14.7% 12.62% 1.50 1.58 1.41% 3.34% 1.96 2.83 2.85 1.75 2.00% 6.84% 1.62 1.77 3.18% 14.70% 2.52% 12.62% Relative Valuation DCF Valuation is problematic with negative Free Cash Flows (FCFs) Relative Valuation uses the rationale o standardizing value, using "Comparables" from the same industry as benchmarks Earnings Price/Earnings Value/EBIT Book Value Price/Book Value Revenue Price/Sales Comparable Multiples: Price/Earnings (P/E) ratio Determining Variables: Price/Book (P/BV) ratio Price/Sales ratio Relative Valuation - Price/Earnings ratio Price-Earnings (P/E) Ratio: = Share price/Earnings/#Shares Outstanding (Share Price* #Shares Outstanding) Earnings (Market capitalization Earnings) (Average P/E ratio for an Industry) * Net Income gives an estimate of the value of Firm Factors that affect P/E ratio: Expected growth rate in Dividends and Earnings Required return on Equity Relative Valuation - Price/Sales Ratio Price/sales ratio While, sales are less susceptible to manipulations, they are not necessarily correlated with profits or cash flows An additional requirement of similar operating margins on comparable businesses. Enterprise Value to EBITDA or EBIT EV/EBITDA or EV/EBIT multiples are popular being closer to cashflows Sample of Industry Average Comparables: Use Avg. P/E Multiple of 21.2 and multiply with earnings to get an estimate of firm value Use Avg. P/Rev. Multiple of 0.9 and multiply with sales to get an estimate of firm valueStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


