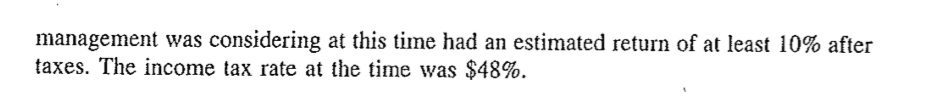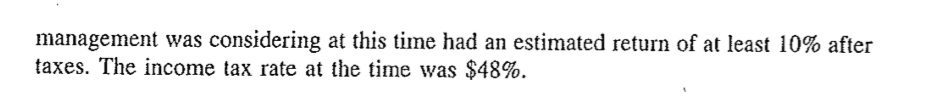

- What are the relevant cash flows associated with rehabilitating the Conway? Be as specific as possible and identify the categories to which each cash flow belongs (i.e., Initial Outlay, Terminal, Operating).
- What are the relevant cash flows for the replacement project (buying a new diesel boat)? Be as specific as possible and identify the categories to which each cash flow belongs (i.e., Initial Outlay, Terminal, Operating).
- Using payback, NPV, and IRR analyses, should the company accept the project of purchasing a new diesel boat? In other words, do the annual cost savings of the new boat relative to rehabilitating and using the Conwayoutweigh the additional expense associated with purchasing the new boat? Or, are they better off rejecting the project and just repairing the Conway? Be sure to show all work and explain your reasoning. [Hint: Perform a single analysis on the incremental differencesin cash flows for parts 1) and 2) above.]
Economy Shipping Company (Abridged) In the spring of 1950 the controller of Economy Shipping Company, located near Pittsburgh, was preparing a report for the executive committee regarding the feasibility of repairing one of the company's steam riverboats or of repacing the steamboat with a new diesel-powered boat. The Economy Shipping Company was engaged mainly in the transportation of coal from the nearby mines to the steel mills, public utilities, and other industries in the Pittsburgh area. Occasionally, the company's several steamboats also carried cargoes to places as far away as New Orleans. The boats owned by Economy Shipping were all steam powered. All were at least 10 years old, and the majority of them were between 15 and 30 years old. The steamboat the controller was concerned about, the Conway, was 23 years old and required immediate rehabilitation or replacement. It was estimated that the Con- way had a useful life of another 20 years provided that adequate repairs and mainte- nance were made. The book value of the Conway was $39,500, but the controller believed that if the company sold the boat in 1950, i would bring only around $25,000. The immediate rehabilitation costs for the Conway were estimated to be $115,000. The controller estimated that these general rehabilitation expenditures would extend the useful life of the Conway for about 20 years New spare parts from another boat, which had been retired in 1948, were available for use in the rehabilitation of the Conway. If these parts were used on the Conway, an estimate of their fair value was $43,500, which was their book value. Use of these parts would, in effect, decrease the immediate rehabilitation costs from $115,000 to $71,500. It was believed that if these parts were sold on the market they would bring only around $30,000. They could not be used on any of the other Economy Shipping steamboats Currently, the Conway was operated by a crew of 20. Annual operating costs for the 20-person crew are shown in Table A. TABLE A Annual Operating Costs for the Conway and Its Crew Vacation and sickness benefits ..._.... .__........................... . Social security payments . . 2400 uel . .34 $203,150 The controller estimated that the cost of dismantling and scrapping the Coniway at the end of its useful life after the overhaul would be offset by the value of the scrap and used parts taken off the boat. An alternative to rehabilitating the steamboat was the purchase of a diesel powered boat. The Quapelle Company, a local boat manufacturer, quoted the price of $325,000 for a diesel boat. An additional $75,000 for a basic parts inventory would be necessary to service a diesel boat, and such an inventory would be sufficient to service up to three diesel boats. If four or more diesels were purchased, however, it was estimated that additional spare parts inventory would be necessary The useful life of a diesel-powered boat was estimated to be 25 years; at the end of that time the boat would be scrapped or completely rehabilitated at a cost approxi-j mately equal to that of a new boat. The controller did not contemplate the possibility diesel engine replacement during the 25-year life, because information from ot companies having limited experience with diesel-powered riverboats did not indicate that such costs needed to be anticipated. A general overhaul of the engines, costing $60,000 at current prices, would, however, be expected every 10 years After consulting the Quapelle Company and other companies operating diesel; powered boats, the controller estimated that the annual operating costs of such a boat would total $156,640 (see Table B) Although the Economy Shipping controller had not considered the matter, at the? end of the twentieth year, the diesel boat would have a realizable value of $32,500 and the inventory of parts, $37,500 Another factor the controller was considering at this time was alternative uses of funds. In the spring of 1950, Economy had sufficient funds to buy four diesel-powered boats; however, there were alternative uses for these funds. The other projects that TABLE B Annual Operating Costs for a Diesel-Powered Boat Vacation and sickness benefits . ..............._ . . . . 680 1,170 10,020 21,700 ..28,800 Fuel Miscellaneous service and supplies 14,650 $156,640 Excluding possible major overhaul of diesel engines management was considering at this time had an estimated return of at least 10% after taxes. The income tax rate at the time was $48% Economy Shipping Company (Abridged) In the spring of 1950 the controller of Economy Shipping Company, located near Pittsburgh, was preparing a report for the executive committee regarding the feasibility of repairing one of the company's steam riverboats or of repacing the steamboat with a new diesel-powered boat. The Economy Shipping Company was engaged mainly in the transportation of coal from the nearby mines to the steel mills, public utilities, and other industries in the Pittsburgh area. Occasionally, the company's several steamboats also carried cargoes to places as far away as New Orleans. The boats owned by Economy Shipping were all steam powered. All were at least 10 years old, and the majority of them were between 15 and 30 years old. The steamboat the controller was concerned about, the Conway, was 23 years old and required immediate rehabilitation or replacement. It was estimated that the Con- way had a useful life of another 20 years provided that adequate repairs and mainte- nance were made. The book value of the Conway was $39,500, but the controller believed that if the company sold the boat in 1950, i would bring only around $25,000. The immediate rehabilitation costs for the Conway were estimated to be $115,000. The controller estimated that these general rehabilitation expenditures would extend the useful life of the Conway for about 20 years New spare parts from another boat, which had been retired in 1948, were available for use in the rehabilitation of the Conway. If these parts were used on the Conway, an estimate of their fair value was $43,500, which was their book value. Use of these parts would, in effect, decrease the immediate rehabilitation costs from $115,000 to $71,500. It was believed that if these parts were sold on the market they would bring only around $30,000. They could not be used on any of the other Economy Shipping steamboats Currently, the Conway was operated by a crew of 20. Annual operating costs for the 20-person crew are shown in Table A. TABLE A Annual Operating Costs for the Conway and Its Crew Vacation and sickness benefits ..._.... .__........................... . Social security payments . . 2400 uel . .34 $203,150 The controller estimated that the cost of dismantling and scrapping the Coniway at the end of its useful life after the overhaul would be offset by the value of the scrap and used parts taken off the boat. An alternative to rehabilitating the steamboat was the purchase of a diesel powered boat. The Quapelle Company, a local boat manufacturer, quoted the price of $325,000 for a diesel boat. An additional $75,000 for a basic parts inventory would be necessary to service a diesel boat, and such an inventory would be sufficient to service up to three diesel boats. If four or more diesels were purchased, however, it was estimated that additional spare parts inventory would be necessary The useful life of a diesel-powered boat was estimated to be 25 years; at the end of that time the boat would be scrapped or completely rehabilitated at a cost approxi-j mately equal to that of a new boat. The controller did not contemplate the possibility diesel engine replacement during the 25-year life, because information from ot companies having limited experience with diesel-powered riverboats did not indicate that such costs needed to be anticipated. A general overhaul of the engines, costing $60,000 at current prices, would, however, be expected every 10 years After consulting the Quapelle Company and other companies operating diesel; powered boats, the controller estimated that the annual operating costs of such a boat would total $156,640 (see Table B) Although the Economy Shipping controller had not considered the matter, at the? end of the twentieth year, the diesel boat would have a realizable value of $32,500 and the inventory of parts, $37,500 Another factor the controller was considering at this time was alternative uses of funds. In the spring of 1950, Economy had sufficient funds to buy four diesel-powered boats; however, there were alternative uses for these funds. The other projects that TABLE B Annual Operating Costs for a Diesel-Powered Boat Vacation and sickness benefits . ..............._ . . . . 680 1,170 10,020 21,700 ..28,800 Fuel Miscellaneous service and supplies 14,650 $156,640 Excluding possible major overhaul of diesel engines management was considering at this time had an estimated return of at least 10% after taxes. The income tax rate at the time was $48%