Question
What is the price of the following zero-coupon bonds if interest rates are (a) 4, (b) 7, and (c) 10 percent? Bond A: zero-coupon;
What is the price of the following zero-coupon bonds if interest rates are (a) 4, (b) 7, and (c) 10 percent?
• Bond A: zero-coupon; maturity 5 years
• Bond B: zero-coupon; maturity 10 years
• Bond C: zero-coupon; maturity 20 years
What generalization can be made concerning the term of a zero-coupon bond and its price in relation to changes in the level of interest rates?
You are in the 24 percent federal income tax bracket. A corporate bond offers you 6.8 percent while a tax-exempt bond with the same credit rating and term to maturity offers 4.1 percent. On the basis of taxation, which bond should be preferred? Explain.
A six-month $10,000 Treasury bill is selling for $9,844. What is the annual yield according to the discount method? Does this yield understate or overstate the true annual compound yield? Explain.
An investor in the 35 percent tax bracket may purchase a corporate bond that is rated A and yields 6.0 percent. The investor may also buy an A-rated municipal bond with a 3.9 percent yield. Why may the corporate bond be preferred?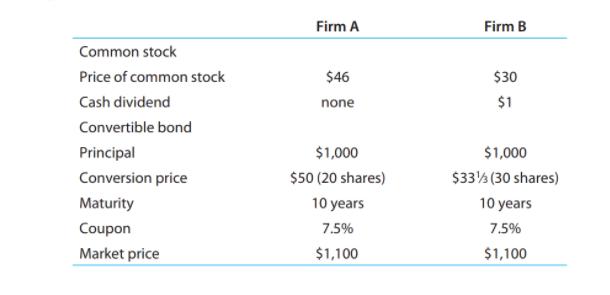
a) What is the value of each bond in terms of stock?
b) What is the premium paid over each bond's value as stock?
c) What is each bond's income advantage over the stock into which the bond may be converted?
d) How long will it take for the income advantage to offset the premium determined in part (b)?
e) If after four years firm A's stock sells for $65 and the firm calls the bond, what is the holding period return and the annual rate of return earned on an investment in the stock or in the bond?
Firm A Firm B Common stock Price of common stock $46 $30 Cash dividend none $1 Convertible bond Principal $1,000 $1,000 Conversion price $50 (20 shares) Maturity 10 years Coupon 7.5% Market price $1,100 $33 (30 shares) 10 years 7.5% $1,100
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
The price of a zerocoupon bond can be calculated using the formula P fracFV1 rn Where P price of the bond FV face value of the bond r interest rate n number of years to maturity For Bond A FV 1000 ass...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


