Question
Landers Ltd is a major Australian bicycle manufacturer. Over the last decade, bicycle manufacturers from Taiwan and Korea have been able to price their bikes
Landers Ltd is a major Australian bicycle manufacturer. Over the last decade, bicycle manufacturers from Taiwan and Korea have been able to price their bikes below the Landers products, but the company has retained its market share due to the poor quality of the imported bikes. Recently, however, the quality of the imported bikes has improved, and Landers has had to cut prices to maintain market share. The managing director, John Landers, is concerned about the viability of the business at these lower prices and asks the accountant, Eloise Martin, to investigate the problem.
Martin’s initial investigation indicates that the lower prices cannot be sustained in the longer term, as they do not cover the costs of manufacture, let alone contribute to the company’s selling and administrative costs. She looks for possible cost reductions. The company has always had a reputation for high quality, but Martin feels that there are substantial costs incurred in attaining this level of quality. She knows that there are extensive quality inspection checks throughout the production process and that many employees spend part of their time reworking defective parts. She has also noticed the buckets full of scrapped parts and components spread throughout the factory. These costs are not recorded separately in the existing accounting system. Martin asks Landers to support the development of a cost of quality system.
- Landers:What do you mean, a system that records the costs of poor quality! Our bikes are among the best in terms of quality!
- Martin:I know that, John, and we know what it costs us to make our bikes, but we’ve got no idea how much of that cost is related to ensuring quality. I think the cost of quality here is very high. What if it’s a third of our manufacturing costs? And what if we could reduce it without compromising our quality? We could keep our prices down and still make a good profit.
Page 807
- Landers:Okay, Eloise. Give your cost of quality system a try, though I don’t see how it will help. Everybody knows that good quality costs money. Even if we do find out our cost of quality, I don’t see how it will help us reduce it.
- Martin:John, good quality doesn’t seem to cost money in Taiwan and Korea. Their prices haven’t gone up, even though their quality has. You’ll soon see that understanding quality costs can help you to reduce them and to improve quality at the same time.
Over the next six months Martin identifies the following costs of quality:
cost of replacement bikes provided under warranty, $7 500
cost of bikes returned by customers and scrapped, $7 500
sales commissions on faulty bikes returned by customers, $750
contribution margin forgone on bikes returned by customers, $1 500
rework on defective wheels, $12 000
quality inspection in the goods receiving area, $22 500
quality inspections during processing, $34 500
laboratory testing of bikes and components, $19 500
contribution margin forgone on lost future bike sales, $7 500
engineering costs to correct production line quality problems, $22 500
lost contribution on machine downtime during correction of production line quality problems, $37 500
operating an X-ray machine to detect faulty welds, $22 500
cost of repairs under warranty, $1 500
cost of rewelding faulty joints discovered during processing, $28 500
cost of quality training programs, $4 500
inspection of bikes put into finished goods warehouse, $24 000
cost of faulty components that are scrapped, $6 000
cost of faulty bikes that are scrapped after finished goods inspection, $15 000.
During this period, total manufacturing costs were $900 000.
Exhibit 16.11 figure
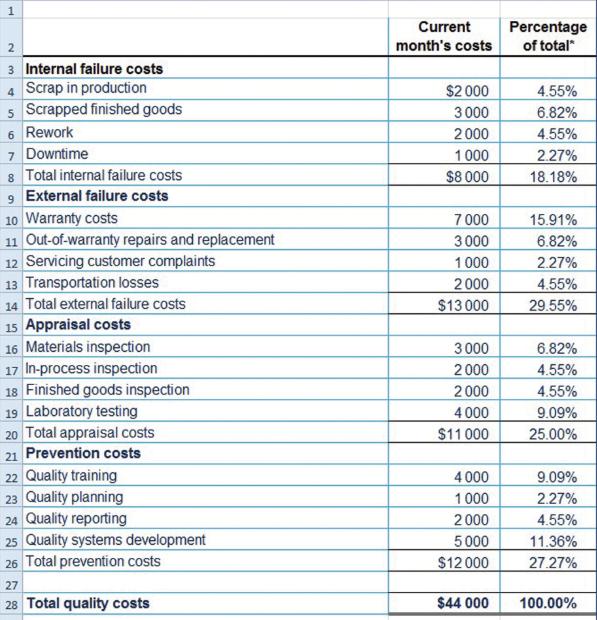
Q1.Prepare a cost of quality report similar to the report shown in Exhibit 16.11
.Q2.Use the information in this report to suggest ways in which the company could reduce its cost of quality.
Q3. When John Landers receives the cost of quality report, he is amazed and says, ‘Eloise, you’re the accountant. Why didn’t you tell me before that our quality costs were this high?’ Explain to Landers why Martin was unable, because of the existing accounting system, to tell him much about the cost of quality.
Percentage of total Current month's costs 3 Internal failure costs 4 Scrap in production 5 Scrapped finished goods 6 Rework 7 Downtime 8 Total internal failure costs $2 000 3 000 4.55% 6.82% 4.55% 2.27% 18.18% 2 000 1000 $8 000 9 External failure costs 10 Warranty costs 11 Out-of-warranty repairs and replacement 12 Servicing customer complaints 13 Transportation losses 14 Total external failure costs 15 Appraisal costs 16 Materials inspection 17 In-process inspection 18 Finished goods inspection 19 Laboratory testing 20 Total appraisal costs 21 Prevention costs 7 000 15.91% 6.82% 3 000 1000 2000 $13 000 2.27% 4.55% 29.55% 3 000 2 000 6.82% 4.55% 4.55% 2000 4 000 $11 000 9.09% 25.00% 22 Quality training 23 Quality planning 24 Quality reporting 25 Quality systems development 26 Total prevention costs 4 000 1000 2 000 9.09% 2.27% 4.55% 5 000 $12 000 11.36% 27.27% 27 28 Total quality costs $44 000 100.00% 1, 2.
Step by Step Solution
3.37 Rating (163 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Required solution of all parts is given below Ans 1 Landers Ltd Quality cost report Current Percentage months cost of total Internal failure costs Rew...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Document Format ( 2 attachments)
635e1dfea3ce1_181593.pdf
180 KBs PDF File
635e1dfea3ce1_181593.docx
120 KBs Word File
Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


