Question
1. The firm's profit function is defined by T(q, x; 3) = s(q-x) + fx-c(q). (1) The firm produces q units of output at
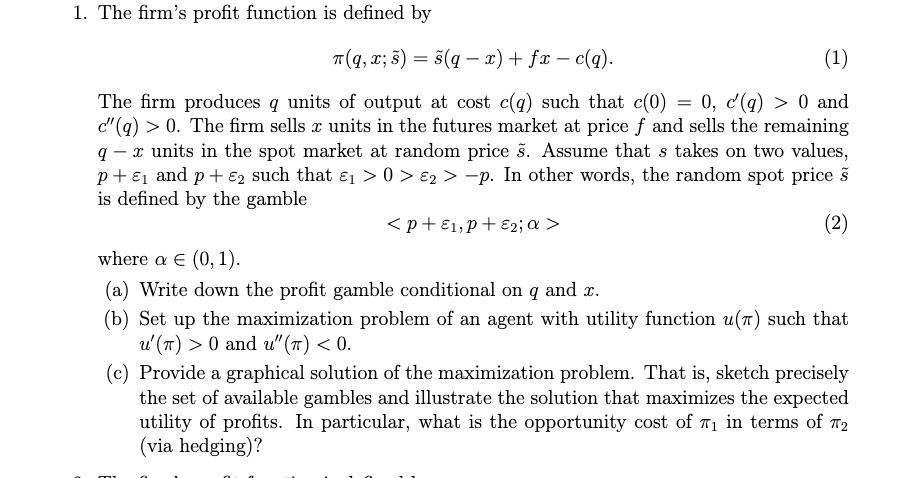
1. The firm's profit function is defined by T(q, x; 3) = s(q-x) + fx-c(q). (1) The firm produces q units of output at cost c(q) such that c(0) 0, c'(q) > 0 and c"(q) > 0. The firm sells x units in the futures market at price f and sells the remaining q- x units in the spot market at random price . Assume that s takes on two values, p+ and p + E2 such that > 0> 2> -p. In other words, the random spot price is defined by the gamble (2) = where a (0, 1). (a) Write down the profit gamble conditional on q and x. (b) Set up the maximization problem of an agent with utility function u(7) such that u' (T) > 0 and u" ()
Step by Step Solution
3.49 Rating (156 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
a The profit gamble conditional on q and x is where qx qx fx cq and qx1 qx p 1 cq b The maximization ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get StartedRecommended Textbook for
Managerial Economics and Strategy
Authors: Jeffrey M. Perloff, James A. Brander
1st edition
978-0137036059, 133379094, 321566440, 137036051, 9780133379099, 978-0321566447
Students also viewed these Economics questions
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
View Answer in SolutionInn App



