Question: Whenever LOAD = 1, the counter state (Q_3 Q_2 Q_1 Q_0) takes on the value supplied by the parallel load inputs (D_3 D_2 D_1 D_0)
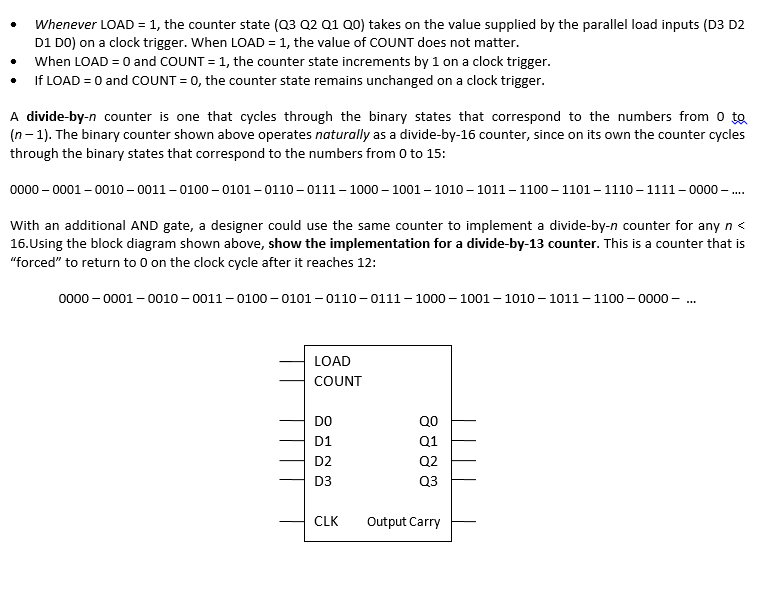
Whenever LOAD = 1, the counter state (Q_3 Q_2 Q_1 Q_0) takes on the value supplied by the parallel load inputs (D_3 D_2 D_1 D_0) on a clock trigger. When LOAD = 1, the value of COUNT does not matter. When LOAD = 0 and COUNT = 1, the counter state increments by 1 on a clock trigger. If LOAD = 0 and COUNT = 0, the counter state remains unchanged on a clock trigger. A divide-by-n counter is one that cycles through the binary states that correspond to the numbers from 0 (n - 1). The binary counter shown above operates naturally as a divide-by-16 counter, since on its own the counter cycles through the binary states that correspond to the numbers from 0 to 15: 0000 - 0001 - 0010 - 0011 - 0100 - 0101 - 0110 - 0111 - 1000 -1001 - 1010 -1011 -1100 -1101 -1110 - 1111 - 0000 -.... With an additional AND gate, a designer could use the same counter to implement a divide-by-n counter for any n
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


