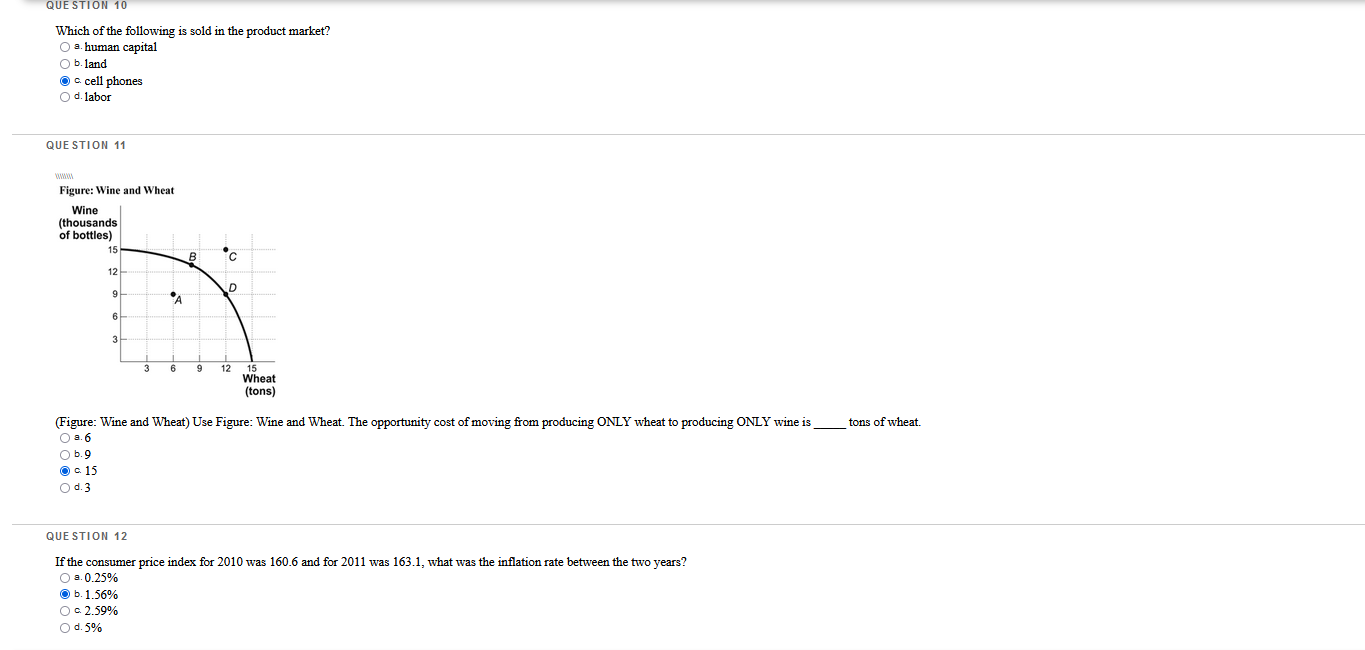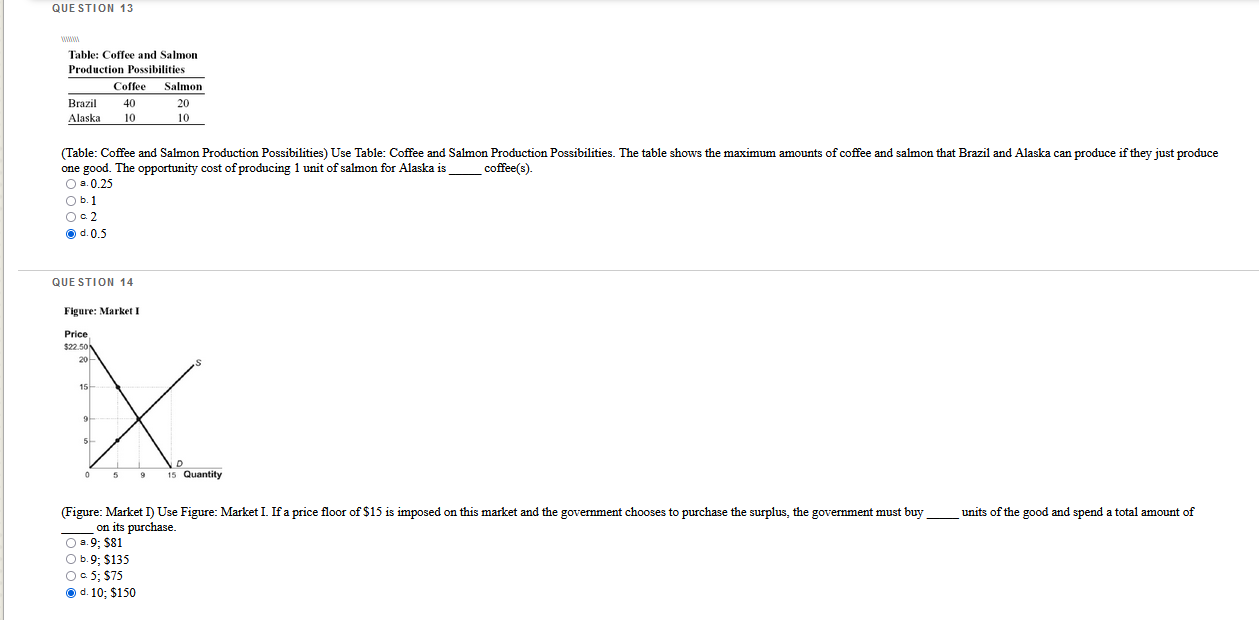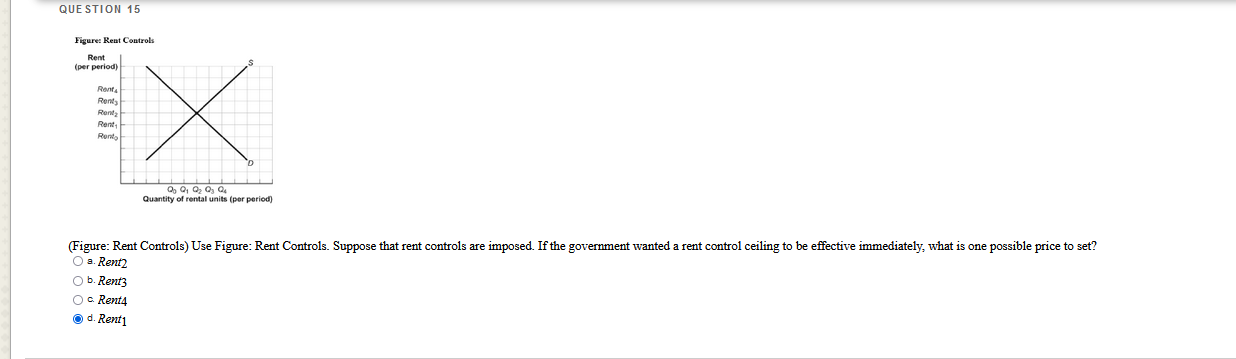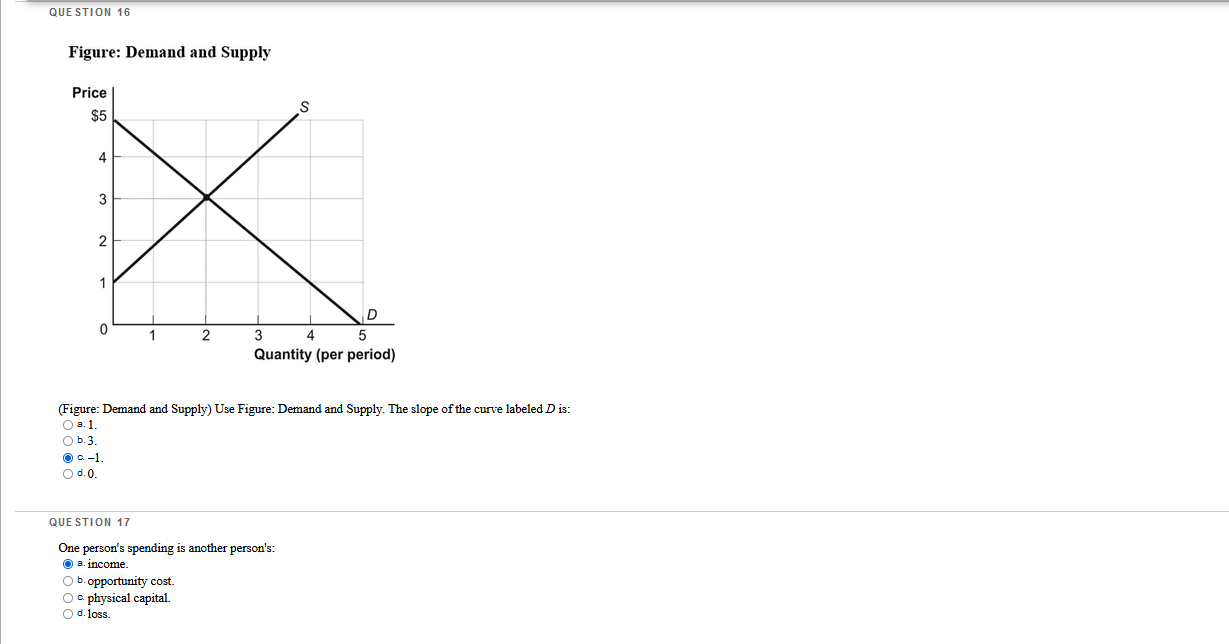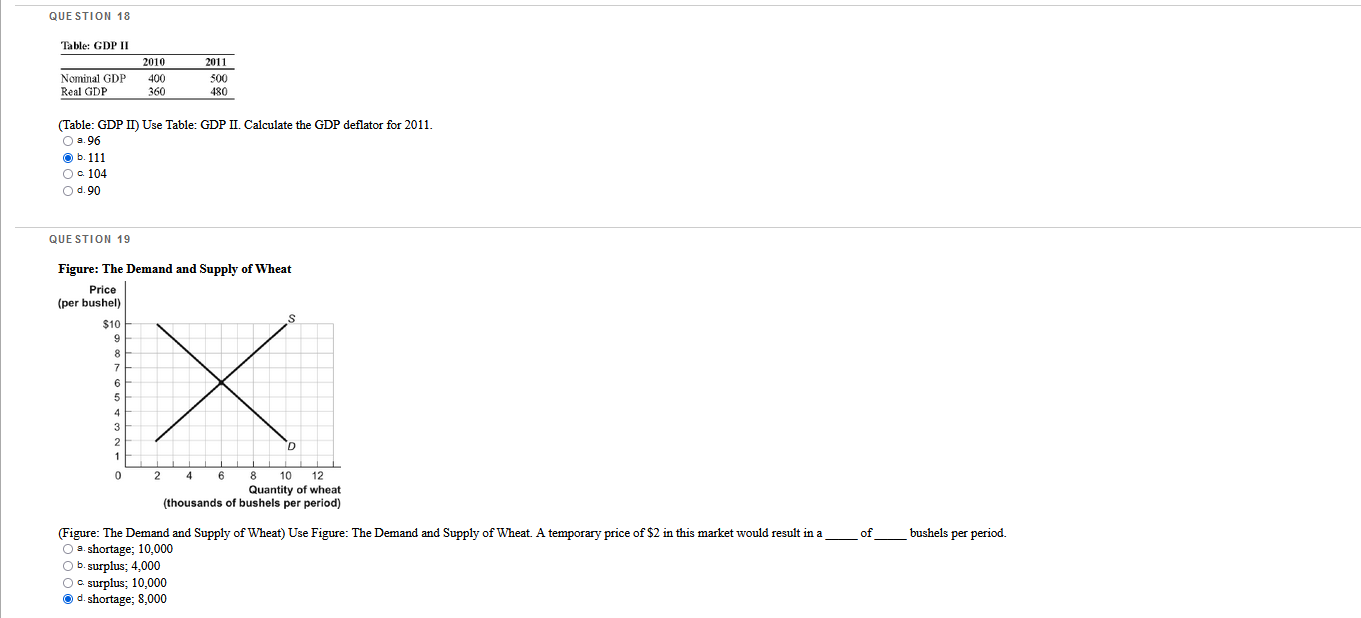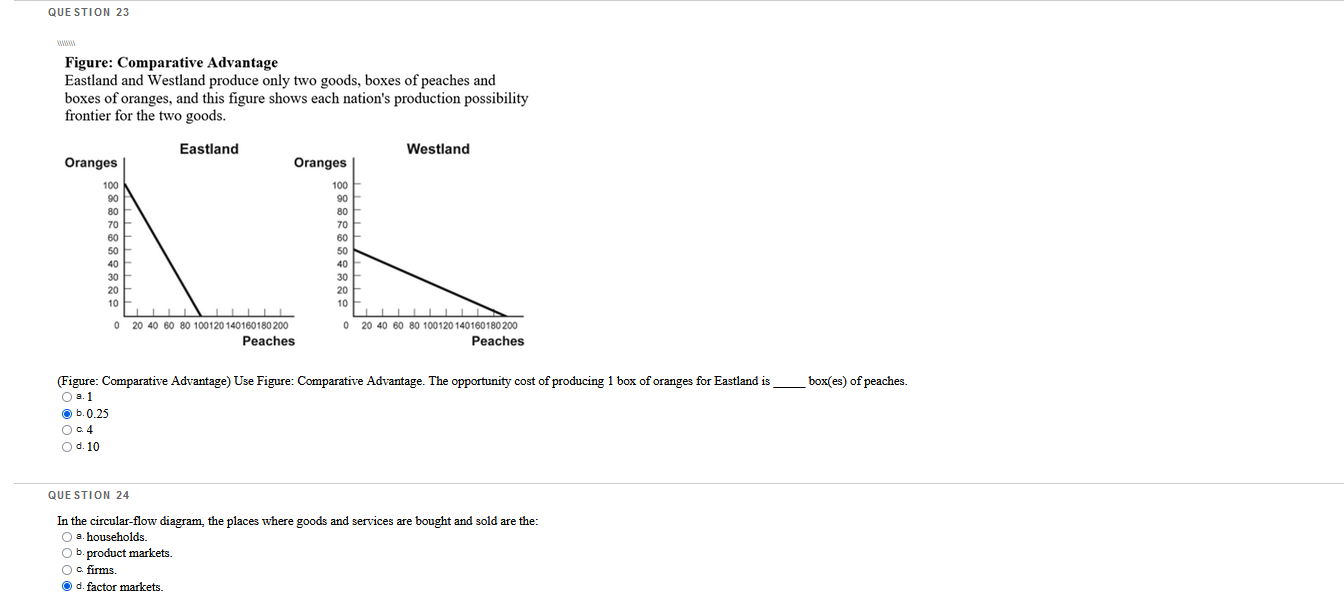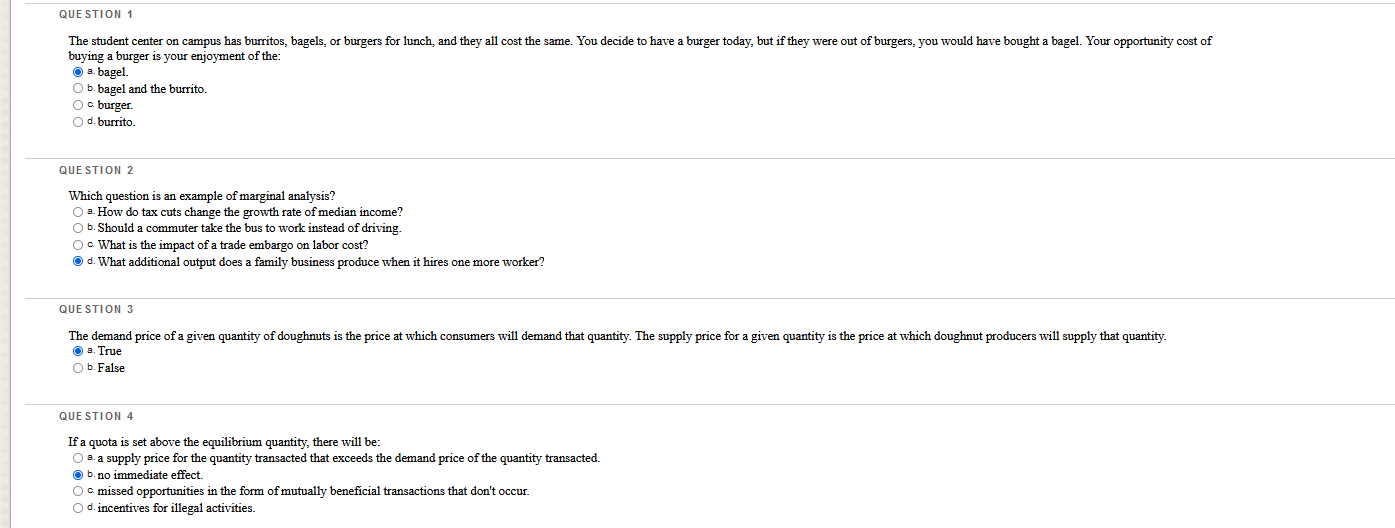
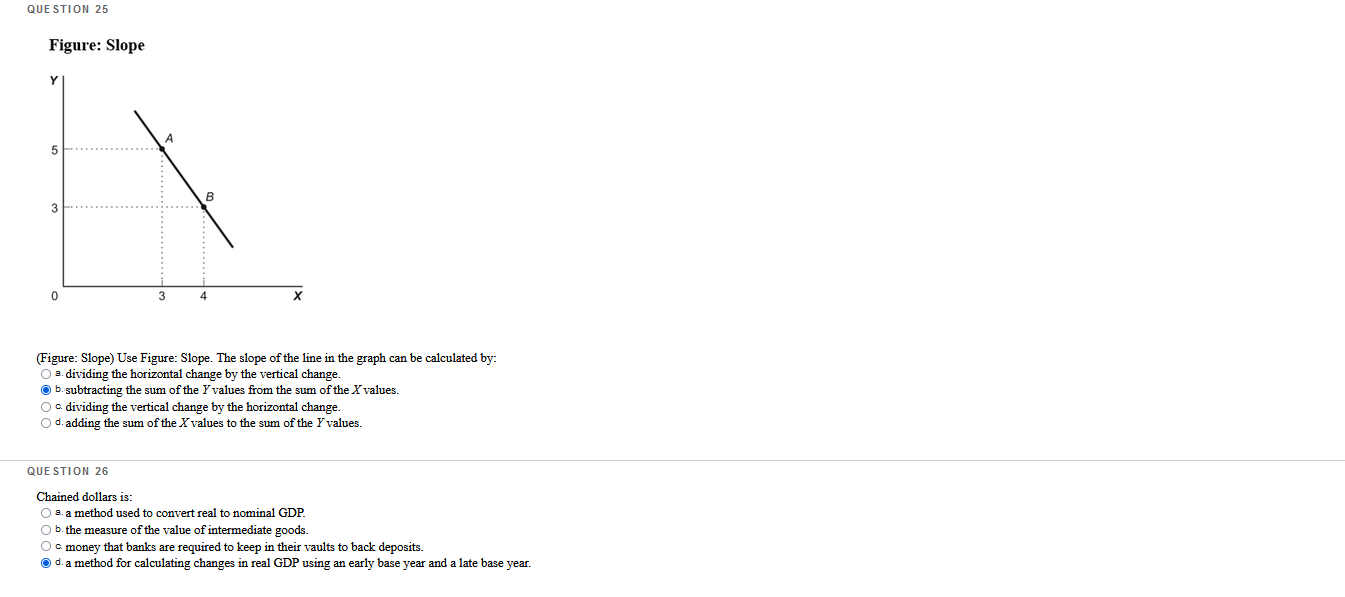
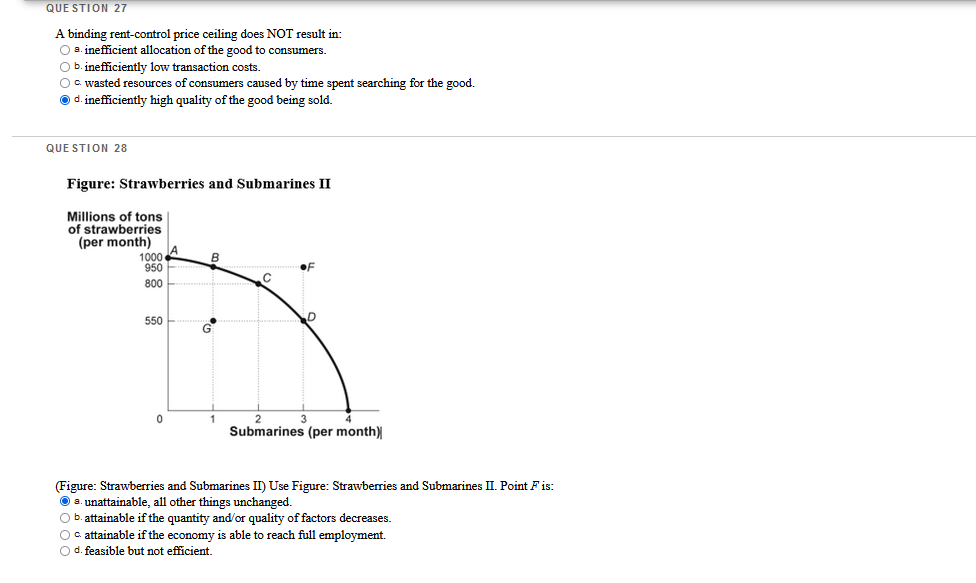
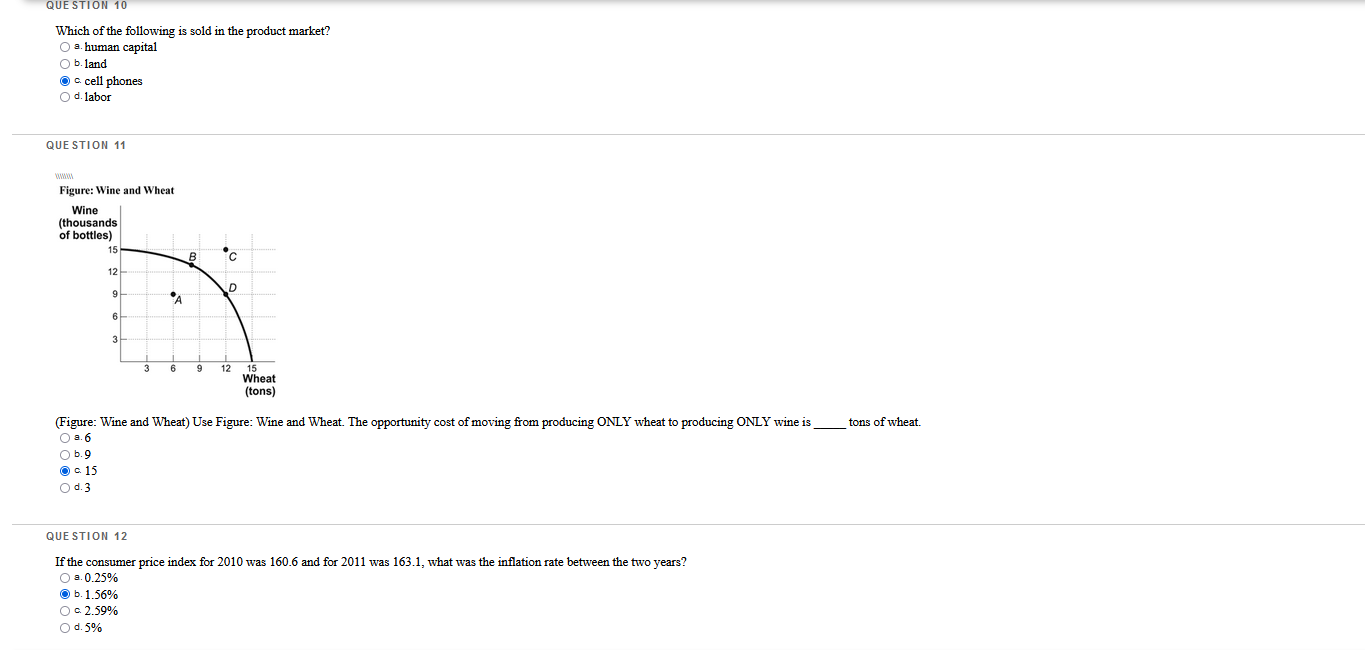
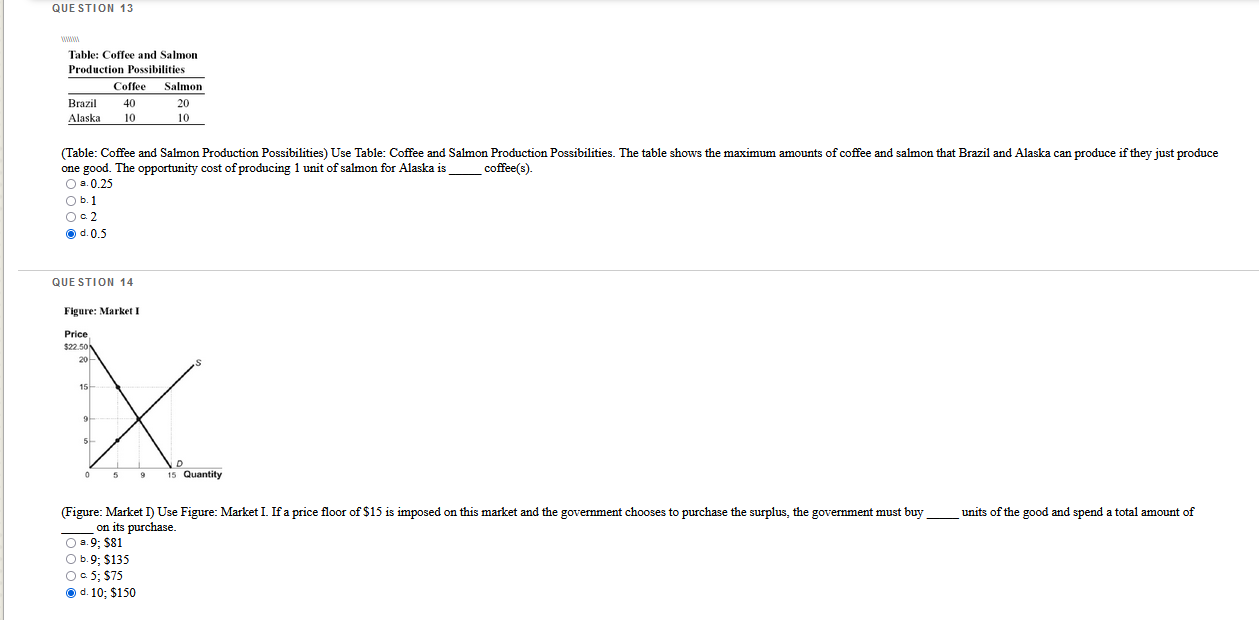
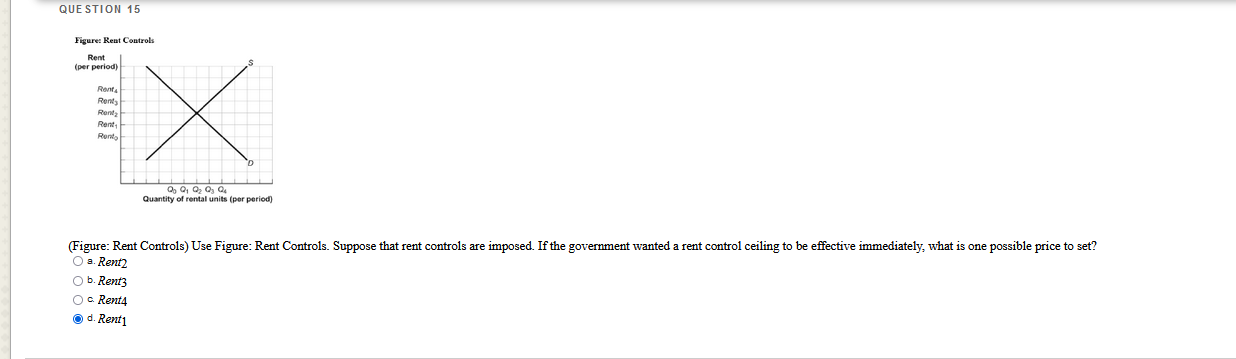
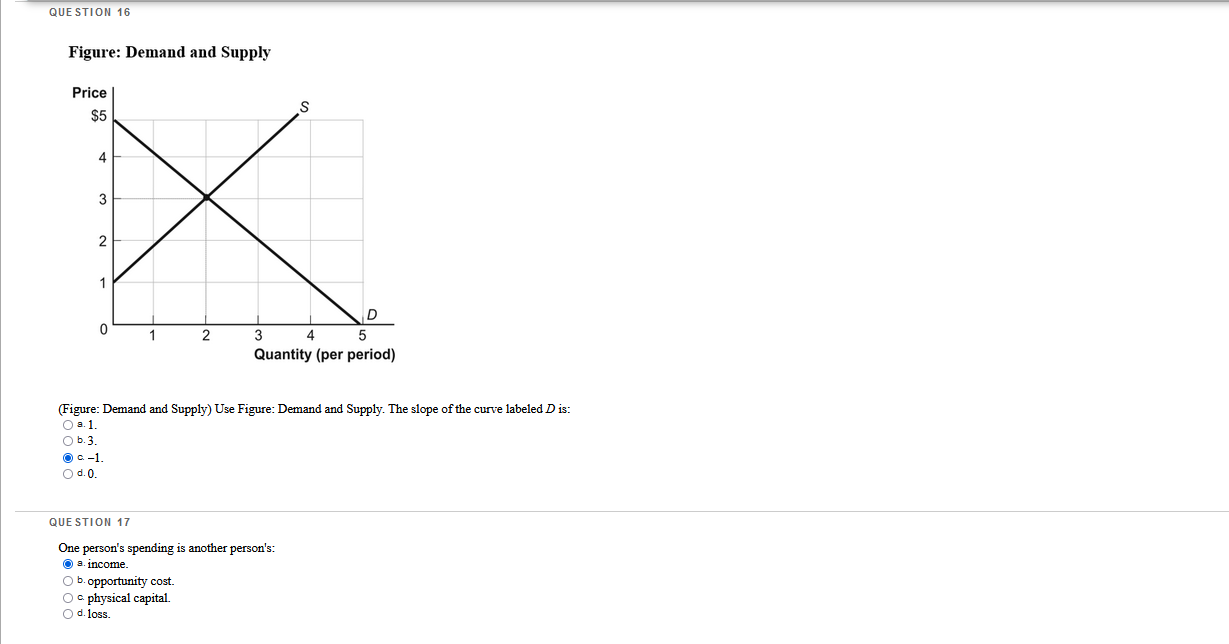
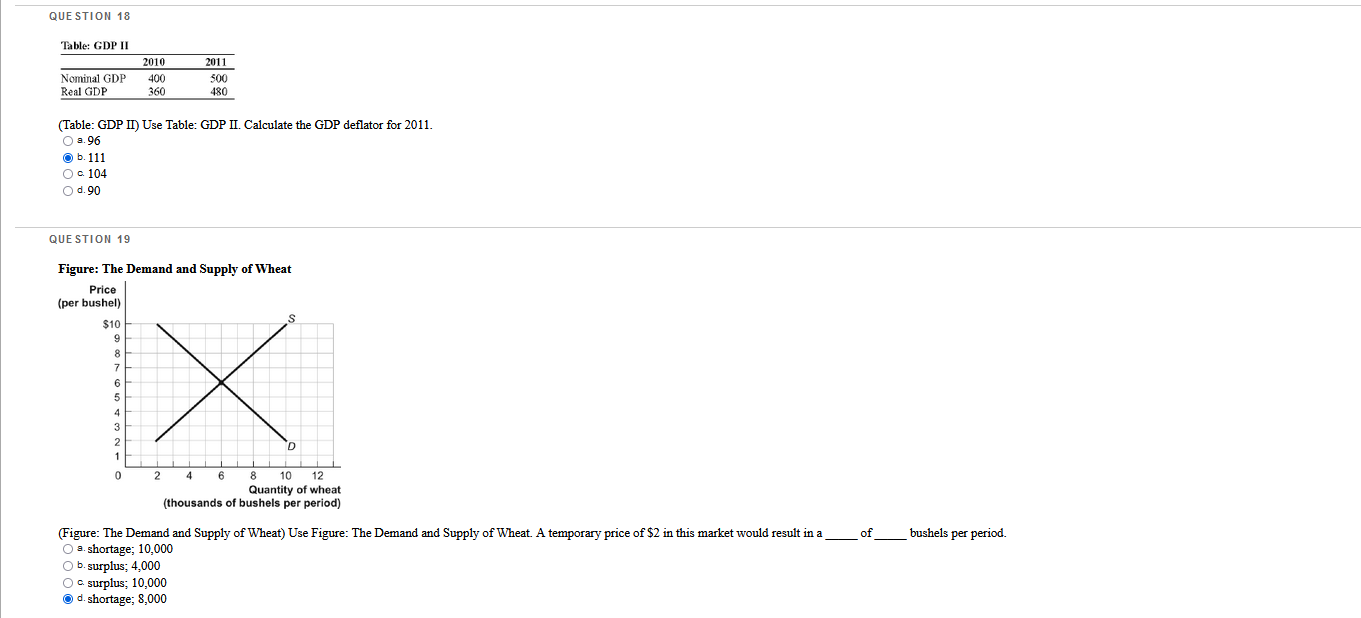

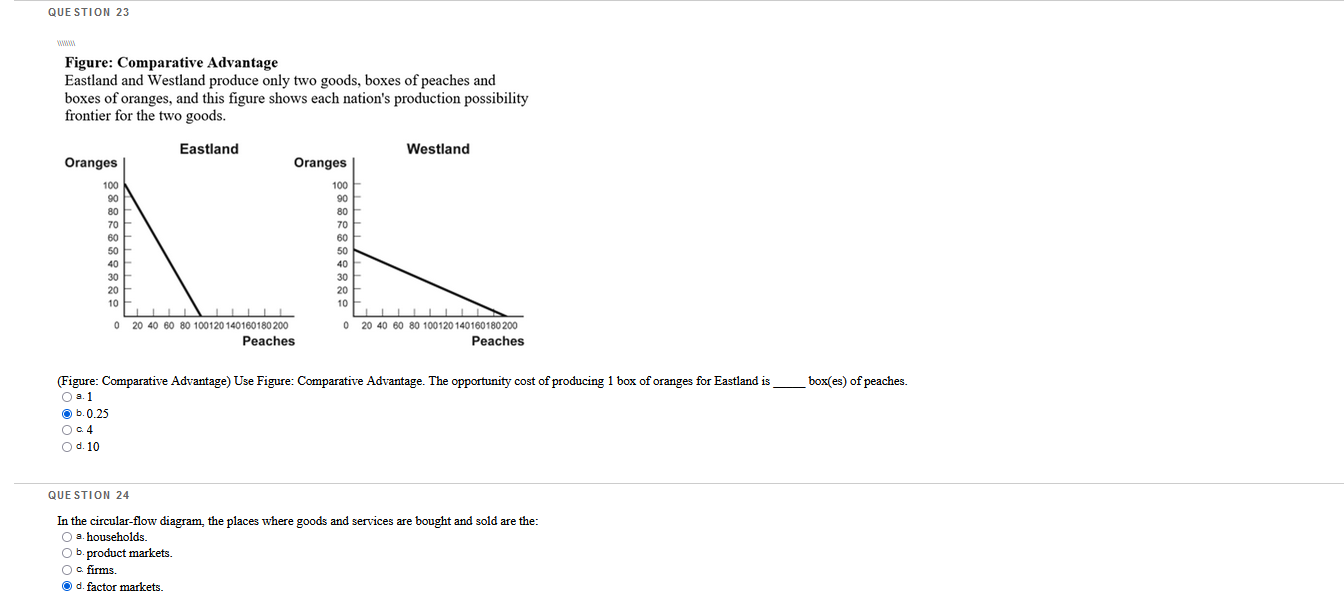
Which questions are correct or incorrect? Explain why they are.
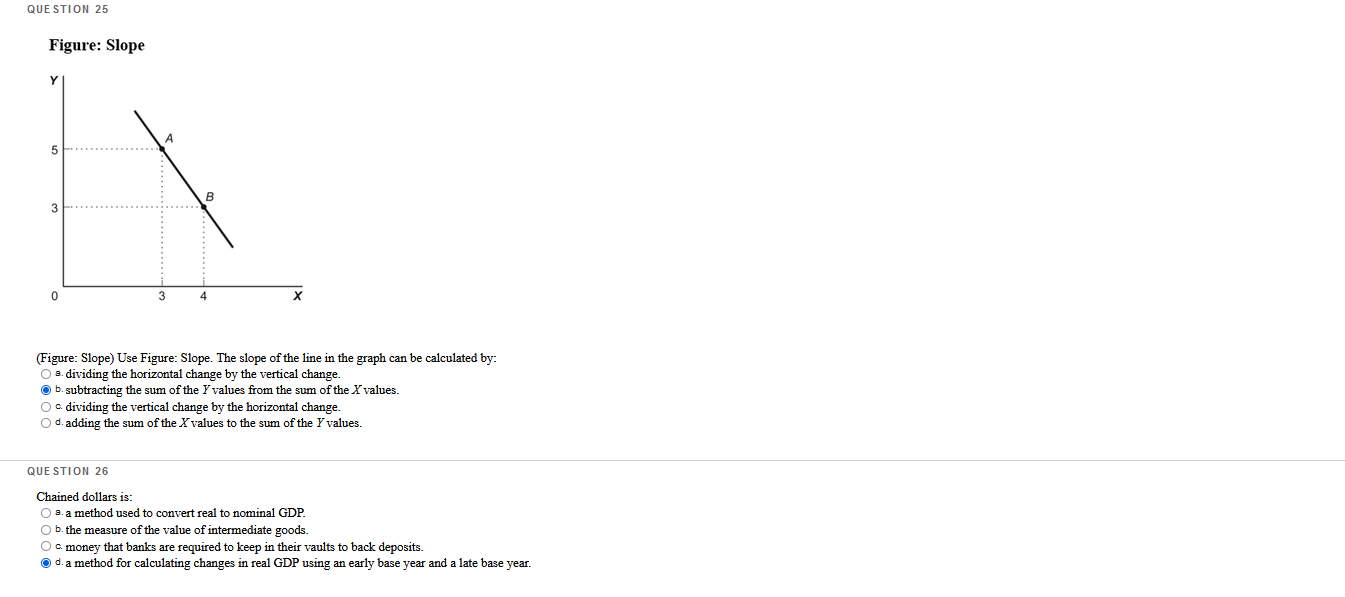
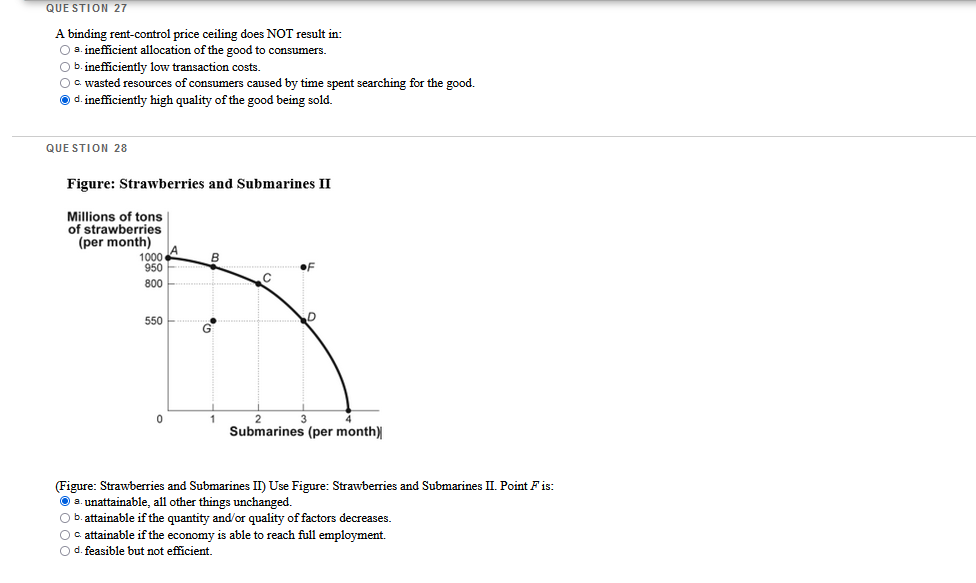
QUESTION 1 The student center on campus has burritos, bagels, or burgers for lunch, and they all cost the same. You decide to have a burger today, but if they were out of burgers, you would have bought a bagel. Your opportunity cost of buying a burger is your enjoyment of the: O a. bagel O b. bagel and the burrito. O c. burger. O d. burrito. QUESTION 2 Which question is an example of marginal analysis? O a. How do tax cuts change the growth rate of median income? O b. Should a commuter take the bus to work instead of driving. O c. What is the impact of a trade embargo on labor cost? O d. What additional output does a family business produce when it hires one more worker? QUESTION 3 The demand price of a given quantity of doughnuts is the price at which consumers will demand that quantity. The supply price for a given quantity is the price at which doughnut producers will supply that quantity. O a. True O b. False QUESTION 4 If a quota is set above the equilibrium quantity, there will be: O a. a supply price for the quantity transacted that exceeds the demand price of the quantity transacted. O b. no immediate effect. O c missed opportunities in the form of mutually beneficial transactions that don't occur. O d. incentives for illegal activities.QUESTION 25 Figure: Slope 5 B 3 4 X (Figure: Slope) Use Figure: Slope. The slope of the line in the graph can be calculated by: O s. dividing the horizontal change by the vertical change. O b. subtracting the sum of the Y values from the sum of the X values. O c. dividing the vertical change by the horizontal change O d. adding the sum of the X values to the sum of the I values. QUESTION 26 Chained dollars is: O a. a method used to convert real to nominal GDP. O b. the measure of the value of intermediate goods. O c. money that banks are required to keep in their vaults to back deposits. O d. a method for calculating changes in real GDP using an early base year and a late base year.QUESTION 27 A binding rent-control price ceiling does NOT result in: O a. inefficient allocation of the good to consumers. O b. inefficiently low transaction costs. O c. wasted resources of consumers caused by time spent searching for the good. O d. inefficiently high quality of the good being sold. QUESTION 28 Figure: Strawberries and Submarines II Millions of tons of strawberries (per month) 1000 A B 950 OF 800 C 550 D G 0 2 3 Submarines (per month) (Figure: Strawberries and Submarines II) Use Figure: Strawberries and Submarines II. Point F is: O a. unattainable, all other things unchanged. O b. attainable if the quantity and/or quality of factors decreases. O c attainable if the economy is able to reach full employment. O d. feasible but not efficient.QUESTION 29 The student center on campus has burritos, bagels, or burgers for lunch, and they all cost the same. You love burgers and bagels, but you decide to have a burger today. If they were out of burgers, you would have bought a bagel. Which economic principle does this statement BEST represent? O a. "How much" is a decision at the margin O b. There are gains from trade. c. The true cost of something is its opportunity cost. O d. One person's spending is another person's income. QUESTION 30 Which statement about GDP is FALSE? O B. GDP can be calculated by summing the value added for all goods and services. O b. GDP can be calculated by summing total market value of all final goods and services produced in a country in a given year. O . GDP can be calculated by summing government spending and tax revenues. O d. GDP can be calculated by summing all factor payments within a country's borders in a given year.QUESTION 5 Economists use models to explain real-life situations because: O s. assumptions found in such models tend to make analyzing the situation more difficult. O b. such models tend to be exactly what is occurring in each situation. O o real-life situations are not relevant to the building of models. O d. simplifications and assumptions often yield results that can help to explain the more difficult real-life situations. QUESTION 6 illustrates a positive relationship between price and quantity. O B. A production possibility frontier O b. Equilibrium O c. A supply curve O d. A demand curve QUESTION 7 When a nation's economy grows: O s. it has been able to reach full employment. O b. it has moved to a more consumer-oriented position on its production possibility frontier. O c. its production possibility frontier shifts outward. O d. its production possibility frontier shifts inward. QUESTION 8 Suppose Congress imposes a price ceiling of $5 per ATM transaction. If the average market-clearing price for an ATM transaction is $2, the price ceiling will not be binding in this instance. O a. True O b. False QUESTION 9 Assume that, in the base year (2011), a country's nominal GDP is $10,000 billion. The country has had 5% inflation each year since 2006. Real GDP of 2011 is equal to: O =. $11,025 billion O b. $9,500 billion. a $10,000 billion. O d. $10,500 billion.QUESTION 10 Which of the following is sold in the product market? O s. human capital O b. land O c. cell phones O d. labor QUESTION 11 WOWWOW Figure: Wine and Wheat Wine (thousands of bottles) 15 B IC 12 12 15 Wheat (tons) (Figure: Wine and Wheat) Use Figure: Wine and Wheat. The opportunity cost of moving from producing ONLY wheat to producing ONLY wine is tons of wheat. O 2.6 O b.9 O c 15 O d. 3 QUESTION 12 If the consumer price index for 2010 was 160.6 and for 2011 was 163.1, what was the inflation rate between the two years? O B. 0.25% O b. 1.56% O c. 2.59% O d. 5%QUESTION 13 Table: Coffee and Salmon Production Possibilities Coffee Salmon Brazil 40 20 Alaska 10 10 (Table: Coffee and Salmon Production Possibilities) Use Table: Coffee and Salmon Production Possibilities. The table shows the maximum amounts of coffee and salmon that Brazil and Alaska can produce if they just produce one good. The opportunity cost of producing 1 unit of salmon for Alaska is coffee(s) O a. 0.25 O b. 1 Oc2 O d.0.5 QUESTION 14 Figure: Market I Price $22.50 20 15 D 15 Quantity (Figure: Market I) Use Figure: Market I. If a price floor of $15 is imposed on this market and the government chooses to purchase the surplus, the government must buy units of the good and spend a total amount of on its purchase. O B.9; $81 O b. 9; $135 O c 5; $75 O d. 10; $150QUESTION 15 Figure: Rent Controls Rent (per period) Renta Rents Ronda Rent Rants X Quantity of rental units (por period) (Figure: Rent Controls) Use Figure: Rent Controls. Suppose that rent controls are imposed. If the government wanted a rent control ceiling to be effective immediately, what is one possible price to set? O a. Rentz O b. Rent3 O c. Rent4 O d. Rent1QUESTION 16 Figure: Demand and Supply Price S $5 4 3 2 2 3 4 5 Quantity (per period) (Figure: Demand and Supply) Use Figure: Demand and Supply. The slope of the curve labeled D is: O a.1. O b. 3. OC -1. O d. 0. QUESTION 17 One person's spending is another person's: O a. income. O b. opportunity cost. O c. physical capital. O d. loss.QUESTION 18 Table: GDP II 2010 2011 Nominal GDP 400 500 Real GDP 360 180 (Table: GDP II) Use Table: GDP II. Calculate the GDP deflator for 2011. O B.96 b. 111 O c. 104 O d. 90 QUESTION 19 Figure: The Demand and Supply of Wheat Price (per bushel) $10 " co . X 8 10 12 Quantity of wheat (thousands of bushels per period) (Figure: The Demand and Supply of Wheat) Use Figure: The Demand and Supply of Wheat. A temporary price of $2 in this market would result in a of bushels per period. O s. shortage; 10,000 O b. surplus; 4,000 O c. surplus; 10,000 O d. shortage; 8,000QUESTION 20 If an economy has to sacrifice only one unit of good X" for each unit of good Y produced throughout the relevant range, then its production possibility frontier has a(n): O a. zero slope. O b. increasing negative slope. O c. decreasing negative slope. O d. constant negative slope. QUESTION 21 Table: Market for Fried Twinkies Market for Fried Twinkies Quantity Demanded Quantity Supplied Price (unit) (units) (units) $1.10 9,000 3,000 1.20 8,000 5,000 1.30 7,000 7,000 1.40 6.090 9,000 1.50 5,000 1,100 (Table: Market for Fried Twinkies) Use Table: Market for Fried Twinkies. If the government imposes a quota of 5,000 on the fried Twinkie market, the quota rent per fried Twinkie will be: O a. $1.00. O b. $0.30. O c. $1.20. O d. $1.50. QUESTION 22 All points inside the production possibility frontier represent: O a. inefficient production points. O b. regions of economic growth. O c. infeasible production points. O d. efficient production points.QUESTION 23 Figure: Comparative Advantage Eastland and Westland produce only two goods, boxes of peaches and boxes of oranges, and this figure shows each nation's production possibility frontier for the two goods. Eastland Westland Oranges Oranges 100 90 80 70 60 688:88388 50 40 30 20 40 60 80 100120 140160180 200 20 40 60 80 100120 140160180 200 Peaches Peaches (Figure: Comparative Advantage) Use Figure: Comparative Advantage. The opportunity cost of producing 1 box of oranges for Eastland is box(es) of peaches. O a.1 O b. 0.25 OG.4 O d. 10 QUESTION 24 In the circular-flow diagram, the places where goods and services are bought and sold are the: O s. households. O b. product markets. O c. firms. O d. factor markets