Which two works is Adam Smith known for.
When was the theory of moral sentiments created.
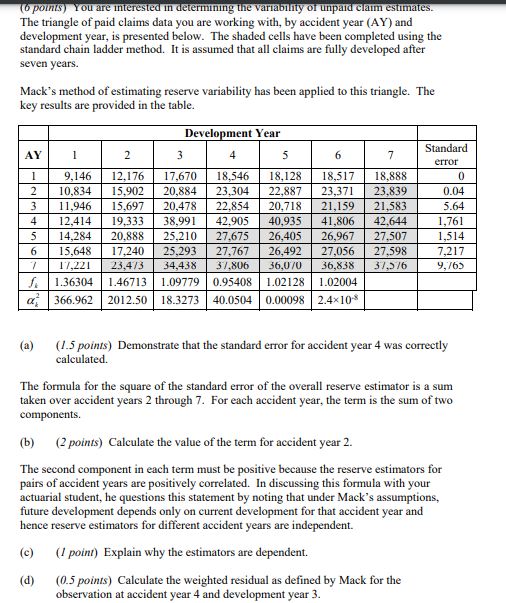
A general insurance company sells personal motor insurance in a small country. Property damage claims amongst the company's insured drivers follow a claim size distribution X. The standard for full credibility when estimating the average property damage claim size is my = 1,000 claims for a given probability P and tolerance k. Liability claims follow a distribution Y, where I' has a standard deviation that is twice as large as that for distribution X, and a mean that is five times that for X. (i) Calculate the standard for full credibility for severity of liability claims. assuming that the same P and & are required for both claim types. [4] The insurer has recently been the first to launch a personal driverless car insurance policy. The policy is designed for consumers who have driverless features in their cars, such as self-parking, as well as those who own a car with autopilot features. (ii) Outline the additional cover that such a policy could provide, compared to a standard motor insurance policy. [2] The government of that country is currently trialling fully driverless cars and expects them to be made available to the public by the year 2020. It has therefore introduced a law that all cars should be driverless by the year 2025. (iii) Assess the potential impacts on insurers of the new legislation on driverless cars. [87(6 points) You are interested in determining the variability of unpaid claim estimates. The triangle of paid claims data you are working with, by accident year (AY) and development year, is presented below. The shaded cells have been completed using the standard chain ladder method. It is assumed that all claims are fully developed after seven years. Mack's method of estimating reserve variability has been applied to this triangle. The key results are provided in the table. Development Year AY 2 3 4 5 6 7 Standard error 9,146 12,176 17,670 18.546 18,128 18,517 18,888 2 10.834 15,902 20,884 23.304 22,887 23,371 23.839 0.04 1 11,946 15.697 20,478 22.854 20,718 21,159 21.583 5.64 4 12.414 19,333 38.991 42.905 40,935 41,806 42.644 1,761 5 14,284 20.888 25,210 27.675 26.405 26,967 27.507 1,514 6 15.648 17,240 25,293 27.767 26,492 27,056 27.598 7,217 17,221 23.473 34,438 37.806 46.070 36,838 37,376 9,763 1.36304 1.46713 1.09779 0.95408 1.02128 1.02004 366.962 2012.50 18.3273 40.0504 0.00098 2.4x10% (a) (1.5 points) Demonstrate that the standard error for accident year 4 was correctly calculated. The formula for the square of the standard error of the overall reserve estimator is a sum taken over accident years 2 through 7. For each accident year, the term is the sum of two components. (b) (2 points) Calculate the value of the term for accident year 2. The second component in each term must be positive because the reserve estimators for pairs of accident years are positively correlated. In discussing this formula with your actuarial student, he questions this statement by noting that under Mack's assumptions, future development depends only on current development for that accident year and hence reserve estimators for different accident years are independent. (c) (/ point) Explain why the estimators are dependent. (d) (0.5 points) Calculate the weighted residual as defined by Mack for the observation at accident year 4 and development year 3