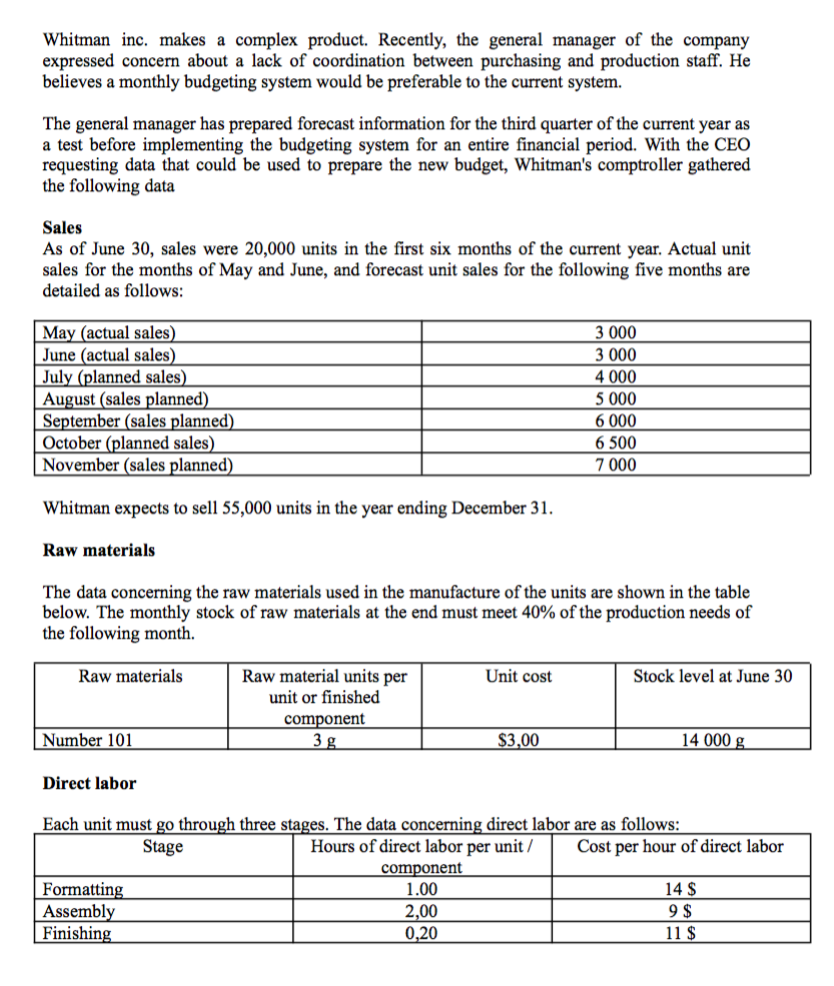
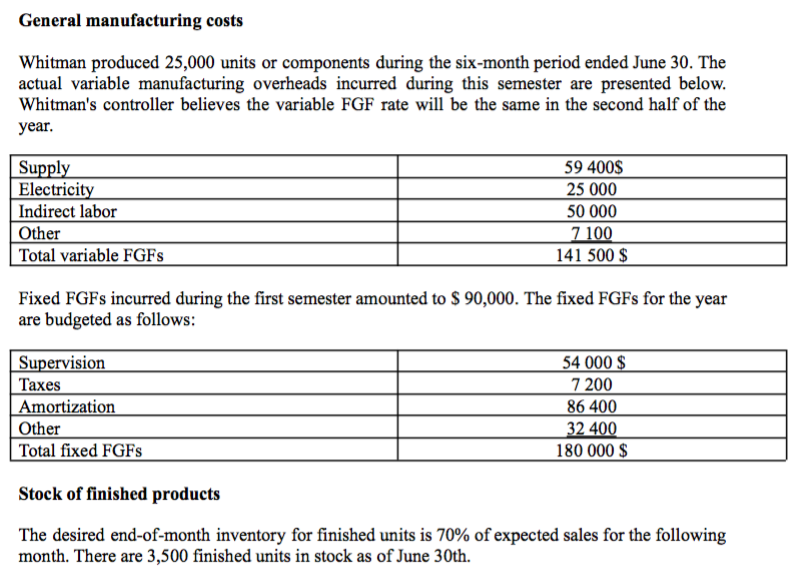

Whitman inc. makes a complex product. Recently, the general manager of the company expressed concern about a lack of coordination between purchasing and production staff. He believes a monthly budgeting system would be preferable to the current system. The general manager has prepared forecast information for the third quarter of the current year as a test before implementing the budgeting system for an entire financial period. With the CEO requesting data that could be used to prepare the new budget, Whitman's comptroller gathered the following data Sales As of June 30, sales were 20,000 units in the first six months of the current year. Actual unit sales for the months of May and June, and forecast unit sales for the following five months are detailed as follows: May (actual sales) June (actual sales) July (planned sales) August (sales planned) September (sales planned) October (planned sales) November (sales planned) 3 000 3 000 4 000 5 000 6 000 6 500 7 000 Whitman expects to sell 55,000 units in the year ending December 31. Raw materials The data concerning the raw materials used in the manufacture of the units are shown in the table below. The monthly stock of raw materials at the end must meet 40% of the production needs of the following month. Raw materials Unit cost Stock level at June 30 Raw material units per unit or finished component Number 101 3g $3,00 14 000 g Direct labor Each unit must go through three stages. The data concerning direct labor are as follows: Stage Hours of direct labor per unit/ Cost per hour of direct labor component Formatting 1.00 14 $ Assembly 2,00 9$ Finishing 0,20 11 $ General manufacturing costs Whitman produced 25,000 units or components during the six-month period ended June 30. The actual variable manufacturing overheads incurred during this semester are presented below. Whitman's controller believes the variable FGF rate will be the same in the second half of the year. Supply Electricity Indirect labor Other Total variable FGFs 59 400$ 25 000 50 000 7 100 141 500 $ Fixed FGFs incurred during the first semester amounted to $ 90,000. The fixed FGFs for the year are budgeted as follows: Supervision Taxes Amortization Other Total fixed FGFs 54 000 $ 7 200 86 400 32 400 180 000 $ Stock of finished products The desired end-of-month inventory for finished units is 70% of expected sales for the following month. There are 3,500 finished units in stock as of June 30th. Question 4) Suppose the company plans to produce 60,000 units during the year. Prepare a FGF budget for the semester ended December 31. It is not necessary to show calculations by month. PS: To solve this problem, you can use the different tables seen in class. These will help you answer the questions asked. Whitman inc. makes a complex product. Recently, the general manager of the company expressed concern about a lack of coordination between purchasing and production staff. He believes a monthly budgeting system would be preferable to the current system. The general manager has prepared forecast information for the third quarter of the current year as a test before implementing the budgeting system for an entire financial period. With the CEO requesting data that could be used to prepare the new budget, Whitman's comptroller gathered the following data Sales As of June 30, sales were 20,000 units in the first six months of the current year. Actual unit sales for the months of May and June, and forecast unit sales for the following five months are detailed as follows: May (actual sales) June (actual sales) July (planned sales) August (sales planned) September (sales planned) October (planned sales) November (sales planned) 3 000 3 000 4 000 5 000 6 000 6 500 7 000 Whitman expects to sell 55,000 units in the year ending December 31. Raw materials The data concerning the raw materials used in the manufacture of the units are shown in the table below. The monthly stock of raw materials at the end must meet 40% of the production needs of the following month. Raw materials Unit cost Stock level at June 30 Raw material units per unit or finished component Number 101 3g $3,00 14 000 g Direct labor Each unit must go through three stages. The data concerning direct labor are as follows: Stage Hours of direct labor per unit/ Cost per hour of direct labor component Formatting 1.00 14 $ Assembly 2,00 9$ Finishing 0,20 11 $ General manufacturing costs Whitman produced 25,000 units or components during the six-month period ended June 30. The actual variable manufacturing overheads incurred during this semester are presented below. Whitman's controller believes the variable FGF rate will be the same in the second half of the year. Supply Electricity Indirect labor Other Total variable FGFs 59 400$ 25 000 50 000 7 100 141 500 $ Fixed FGFs incurred during the first semester amounted to $ 90,000. The fixed FGFs for the year are budgeted as follows: Supervision Taxes Amortization Other Total fixed FGFs 54 000 $ 7 200 86 400 32 400 180 000 $ Stock of finished products The desired end-of-month inventory for finished units is 70% of expected sales for the following month. There are 3,500 finished units in stock as of June 30th. Question 4) Suppose the company plans to produce 60,000 units during the year. Prepare a FGF budget for the semester ended December 31. It is not necessary to show calculations by month. PS: To solve this problem, you can use the different tables seen in class. These will help you answer the questions asked









