Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
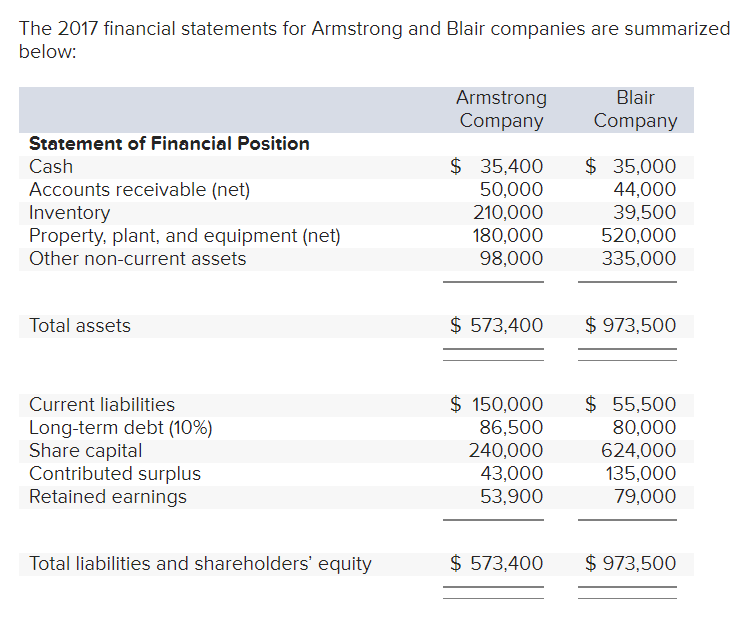
Will give thumbs up! The 2017 financial statements for Armstrong and Blair companies are summarized below: Armstrong Company Blair Company Statement of Financial Position Cash


Will give thumbs up!
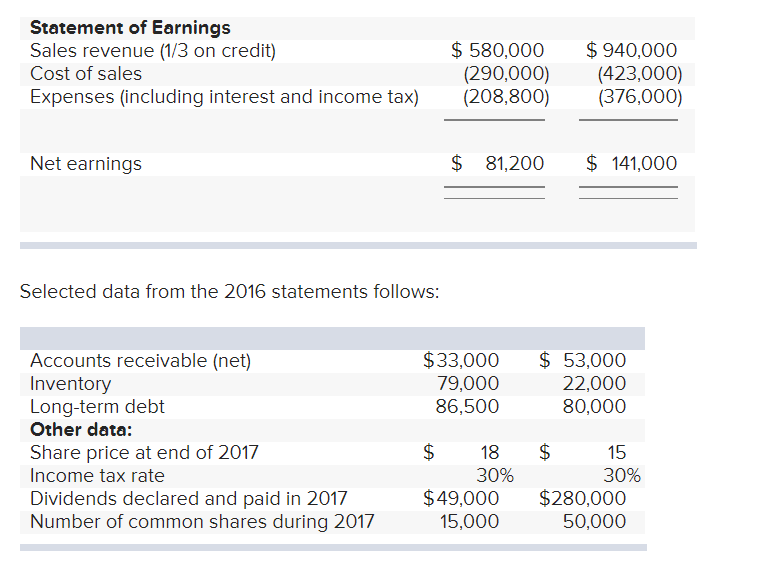
The 2017 financial statements for Armstrong and Blair companies are summarized below: Armstrong Company Blair Company Statement of Financial Position Cash Accounts receivable (net) Inventory Property, plant, and equipment (net) Other non-current assets $ 35,400 50,000 210,000 180,000 98,000 $ 35,000 44,000 39,500 520,000 335,000 Total assets $ 573,400 $ 973,500 Current liabilities Long-term debt (10%) Share capital Contributed surplus Retained earnings $ 150,000 86,500 240,000 43,000 53,900 $ 55,500 80,000 624,000 135,000 79,000 Total liabilities and shareholders' equity $ 573,400 $ 973,500 Statement of Earnings Sales revenue (1/3 on credit) Cost of sales Expenses (including interest and income tax) $ 580,000 (290,000) (208,800) $ 940,000 (423,000) (376,000) Net earnings $ 81,200 $ 141,000 Selected data from the 2016 statements follows: $33,000 79,000 86,500 $ 53,000 22,000 80,000 Accounts receivable (net) Inventory Long-term debt Other data: Share price at end of 2017 Income tax rate Dividends declared and paid in 2017 Number of common shares during 2017 $ 18 30% $49,000 15,000 $ 15 30% $280,000 50,000 The companies are in the same line of business and are direct competitors in a large metropolitan area. Both have been in business approximately 10 years, and each has had steady growth. The management of each has a different viewpoint in many respects. Blair Company is more conservative, and as its president said, "We avoid what we consider to be undue risk." Neither company is publicly held. Armstrong Company has an annual audit by an independent auditor, but Blair Company does not. Required: 1. Complete a schedule that reflects a ratio analysis of each company. Use ending balances if average balances are not available. (Round intermediate calculations and final answers to 2 decimal places.) Armstrong Company Blair Company % % % % % % per share % per share % times times Ratio Tests of profitability: Return on equity Return on assets Financial leverage percentage Earnings per share Profit margin Fixed asset turnover Tests of liquidity Cash ratio Current ratio Quick ratio Receivables turnover Inventory turnover Tests of solvency: Times-interest-earned ratio Debt-to-equity ratio Market tests: Pricelearnings ratio Dividend yield ratio times times times times times times % %Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


