Question
Wk6-HW6 Confidence Intervals and Hypothesis Tests Comparing TWO Proportions, Differences or Means AND ANOVA (Analysis of Variance) This first part of this Homework involves calculating:
Wk6-HW6 Confidence Intervals and Hypothesis Tests Comparing TWO Proportions, Differences or Means AND ANOVA (Analysis of Variance)
This first part of this Homework involves calculating: Confidence Interval for two population Proportions Hypothesis Test for two population Proportions Hypothesis Test for two population Differences Confidence Interval for two population differences Hypothesis Test comparing two population Means
IF you need additional guidance, there is a Supplement Guidance attachment for your use. It does relate to these problem types and should be useful in saving you time working them.
1) (made-up data) Confidence Interval Problem for Proportions: Calculate a 95% confidence interval for these proportions. SHOW YOUR "E" SETUP & CALCULATIONS. The same assumptions must be met to insure the statistical analysis is valid and Make sure to calculate the proportions first.
High school students take the AP tests in different subject areas. This year 150 students took the biology exam of which 85 were female. And, 220 students took the calculus exam of which 100 were female. Calculate the difference in the PROPORTION of female students taking the biology exam verses female students taking the calculus exam using a 95% confidence level. E = z-critical * sqrt[ (p-hat1 * q-hat1)1) + (p-hat2 * q-hat2)2)]
2) (made-up data) Hypothesis Test problem for Proportions: Assume a 1% significance level. The same assumptions must be met to insure the statistical analysis is valid and calculate the proportions first.
SHOW Z-Test SETUP AND Z-Critical value the z-Test was compared to. Also, use software to calculate the p-Value. Do both support the same conclusion? (they MUST). State your real-world conclusion?
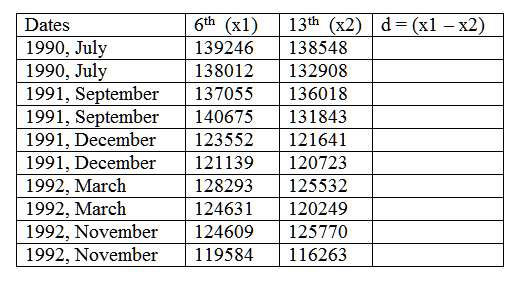
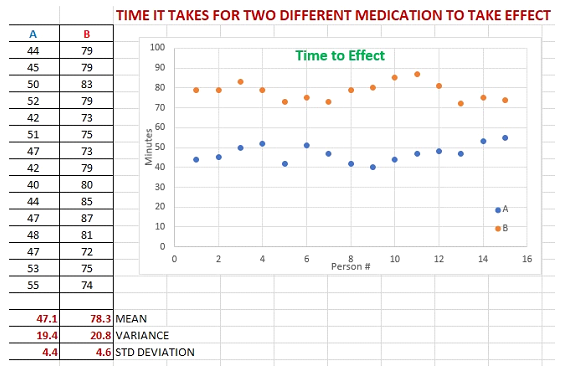
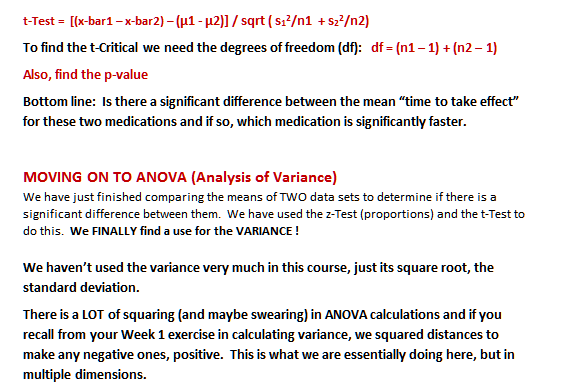
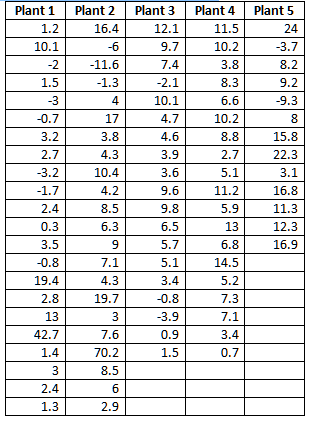
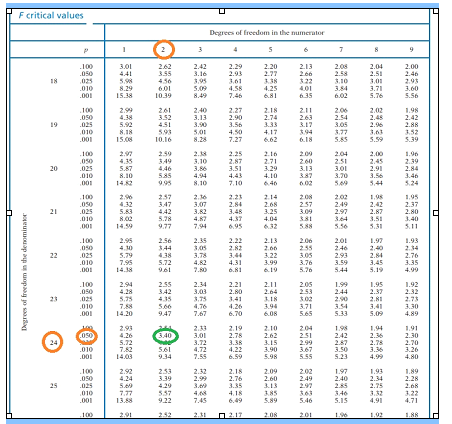
Are more children diagnosed with Autism Spectrum Disorder in States that have urban areas over States that are mostly rural? In an urban State there were are 300 3rd grade students diagnosed with ASD out of 18,500 3rd graders tested. In a rural state, there were 55 3rd grade students diagnosed with ASD out of 2,300 3rd graders tested. Is there enough evidence to show that the proportion of children diagnosed with ASD in an urban State is more than the proportion in a rural State? Test at the = 1% level. 3) Coin-Toss Data - We had ____ sets of 30-flipped coin sets. Some used ONE coin and some 30 different coins. Conduct a hypothesis test on the proportion of HEADS using ONE coin verses proportion of HEADS using 30 coins. IS there a significant difference (5% level)? t-Test = [(x-bar1 - x-bar2) - (1 - 2)] / sqrt ( s121 + s222) To find the t-Critical we need the degrees of freedom (df) and the formula to calculate df is "hairy". As presented earlier, there simpler formula that is used by some statisticians: df = (n1 - 1) + (n2 - 1) 4) (made-up data) Hypothesis Test problem for TWO population DIFFERENCES (not proportions or means) comparison hypothesis test (NOT a proportion problem - so we use t-values, not z-values). SHOW t-TEST SETUP and calculation, AND for the t-Critical, what SIGNIFICANCE LEVEL (the column) and what df (which row) were used and what the t-Critical value is. Do people avoid driving on Friday the 13th ? Here are data on 20 Fridays: 10 on the 13th and the other 10 on the Friday before. For the DIFFERENCES, Calculate the MEAN and SD between traffic on these two Fridays at the 95% level (alpha = 5%); Traffic Count
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


