Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
work needed The table below lists shale transit times for a well in Jefferson County, Texas. Please plot the data and determine pore pressure (equivalent
work needed
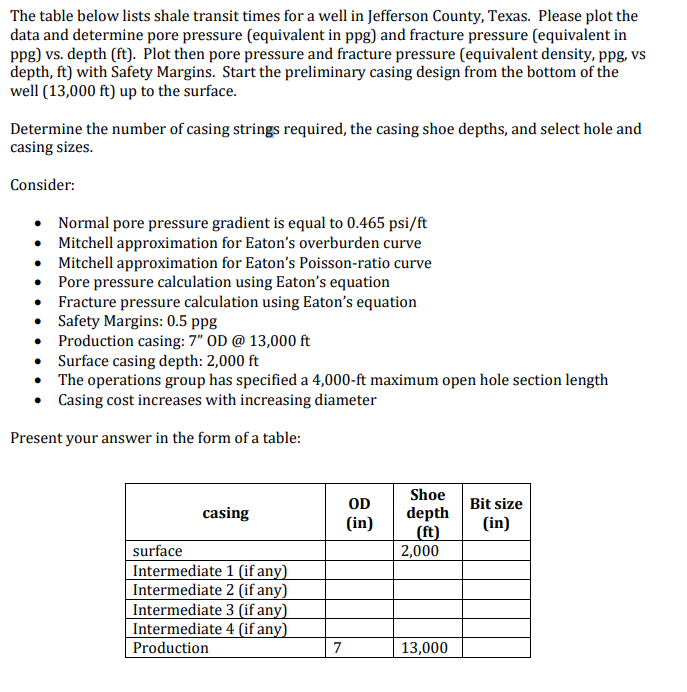
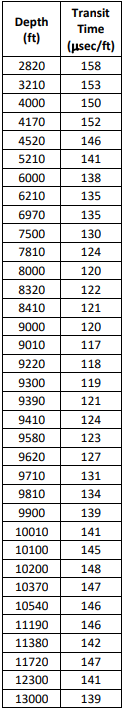
The table below lists shale transit times for a well in Jefferson County, Texas. Please plot the data and determine pore pressure (equivalent in ppg) and fracture pressure (equivalent in ppg) vs. depth (ft). Plot then pore pressure and fracture pressure (equivalent density, ppg, Vs depth, ft) with Safety Margins. Start the preliminary casing design from the bottom of the well (13,000 ft) up to the surface. Determine the number of casing strings required, the casing shoe depths, and select hole and casing sizes. Consider: Normal pore pressure gradient is equal to 0.465 psi/ft Mitchell approximation for Eaton's overburden curve Mitchell approximation for Eaton's Poisson-ratio curve Pore pressure calculation using Eaton's equation Fracture pressure calculation using Eaton's equation Safety Margins: 0.5 ppg Production casing: 7" OD @ 13,000 ft Surface casing depth: 2,000 ft The operations group has specified a 4,000-ft maximum open hole section length Casing cost increases with increasing diameter Present your answer in the form of a table: OD casing in Shoe depth (ft) 2,000 Bit size (in) surface Intermediate 1 (if any) Intermediate 2 (if any) Intermediate 3 (if any) Intermediate 4 (if any) Production 13,000 Depth (ft) 2820 3210 4000 4170 4520 5210 6000 6210 6970 7500 7810 8000 8320 8410 9000 9010 9220 9300 9390 9410 9580 9620 9710 9810 Transit Time (usec/ft) 158 153 150 152 146 141 138 135 135 130 124 120 122 121 120 117 118 119 121 124 123 127 131 134 9900 139 141 145 148 10010 10100 10200 10370 10540 11190 11380 147 146 146 142 11720 12300 13000 147 141 139 The table below lists shale transit times for a well in Jefferson County, Texas. Please plot the data and determine pore pressure (equivalent in ppg) and fracture pressure (equivalent in ppg) vs. depth (ft). Plot then pore pressure and fracture pressure (equivalent density, ppg, Vs depth, ft) with Safety Margins. Start the preliminary casing design from the bottom of the well (13,000 ft) up to the surface. Determine the number of casing strings required, the casing shoe depths, and select hole and casing sizes. Consider: Normal pore pressure gradient is equal to 0.465 psi/ft Mitchell approximation for Eaton's overburden curve Mitchell approximation for Eaton's Poisson-ratio curve Pore pressure calculation using Eaton's equation Fracture pressure calculation using Eaton's equation Safety Margins: 0.5 ppg Production casing: 7" OD @ 13,000 ft Surface casing depth: 2,000 ft The operations group has specified a 4,000-ft maximum open hole section length Casing cost increases with increasing diameter Present your answer in the form of a table: OD casing in Shoe depth (ft) 2,000 Bit size (in) surface Intermediate 1 (if any) Intermediate 2 (if any) Intermediate 3 (if any) Intermediate 4 (if any) Production 13,000 Depth (ft) 2820 3210 4000 4170 4520 5210 6000 6210 6970 7500 7810 8000 8320 8410 9000 9010 9220 9300 9390 9410 9580 9620 9710 9810 Transit Time (usec/ft) 158 153 150 152 146 141 138 135 135 130 124 120 122 121 120 117 118 119 121 124 123 127 131 134 9900 139 141 145 148 10010 10100 10200 10370 10540 11190 11380 147 146 146 142 11720 12300 13000 147 141 139Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


