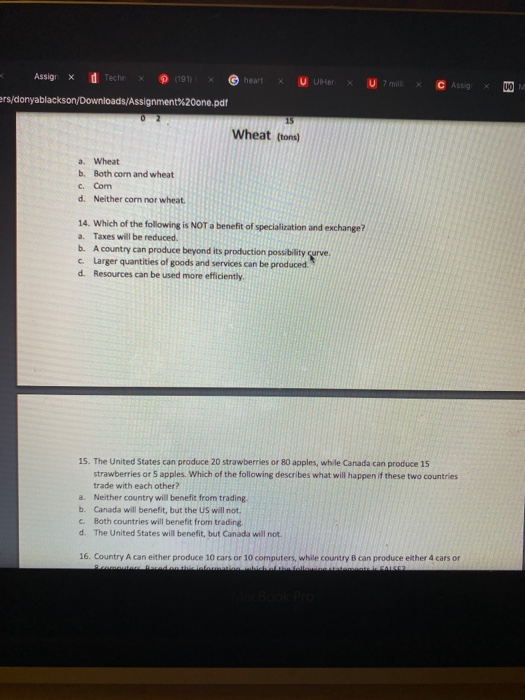
X Assig dTech 191 Umic Asso rs/donyablackson/Downloads/Assignment%20one.pdf INSTRUCTIONS: This homework has two parts. Answer all questions from the two parts. Part 1: Answer all questions. Clrde the correct answer for each question. Each question is worth 0.12 points. 1. Matilda is the CEO of a large marketing company. After paying taxes, her company was left with $18,000,000 of disposable income. She can reinvest this money into her company in infrastructure spending and salary increase, or she can invest it into the stock market. The cost of choosing one over the other is called the cost. a. Production b. Opportunity c. Marginal d. Deductible 2. Rose is considering how several factors may help her company's productivity. She is considering using advances in technology and making more investment in human capital. She is also trying to predict the changing trends in the labor force. Which of the following would be MOST beneficial to this scenario? a. The production possibilities curve b. The supply curve c. The Phillips curve d. The income-consumption curve 3. Which of the following is a key assumption of the production possibilities model? a. All of the answers are correct. b. Technology remains completely constant. c. Resources are scarce. d. Resources are used to maximize capacity. 4. With the same amount of resources, Country A can produce 25 tons of chicken or 50 tons of wheat. What is Country A's opportunity cost of producing 1 ton of wheat? a. 2 tons of chicken b. 25 tons of wheat C. 25 tons of chicken d. % ton of chicken Assige X Tech 1911 U UHO CAS 10 Mens ablackson/Downloads/Assignment%20one.pdf 5. It takes Joan 1 hour to make a pizza and 2 hours to make a cake, Joan's opportunity cost of making a pizza is which of the following? a. 2 cakes b. X pizzas C. of a cake d. 2 pizzas 6. A point that is located inside the production possibility curve is: a. Efficient b. Unattainable c Equally efficient as all other points d. Inefficient 7. Which is TRUE of points located outside of the production possibility curve? a. They are profitable. b. They are unobtainable. c. They are less efficient than average. d. They demonstrate unlimited capacity 8. A CFO can invest company profits in stocks with projected returns of 10%, or use the money to add a new assembly line, projected to yield 14% after payment of the debt. What is the opportunity cost of investing in stocks instead of the factory upgrade? a. 14% b. 4% c. 10% UO Men's Assig UUHer C Assig onyablackson/Downloads/Assignment%20one.pat 8. A CFO can invest company profits in stockis with projected returns of 10%, or use the money to add a new assembly line, projected to yield 14% after payment of the debt. What is the opportunity cost of investing in stocks instead of the factory upgrade? a 14% b. 4x c. 10% d. 24% 9. All of the following factors impact an economy's production possibility curve except a. a technological advance b. a newly discovered energy source c. technological stagnation d. increases in the population 10. Assuming there are only two countries, Country A can produce 10 tons of wheat or 20 tons of rice, while Country B can produce 5 tons of wheat or 15 tons of rice. Which country has the highest opportunity cost for producing 1 ton of rice? a. Country A up to 1/2 ton then it is Country B b. Country B c. Country A d. Both countries are the same 11. When countries specialize in the goods in which they have a comparative advantage, which of the following is true? a. Production costs will increase for both countries. b. Both countries will experience gains from trade. c. Both countries are worse off. CASSO Hackson/Downloads/Assignment%20one.pdf d. One country is usually better off, and the other is worse off. 12. Country A's opportunity cost of producing 1 ton of com is 5 tons of wheat, while Country B's opportunity cost of producing 1 ton of corn is 1/3 of a ton of wheat. Which of the following statements is true? a. Country A should specialize in producing corn, while Country B should specialize in producing wheat. b. Country B should specialize in producing corn, while fountry A should specialize in producing wheat. c. There will be no gains from trade if these two countries exchange goods, d. Both countries should produce both goods. 13. According to the two production possibility curves shown, Country A should specialize in the production of which of the following? Corn (tons) 5 4 3 2 Country A Country B 02 15 Wheat (tons) a. Wheat b. Both corn and wheat Assign X Techin (191) heart X U Her U Zmi C Assig UOM ers/donyablackson/Downloads/Assignment%20one.pdf 15 Wheat (tons) a. Wheat b. Both com and wheat C. Com d. Neither corn nor wheat. 14. Which of the following is NOT a benefit of specialization and exchange? a. Taxes will be reduced. b. A country can produce beyond its production possibility curve. c. Larger quantities of goods and services can be produced d. Resources can be used more efficiently 15. The United States can produce 20 strawberries or 80 apples, while Canada can produce 15 strawberries or 5 apples. Which of the following describes what will happen if these two countries trade with each other? a. Neither country will benefit from trading b. Canada will benefit, but the US will not C Both countries will benefit from trading d. The United States will benefit, but Canada will not 16. Country A can either produce 10 cars or 10 computers, while country can produce either 4 cars or SALLE TechnX (191) P x heartex U DlHere X U 7 milli X C Assign X Eson/Downloads/Assignment%20one.pdf d. The United States will benefit, but Canada will not. 16. Country A can either produce 10 cars or 10 computers, while country B can produce either 4 cars or 8 computers. Based on this information, which of the following statements is FALSE? a. Country A has an absolute advantage in cars. b. Country A has an absolute advantage in computers. c. Country B has a comparative advantage in computers. d. Country A has a comparative advantage in computers. 17. A person or nation that has a comparative advantage in the production of a good, should a. have the highest opportunity cost b. decrease their production of that good c. specialize in the production of that good d. automatically has an absolute advantage a. 18. According to the Law of Comparative Advantage, where should a good be produced? Where there are more consumers. b. In the country with the highest absolute advantage. c Where opportunity costs are the highest. d. Where opportunity costs are the lowest. 19. If Sally can produce 1 term paper or 4 cookies in one hour, and Adam can produce 2 term papers or 1 cookie in the same amount of time, which of these statements is true? a. Sally has a comparative advantage in cookies, while Adam a comparative advantage in term papers b. Both Sally and Adam have the same opportunity costs for these two goods. c Sally uses more resources to produce cookies than she does to produce term papers. d. Adam has a comparative advantage in cookies, while Sally has a comparative advantage in term papers 20. Which of the following are problems that all economies face? How to use scarce resources to satisfy unlimited wants, and how to shrink the money supply How to decide what goods and services to produce, how much to produce, and for whom to blackson/Downloads/Assignment%20one.pdf d. How to use scarce resources to satisfy unlimited wants, how to decide what goods and services to produce, how much to produce, and for whom to produce. 21. Assume that there are only two countries, Country A and Country B, producing only two goods, corn cereal and designer jeans. The table here shows the production possibilities for these two countries. Which of the following statements is correct? Country A Country B Good 1 80 150 Good 2 65 70 a. Country A has an absolute advantage in one good, but not both. b. Country B has an absolute advantage in one good, but not both C. Neither country has an absolute advantage in the production of these two goods. d. Country B has an absolute advantage in both goods. 22. Which of the following refers to the point where the supply and demand curves intersect? a. Price point b. Double point C. Equilibrium point d. Strike point 23. Both the supply curve and the demand curve have shifted. What does this mean for the price? a. It went down b. It went up it did not change d. It could go up, down, or not change. 24. A surplus exists when occurs. 3. demand outstrips production b. economy outstrips inflation inflation outstrips economy d. production outstrips demand 25. In which direction will the market supply curve slope when suppliers want to sell more goods at 30 2 3 5 & 7 8. Assign X Techn X (191) FX G heart X U VIHer x U 7 ml X C Assig X U -nyablackson/Downloads/Assignment%20one.pdf c. A change in quantity will not shift the supply curve. d. It depends on the limit of the change. 27. Demand has increased for goods and services. How would this be represented on a demand curve? a. A shift down. b. A shift to the right. c. A shift to the left. d. A shift up. 28. Which of the following refers to a list of goods at a price that a person is willing to pay across all markets? a. Market demand schedule b. Demand schedule c Demographic demand schedule d. Demand schedule multiplier 29. Which of the following refers to a table that lists the demand for a product across all markets? a. Retail economy chart b. Market demand schedule C Equilibrium point d. Sell table 30. There is a request for 10 million widgets at $0.10 each. What is this called? a. Demand quantity b. Item quantity c Equilibrium quantity d Supply quantity 31. Which of the following is an example of a list of goods at a price that a person is willing to pay? a. Demand schedule b. Equilibrium point Supply schedule d Demographic indicator 32. In which direction would the demand curve slope when people bewer raodsathishwices? X Assign X TechnX (191) X heart U VIHer C Assig nyablackson/Downloads/Assignment%20one.pdf 32. In which direction would the demand curve slope when people buy fewer goods at higher prices? a. Flat b. Upward c. Vertical d. Downward 33. In what way does change in price shift demand? a. It does not shift demand. b. It will decrease demand. c. It will increase demand. d. It will depend on the whether the change is up or down. 34. The cost per widget and the number of widgets to be supplied is shown on the a market supply schedule b. sales demand schedule c quantity retail schedule d. purchase/cost schedule 35. The market supply schedule is a table that lists the quantity supplied in all economies at all possible Prices b. Locations c. Agreements U 7 milli X C Assig ackson/Downloads/Assignment%20one.pdf 36. What is quantity supplied? a. It refers to the quality of goods and services in an economy. b. It is how much of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to buy. It is how much of a good or service that sellers are willing and able to supply at a particular price. d. It is how much money consumers want to borrow in an economy. 37. Which of the following statements is inaccurate regarding the demand curve? a. It is upward sloping b. A visual representation of the demand schedule c. It is downward sloping d. It shows quantity demanded at different prices 38. What is the correct relationship between price and quantity demanded shown by the law of demand? a. When prices go down demand goes up b. when prices go down, demand goes down when prices go up, demand goes up d. there is no direct relationship between price and demand 39. Which of the following statements is NOT true regarding the market equilibrium? a. It is the only price at which quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplied b. It is where quantity demanded equals quantity supplied c. It is found at the intersection of the supply and demand curves d. Unless something causes a shift in supply or demand, it will not change X (191) U UlHer . G heart U 7 mil x C Assig Assign X Techn myablackson/Downloads/Assignment%20one.pdf 40. When a market price is set below the market equilibrium price, a exists, which will a. surplus, create upward pressure on the price b. supply, increase the amount of goods and services available cshortage, create downward pressure on the price d. shortage, create upward pressure on the price 41. What is quantity demanded? a. It is the quantity of a good or service supplied by producers. b. It is the quantity of a good or service that an individual is willing and able to buy at a certain price. c. It is the quality of a good or service that an individual is looking for. d. It is the quantity of a good or service that is unavailable because of regulations. 42. Which of the following statements is FALSE regarding the supply curve? a. It is downward-sloping b. It is upward-sloping c. A change in price results in movement along the curve d. It is a graph illustrating the relationship between price and quantity supplied Part 2: Answer all questions. Use the blank space for your answers. Each question is worth 0.49 point. 43. With the aid of diagrams (graph), explain how an initial unattainable point of a Production Possibility Frontier (PPF) can subsequently become attainable. Assigex dTech 11911 X X G heart UO U Her U 7 ml C Assig s/donyablackson/Downloads/Assignment%20one.pdf 8/10 43. With the aid of diagrams (graph), explain how an initial unattainable point of a Production Possibility Frontier (PPF) can subsequently become attainable 44. Graphically illustrate the difference between an increase in quantity supplied and an increase in supply Assign X d Tech (1911 X heart U U Her U 7 mill C Assig onyablackson/Downloads/Assignment%20one.pdf 9 / 10 44. Graphically illustrate the difference between an increase in cantity supplied and an increase in supply. 45. Graphically illustrate the difference between an increase in quantity demanded and an increase in demand X Assig dTech 191 Umic Asso rs/donyablackson/Downloads/Assignment%20one.pdf INSTRUCTIONS: This homework has two parts. Answer all questions from the two parts. Part 1: Answer all questions. Clrde the correct answer for each question. Each question is worth 0.12 points. 1. Matilda is the CEO of a large marketing company. After paying taxes, her company was left with $18,000,000 of disposable income. She can reinvest this money into her company in infrastructure spending and salary increase, or she can invest it into the stock market. The cost of choosing one over the other is called the cost. a. Production b. Opportunity c. Marginal d. Deductible 2. Rose is considering how several factors may help her company's productivity. She is considering using advances in technology and making more investment in human capital. She is also trying to predict the changing trends in the labor force. Which of the following would be MOST beneficial to this scenario? a. The production possibilities curve b. The supply curve c. The Phillips curve d. The income-consumption curve 3. Which of the following is a key assumption of the production possibilities model? a. All of the answers are correct. b. Technology remains completely constant. c. Resources are scarce. d. Resources are used to maximize capacity. 4. With the same amount of resources, Country A can produce 25 tons of chicken or 50 tons of wheat. What is Country A's opportunity cost of producing 1 ton of wheat? a. 2 tons of chicken b. 25 tons of wheat C. 25 tons of chicken d. % ton of chicken Assige X Tech 1911 U UHO CAS 10 Mens ablackson/Downloads/Assignment%20one.pdf 5. It takes Joan 1 hour to make a pizza and 2 hours to make a cake, Joan's opportunity cost of making a pizza is which of the following? a. 2 cakes b. X pizzas C. of a cake d. 2 pizzas 6. A point that is located inside the production possibility curve is: a. Efficient b. Unattainable c Equally efficient as all other points d. Inefficient 7. Which is TRUE of points located outside of the production possibility curve? a. They are profitable. b. They are unobtainable. c. They are less efficient than average. d. They demonstrate unlimited capacity 8. A CFO can invest company profits in stocks with projected returns of 10%, or use the money to add a new assembly line, projected to yield 14% after payment of the debt. What is the opportunity cost of investing in stocks instead of the factory upgrade? a. 14% b. 4% c. 10% UO Men's Assig UUHer C Assig onyablackson/Downloads/Assignment%20one.pat 8. A CFO can invest company profits in stockis with projected returns of 10%, or use the money to add a new assembly line, projected to yield 14% after payment of the debt. What is the opportunity cost of investing in stocks instead of the factory upgrade? a 14% b. 4x c. 10% d. 24% 9. All of the following factors impact an economy's production possibility curve except a. a technological advance b. a newly discovered energy source c. technological stagnation d. increases in the population 10. Assuming there are only two countries, Country A can produce 10 tons of wheat or 20 tons of rice, while Country B can produce 5 tons of wheat or 15 tons of rice. Which country has the highest opportunity cost for producing 1 ton of rice? a. Country A up to 1/2 ton then it is Country B b. Country B c. Country A d. Both countries are the same 11. When countries specialize in the goods in which they have a comparative advantage, which of the following is true? a. Production costs will increase for both countries. b. Both countries will experience gains from trade. c. Both countries are worse off. CASSO Hackson/Downloads/Assignment%20one.pdf d. One country is usually better off, and the other is worse off. 12. Country A's opportunity cost of producing 1 ton of com is 5 tons of wheat, while Country B's opportunity cost of producing 1 ton of corn is 1/3 of a ton of wheat. Which of the following statements is true? a. Country A should specialize in producing corn, while Country B should specialize in producing wheat. b. Country B should specialize in producing corn, while fountry A should specialize in producing wheat. c. There will be no gains from trade if these two countries exchange goods, d. Both countries should produce both goods. 13. According to the two production possibility curves shown, Country A should specialize in the production of which of the following? Corn (tons) 5 4 3 2 Country A Country B 02 15 Wheat (tons) a. Wheat b. Both corn and wheat Assign X Techin (191) heart X U Her U Zmi C Assig UOM ers/donyablackson/Downloads/Assignment%20one.pdf 15 Wheat (tons) a. Wheat b. Both com and wheat C. Com d. Neither corn nor wheat. 14. Which of the following is NOT a benefit of specialization and exchange? a. Taxes will be reduced. b. A country can produce beyond its production possibility curve. c. Larger quantities of goods and services can be produced d. Resources can be used more efficiently 15. The United States can produce 20 strawberries or 80 apples, while Canada can produce 15 strawberries or 5 apples. Which of the following describes what will happen if these two countries trade with each other? a. Neither country will benefit from trading b. Canada will benefit, but the US will not C Both countries will benefit from trading d. The United States will benefit, but Canada will not 16. Country A can either produce 10 cars or 10 computers, while country can produce either 4 cars or SALLE TechnX (191) P x heartex U DlHere X U 7 milli X C Assign X Eson/Downloads/Assignment%20one.pdf d. The United States will benefit, but Canada will not. 16. Country A can either produce 10 cars or 10 computers, while country B can produce either 4 cars or 8 computers. Based on this information, which of the following statements is FALSE? a. Country A has an absolute advantage in cars. b. Country A has an absolute advantage in computers. c. Country B has a comparative advantage in computers. d. Country A has a comparative advantage in computers. 17. A person or nation that has a comparative advantage in the production of a good, should a. have the highest opportunity cost b. decrease their production of that good c. specialize in the production of that good d. automatically has an absolute advantage a. 18. According to the Law of Comparative Advantage, where should a good be produced? Where there are more consumers. b. In the country with the highest absolute advantage. c Where opportunity costs are the highest. d. Where opportunity costs are the lowest. 19. If Sally can produce 1 term paper or 4 cookies in one hour, and Adam can produce 2 term papers or 1 cookie in the same amount of time, which of these statements is true? a. Sally has a comparative advantage in cookies, while Adam a comparative advantage in term papers b. Both Sally and Adam have the same opportunity costs for these two goods. c Sally uses more resources to produce cookies than she does to produce term papers. d. Adam has a comparative advantage in cookies, while Sally has a comparative advantage in term papers 20. Which of the following are problems that all economies face? How to use scarce resources to satisfy unlimited wants, and how to shrink the money supply How to decide what goods and services to produce, how much to produce, and for whom to blackson/Downloads/Assignment%20one.pdf d. How to use scarce resources to satisfy unlimited wants, how to decide what goods and services to produce, how much to produce, and for whom to produce. 21. Assume that there are only two countries, Country A and Country B, producing only two goods, corn cereal and designer jeans. The table here shows the production possibilities for these two countries. Which of the following statements is correct? Country A Country B Good 1 80 150 Good 2 65 70 a. Country A has an absolute advantage in one good, but not both. b. Country B has an absolute advantage in one good, but not both C. Neither country has an absolute advantage in the production of these two goods. d. Country B has an absolute advantage in both goods. 22. Which of the following refers to the point where the supply and demand curves intersect? a. Price point b. Double point C. Equilibrium point d. Strike point 23. Both the supply curve and the demand curve have shifted. What does this mean for the price? a. It went down b. It went up it did not change d. It could go up, down, or not change. 24. A surplus exists when occurs. 3. demand outstrips production b. economy outstrips inflation inflation outstrips economy d. production outstrips demand 25. In which direction will the market supply curve slope when suppliers want to sell more goods at 30 2 3 5 & 7 8. Assign X Techn X (191) FX G heart X U VIHer x U 7 ml X C Assig X U -nyablackson/Downloads/Assignment%20one.pdf c. A change in quantity will not shift the supply curve. d. It depends on the limit of the change. 27. Demand has increased for goods and services. How would this be represented on a demand curve? a. A shift down. b. A shift to the right. c. A shift to the left. d. A shift up. 28. Which of the following refers to a list of goods at a price that a person is willing to pay across all markets? a. Market demand schedule b. Demand schedule c Demographic demand schedule d. Demand schedule multiplier 29. Which of the following refers to a table that lists the demand for a product across all markets? a. Retail economy chart b. Market demand schedule C Equilibrium point d. Sell table 30. There is a request for 10 million widgets at $0.10 each. What is this called? a. Demand quantity b. Item quantity c Equilibrium quantity d Supply quantity 31. Which of the following is an example of a list of goods at a price that a person is willing to pay? a. Demand schedule b. Equilibrium point Supply schedule d Demographic indicator 32. In which direction would the demand curve slope when people bewer raodsathishwices? X Assign X TechnX (191) X heart U VIHer C Assig nyablackson/Downloads/Assignment%20one.pdf 32. In which direction would the demand curve slope when people buy fewer goods at higher prices? a. Flat b. Upward c. Vertical d. Downward 33. In what way does change in price shift demand? a. It does not shift demand. b. It will decrease demand. c. It will increase demand. d. It will depend on the whether the change is up or down. 34. The cost per widget and the number of widgets to be supplied is shown on the a market supply schedule b. sales demand schedule c quantity retail schedule d. purchase/cost schedule 35. The market supply schedule is a table that lists the quantity supplied in all economies at all possible Prices b. Locations c. Agreements U 7 milli X C Assig ackson/Downloads/Assignment%20one.pdf 36. What is quantity supplied? a. It refers to the quality of goods and services in an economy. b. It is how much of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to buy. It is how much of a good or service that sellers are willing and able to supply at a particular price. d. It is how much money consumers want to borrow in an economy. 37. Which of the following statements is inaccurate regarding the demand curve? a. It is upward sloping b. A visual representation of the demand schedule c. It is downward sloping d. It shows quantity demanded at different prices 38. What is the correct relationship between price and quantity demanded shown by the law of demand? a. When prices go down demand goes up b. when prices go down, demand goes down when prices go up, demand goes up d. there is no direct relationship between price and demand 39. Which of the following statements is NOT true regarding the market equilibrium? a. It is the only price at which quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplied b. It is where quantity demanded equals quantity supplied c. It is found at the intersection of the supply and demand curves d. Unless something causes a shift in supply or demand, it will not change X (191) U UlHer . G heart U 7 mil x C Assig Assign X Techn myablackson/Downloads/Assignment%20one.pdf 40. When a market price is set below the market equilibrium price, a exists, which will a. surplus, create upward pressure on the price b. supply, increase the amount of goods and services available cshortage, create downward pressure on the price d. shortage, create upward pressure on the price 41. What is quantity demanded? a. It is the quantity of a good or service supplied by producers. b. It is the quantity of a good or service that an individual is willing and able to buy at a certain price. c. It is the quality of a good or service that an individual is looking for. d. It is the quantity of a good or service that is unavailable because of regulations. 42. Which of the following statements is FALSE regarding the supply curve? a. It is downward-sloping b. It is upward-sloping c. A change in price results in movement along the curve d. It is a graph illustrating the relationship between price and quantity supplied Part 2: Answer all questions. Use the blank space for your answers. Each question is worth 0.49 point. 43. With the aid of diagrams (graph), explain how an initial unattainable point of a Production Possibility Frontier (PPF) can subsequently become attainable. Assigex dTech 11911 X X G heart UO U Her U 7 ml C Assig s/donyablackson/Downloads/Assignment%20one.pdf 8/10 43. With the aid of diagrams (graph), explain how an initial unattainable point of a Production Possibility Frontier (PPF) can subsequently become attainable 44. Graphically illustrate the difference between an increase in quantity supplied and an increase in supply Assign X d Tech (1911 X heart U U Her U 7 mill C Assig onyablackson/Downloads/Assignment%20one.pdf 9 / 10 44. Graphically illustrate the difference between an increase in cantity supplied and an increase in supply. 45. Graphically illustrate the difference between an increase in quantity demanded and an increase in demand