ygeyfgeygfyegfyrgfyrgfygryfgryfgryurfhruhfur
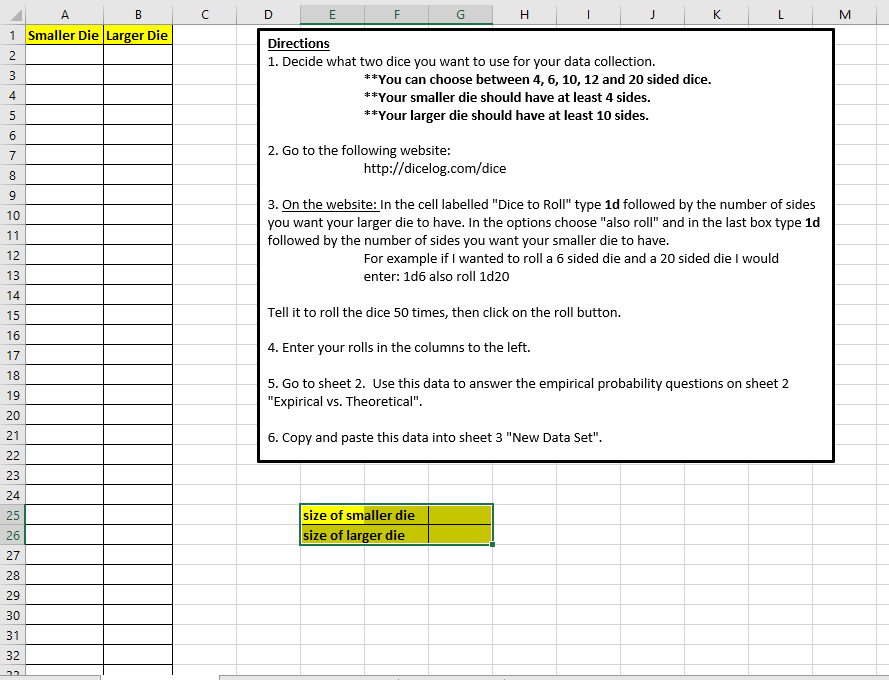
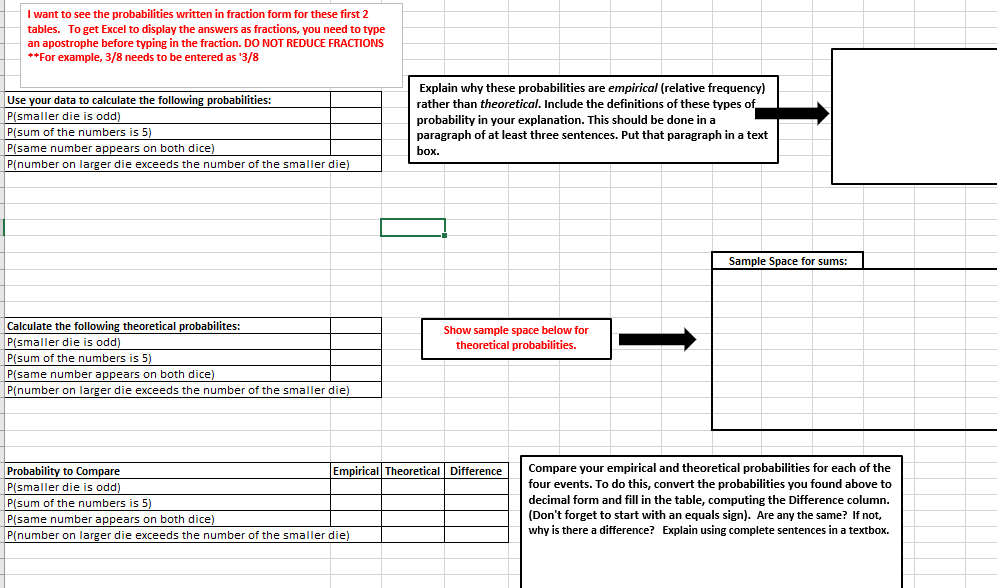
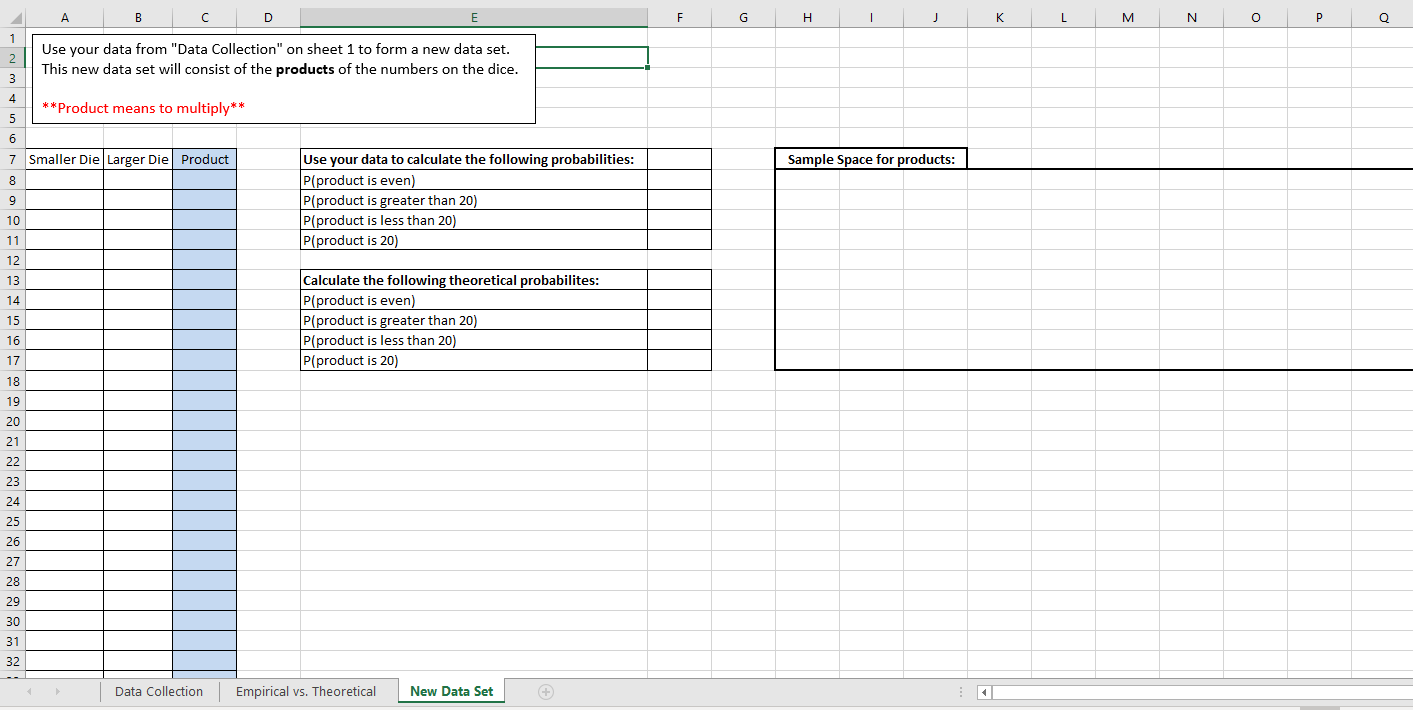
A B C D E F G H K L M Smaller Die Larger Die Directions W N 1. Decide what two dice you want to use for your data collection. **You can choose between 4, 6, 10, 12 and 20 sided dice. **Your smaller die should have at least 4 sides. **Your larger die should have at least 10 sides. NO UI & 2. Go to the following website: http://dicelog.com/dice 3. On the website: In the cell labelled "Dice to Roll" type 1d followed by the number of sides you want your larger die to have. In the options choose "also roll" and in the last box type 1d followed by the number of sides you want your smaller die to have. For example if I wanted to roll a 6 sided die and a 20 sided die I would enter: 1d6 also roll 1d20 Tell it to roll the dice 50 times, then click on the roll button. 4. Enter your rolls in the columns to the left. 5. Go to sheet 2. Use this data to answer the empirical probability questions on sheet 2 "Expirical vs. Theoretical" 20 IN 6. Copy and paste this data into sheet 3 "New Data Set". size of smaller die size of larger die 29 30 31 32I want to see the probabilities written in fraction form for these first 2 tables. To get Excel to display the answers as fractions, you need to type an apostrophe before typing in the fraction. DO NOT REDUCE FRACTIONS *+For example, 3/8 needs to be entered as '3/8 Explain why these probabilities are empirical (relative frequency) Use your data to calculate the following probabilities: rather than theoretical. Include the definitions of these types of P(smaller die is odd) probability in your explanation. This should be done in a P(sum of the numbers is 5) paragraph of at least three sentences. Put that paragraph in a text P(same number appears on both dice) box. P(number on larger die exceeds the number of the smaller die) Sample Space for sums: Calculate the following theoretical probabilites: Show sample space below for P(smaller die is odd) theoretical probabilities. P(sum of the numbers is 5) P(same number appears on both dice) P(number on larger die exceeds the number of the smaller die) Probability to Compare Empirical Theoretical | Difference Compare your empirical and theoretical probabilities for each of the P(smaller die is odd) four events. To do this, convert the probabilities you found above to P(sum of the numbers is 5) decimal form and fill in the table, computing the Difference column. P(same number appears on both dice) [Don't forget to start with an equals sign). Are any the same? If not, P(number on larger die exceeds the number of the smaller die) why is there a difference? Explain using complete sentences in a textbox.A B D E F G H J K L M N O P Q Use your data from "Data Collection" on sheet 1 to form a new data set. This new data set will consist of the products of the numbers on the dice. w * *Product means to multiply** Smaller Die Larger Die| Product Use your data to calculate the following probabilities: Sample Space for products: P(product is even) P(product is greater than 20) 10 P(product is less than 20) 11 P(product is 20) 12 13 Calculate the following theoretical probabilites: 14 P(product is even) P(product is greater than 20) P(product is less than 20) P(product is 20) 22 24 26 IN 28 29 30 31 32 Data Collection Empirical vs. Theoretical New Data Set +