Question
You are to use the parse function from the previous lab to parse an input delimited text string to tokens in a vector. Additional vector


You are to use the parse function from the previous lab to parse an input delimited text string to tokens in a vector. Additional vector programming examples can be found in cplusplus.com (Links to an external site.)Links to an external site..
The Starter:
Use the quicksort_starter.cpp from github.
The user is expected to enter the entire collection (of test data) within one single line of delimited data.
quicksort.cpp and appropriate validations.
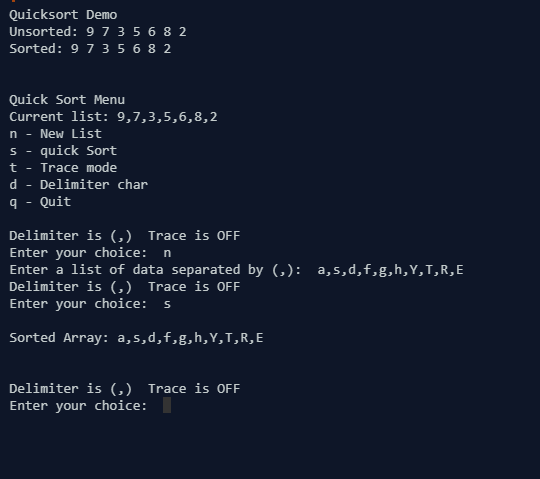
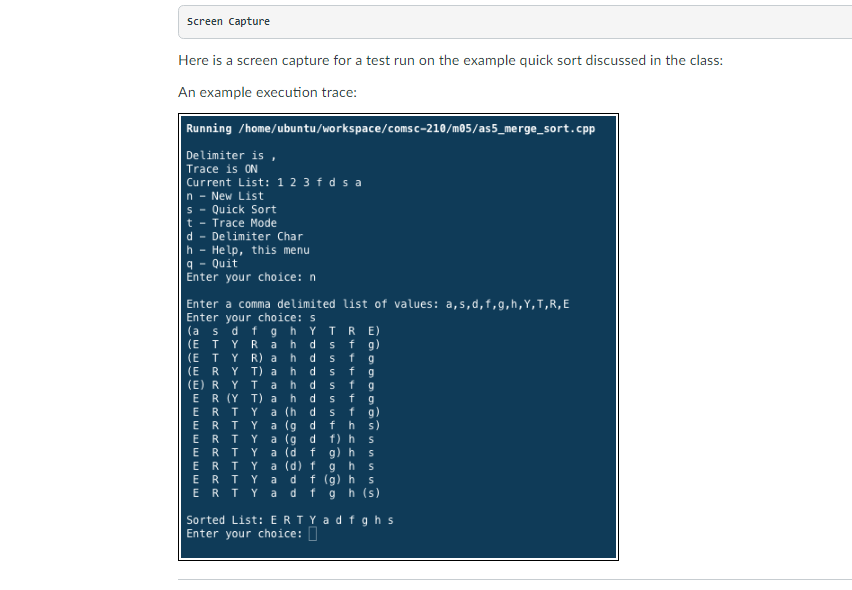
As an example, the program should be able to produce the trace output when the TRACE option is enabled. Here is an example output:
Enter your choice> s (9 7 3 5 6 8 2) (2 7 3 5 6 8 9) (2 3)5 8 6 7 9 2 3 5 (8 6 7 9) 2 3 5 (6 8 7 9) 2 3 5 (6 7)8 9 2 3 5 6 7 8 (9) Sorted Array: 2,3,5,6,7,8,9
quick_sort.cpp
| #include #include #include #include #include
#define under "\33[4m" #define over "\33[0m"
// example cout
using namespace std;
static const int MIN_SIZE = 2; //smaller use swap char delimiter = ','; bool trace = false;
void showTrace(vector void show(vector int comp(const void *one, const void *two); void order(vector void sortFirstMiddleLast(vector int partition(vector void quickSort(vector
int main() { cout vector
cout for(auto item:a) cout cout
// Try lambda for local meaning auto acomp = [] (const void* a, const void* b) {return ( (a > b)?1:( (a==b)?0:-1) );};
vector qsort(&demo[0], demo.size(), sizeof(int), acomp); cout for(auto item:demo) { cout } cout
vector
auto menu = [&] () { cout
show(ar); cout
menu( ); char choice; // user choice of command do { cout
cin >> choice; cin.ignore(1000, ' '); choice = tolower(choice); string input, token; vector stringstream ss; switch(choice) { // main menu switch starts case 'n': // new cout getline (cin, input); ss ar.clear(); while(getline(ss, token, delimiter)) ar.push_back(token); break; case 't': trace = !trace; break; case 'd': // delimiter cout cin >> delimiter; break; case 's': // quickSort(test, 0, test.size() - 1); cout show(test); cout break; case 'm': menu(); break; case 'q': break; default: cout } } while (choice!='q'); }
// void quickSort(vector // { // }
void sortFirstMiddleLast(vector int middle = (first + last)/2; order(arr, first, middle); order(arr, middle, last); order(arr, first, middle); }
// int partition(vector // }
int comp(const void *one, const void *two) { int a = *((int*)one); int b = *((int*)two); if (a if (a == b) return 0; return 1; }
void show(vector string output; // how does this one work? for(auto item:arr) { if (!output.empty()) output += ","; output += item; } cout }
void showTrace(vector for(int i=0; i cout } cout } void order(vector if (arr[i] > arr[j]) std::swap(arr[i], arr[j]); } | |
| Current output:
|
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started