Question
Your assignment is to write an assembler for a subset of the MIPS instruction set. It should read the assembly file from standard input and
Your assignment is to write an assembler for a subset of the MIPS instruction set. It should read the assembly file from standard input and write the machine code to standard output. Below are the MIPS assembly directives that you are required to recognize.
Directive: Explanation
.text: Switch to the text (code) segment.
.data: Switch to the (static) data segment.
.word: w1,...,wn Store n 32-bit integer values in successive memory words.
.space: n Allocate n words that are initialized to zero in the data segment.
You can assume that an assembly file will have instructions preceding data and the general format of a file will be as follows: .text .data Each instruction or data word can have a symbolic label. Each assembly line can have a comment starting with the # character, which indicates a comment until the end of the line. You can assume that the maximum number of instructions is 32768 and the maximum number of data words is also 32768. You can also assume the maximum length of an assembly line is 80 characters and the maximum size of a symbolic label is 10 characters. Finally, you can assume there are no whitespace (blank or tab) characters between the arguments in each assembly instruction.
Below is an example assembly file that reads a number n, reads n values, and then prints the sum of those n values.

The first line of the machine code file contains an object file header that consists of the number of instructions and the number of words of data, written as decimal values. The next set of lines consists of hexadecimal values representing the encoding of the machine instructions in the text segment of the assembly instructions. The final set of lines consists of hexadecimal values representing the initial values of the words in the data segment.
The output should look like this:
18 1
00008021
00008821
24020005
0000000c
af820000
8f920000
0232402a
11000006
24020005
0000000c
02028021
26310001
08000005
02002021
24020001
0000000c
2402000a
0000000c
00000000
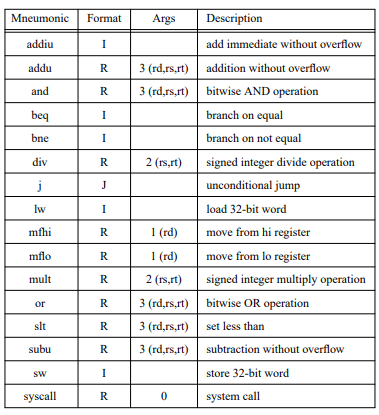
Mneumonic Form ArgsDescription addiu add immediate without overflow R 3 (rd,rs.rt) addition without overflow R 3 (rd.rs.rt)bitwise AND operation branch on equal branch on not equal R 2 (rs,rt) signed integer divide operation unconditional jump load 32-bit word l (rd move from hi register l (rd move from lo register R 2 (rs,rt signed integer multiply operation mult (rd.rs,rt) bitwise OR operation 3 (rd.rs.rt) set less than 3 (rd,rs,rt) subtraction without overflow subu store 32-bit word syscall 0 system call text addu addu addiu $vO, $zero,5 syscall S W $s0, $zero, $zero $s1, $zero, $zero # v0 read value cmd # v0 read ( ) $v0, n (Sgp) $s2, n (Sgp) $t0, $s1, $s2 $t0, $zero, L2 L1 : sit beq addiu $vO, $zero,5 syscall addu addiu $s1, $s1,1 # if s1 >= s2 then goto L2 # v0 read value cmd # v0 read ( ) $s0, $0, $vO #s1 + 1 # goto L1 L1 $a0, $s0, $zero addu addiu $vO, $zero,1 syscall addiu $v0, $zero, 10 syscall L2 : # v0 print value crnd # print (a0) #v0 exit cmd # exit() data n : word 0Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


