Question
You're driving along, listening to the car radio and following the rules of the road, when, all of a sudden, a silver sedan comes out
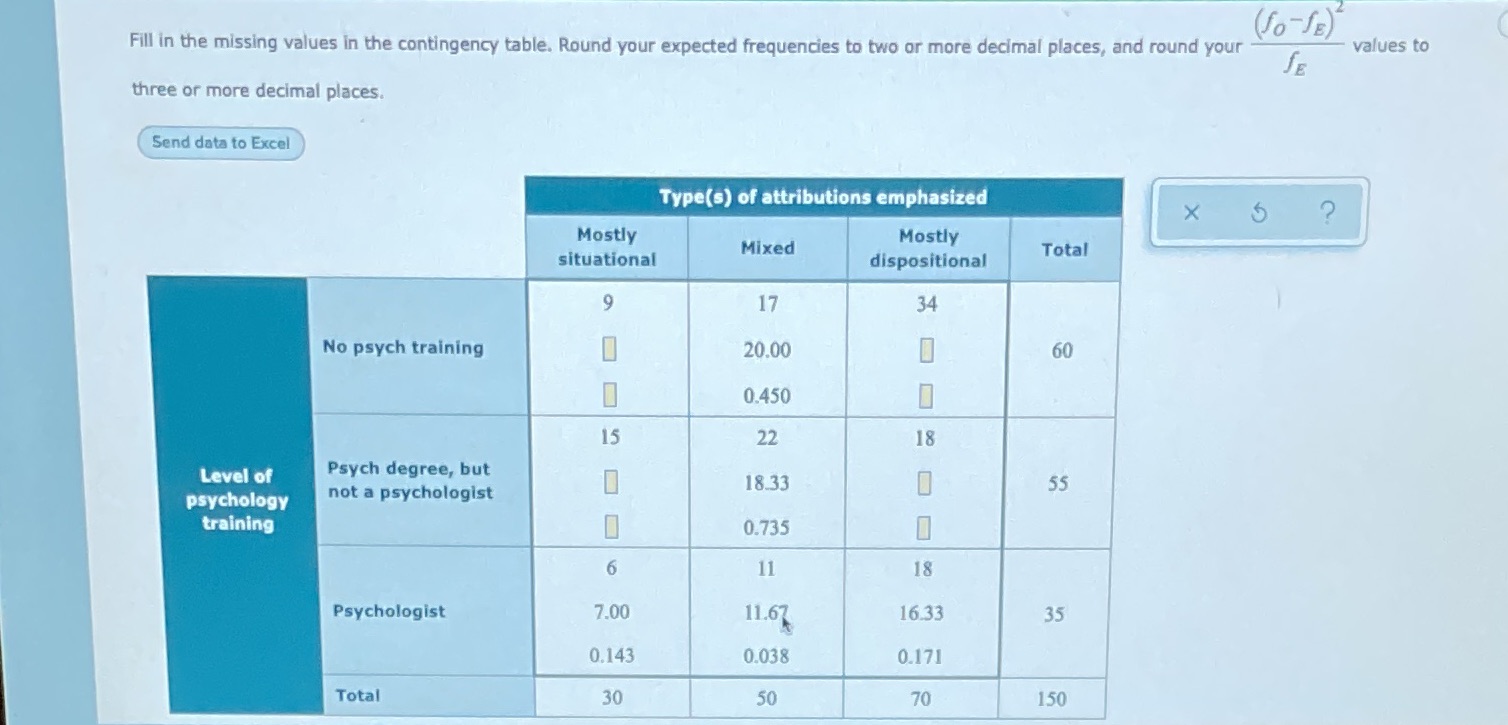
You're driving along, listening to the car radio and following the rules of the road, when, all of a sudden, a silver sedan comes out of nowhere and darts in front of you, causing you to slam on your brakes and spill your chicken nuggets all over the place."Why did that guy just cut me off?!?!?" Most of us, drivers and observers alike, would tend to attribute his actions to "dispositional" factors: he's a terrible driver, he likes to scare people on the road, etc. We tend to overlook the possible "situational" factors that may be contributing to his recklessness: he's rushing to the hospital, he just spilled his own chicken nuggets and temporarily lost control of the car, etc. Psychologists call this tendency to attribute (often incorrectly) others' actions to dispositional factors rather than to situational factors as the fundamental attribution error.We're interested in seeing if there's a difference in inclination to commit the fundamental attribution error among groups that differ in level of psychology training. We choose three groups of adults to participate in a study: adults who have no psychology training, adults who have a psychology degree but who are not practicing psychologists, and adults who are practicing psychologists. We show each participant a videotape on which a scenario similar to the one described above was enacted. Then we ask the participants questions about why the characters in the enactment behaved as they did. We are examining the variables level of psychology training ("no psych training", "psych degree, but not a psychologist", and "psychologist") and type(s) of attributions emphasized ("mostly situational", "mixed", and "mostly dispositional").Suppose that our data are those summarized in the contingency table below. Each cell of the table contains three numbers: the first number is the observed cell frequency (fO), the second number is the expected cell frequency (fE) under the assumption that the two variables level of psychology training and type(s) of attributions emphasized are not associated, and the third number is the following value.Could not fit part 2 in the picture but the questions are asking for: type of test statisticvalue of test statistic critical value with level of significance of 0.10and can we conclude that the variables level of psychology training and types of attributes emphasized are associated? use the level of significance 0.10. yes or no
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


