Question
zgrkey Frozen Foods is one of the main producer company of frozen foods. Their brand Feast produces a variety of frozen foods including vegetables, snacks
Özgörkey Frozen Foods is one of the main producer company of frozen foods. Their brand “Feast” produces a variety of frozen foods including vegetables, snacks and patisserie. Their production plant in Torbalı, Izmir operates at capacity and processes vegetables into frozen vegetable cuts. It sells frozen vegetables to the retail consumer market and to the wholesale market, which includes restaurants and cafeterias. Currently they are using a simple which has a single direct‐cost category (direct materials, i.e. raw vegetables) regardless of their targeted customers (retail and wholesale) and a single indirect‐cost pool (production support, including packaging materials). Kilograms of vegetable cuts processed are used as allocation base of the indirect costs. In order to produce 1,000,000 kg of vegetable cuts, the company uses 1,200,000 kg of raw vegetables to process.
At the end of 2018, “Feast” bid for a large wholesale contract for a restaurant chain. While making the bid, they included only a minimum profit margin. Later on, their bid was
reported to be 30% above the winning bid. As a result of its review process of the lost contract bid, “Feast” decided to explore ways to find a better approach for their costing system. After the analysis they concluded that 90% of the direct materials (raw vegetables) related to the retail market and 10% to the wholesale market. In addition, the company identified that packaging materials could be directly traced to individual jobs ($180,000 for retail and $8,000 for wholesale). In order to decide on the costing structure, the company used ABC to identify three main activities that generated support costs: cleaning, cutting, and packaging.
Following information is provided about the activities by the company;
Cleaning—The cost‐allocation base is kilograms of raw vegetables cleaned.
Cutting—The production line produces (a) 250 kg of retail vegetable cuts per cutting‐hour and (b) 400 kg of wholesale vegetable cuts per cutting‐hour. The cost allocation base is cutting‐hours on the production line.
Packaging—The packaging line packages (a) 25 kg of retail vegetable cuts per packaging‐hour and (b) 100 kg of wholesale vegetable cuts per packaging‐hour. The cost‐allocation base is packaging‐hours on the production line.
1. What is the cost per kg of vegetable cuts under the simple costing system?
2. Calculate the cost rate per unit of the cost driver for (a) cleaning, (b) cutting, and (c) packaging.
3. Suppose that information from activity cost rates are used to calculate costs incurred on retail vegetable cuts and wholesale vegetable cuts. Using the ABC system, what is the cost per kg of (i) retail vegetable cuts and (ii) wholesale vegetable cuts?
4. What are the cost differences between the two costing systems? Explain how might “Feast” use the information in requirement 3 to make better decisions?
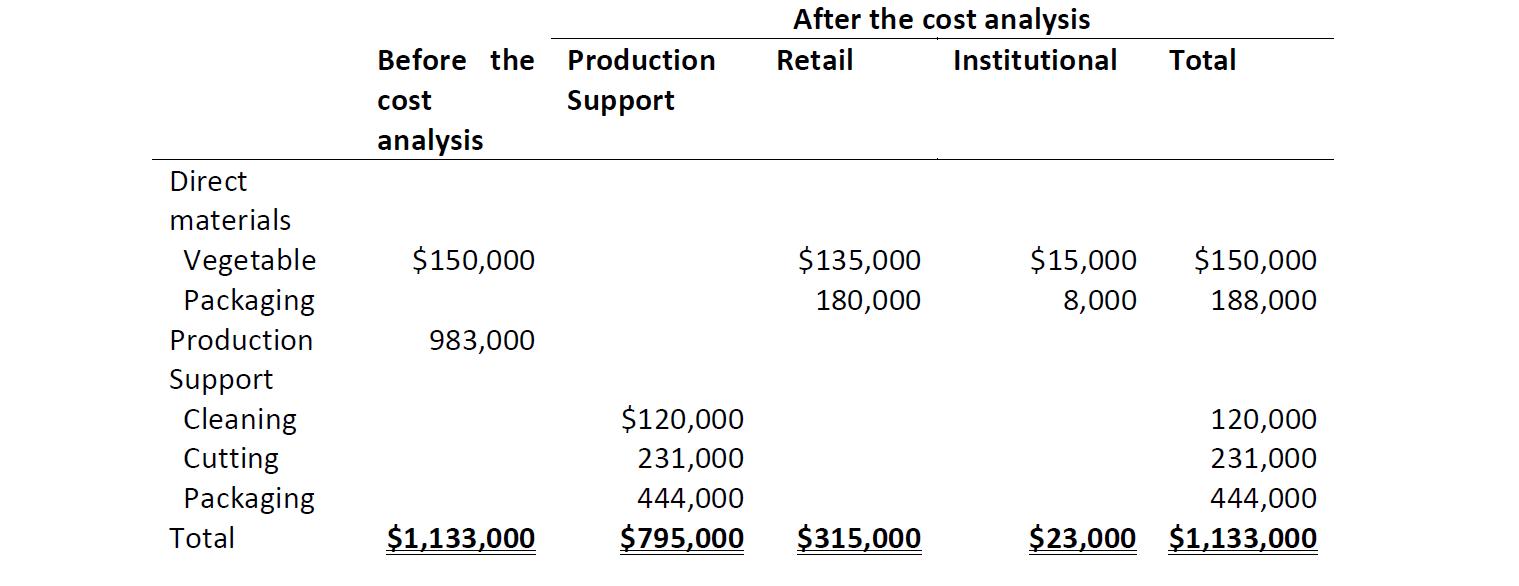
After the cost analysis Before the Production Retail Institutional Total cost Support analysis Direct materials $150,000 $135,000 $15,000 $150,000 Vegetable Packaging 180,000 8,000 188,000 Production 983,000 Support Cleaning Cutting $120,000 120,000 231,000 231,000 Packaging 444,000 444,000 Total $1,133,000 $795,000 $315,000 $23,000 $1,133,000
Step by Step Solution
3.51 Rating (161 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
1 2 Simple Costing Sysytem 3 Direct Costs 4 Direct ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


