On 28 January 1986 the space shuttle Challenger was destroyed in an explosion shortly after launch from
Question:
On 28 January 1986 the space shuttle Challenger was destroyed in an explosion shortly after launch from Cape Kennedy. The cause of the explosion was eventually identified as catastrophic failure of the O-rings on the solid rocket booster. The failure likely occurred because the O-ring material was subjected to a lower temperature at launch \(\left(31^{\circ} \mathrm{F}\right)\) than was apropriate. The material and the solid rocket joints had never been tested at temperatures this low. Some O-ring failures had occurred during other shuttle launches (or engine static tests). The failure data observed prior to the Challenger launch is shown in the following table.
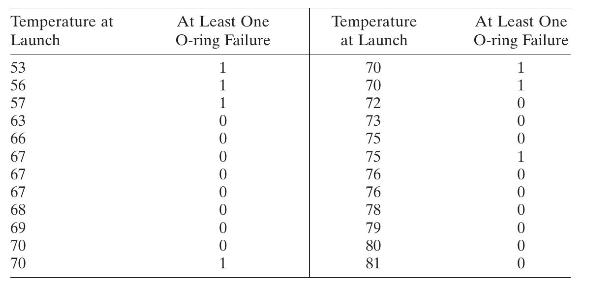
a. Fit a logistic regression model to these data. Construct a graph of the data and display the fitted model. Discuss how well the model fits the data.
b. Calculate and interpret the odds ratio.
c. What is the estimated failure probability at \(50^{\circ} \mathrm{F}\) ?
d. What is the estimated failure probability at \(75^{\circ} \mathrm{F}\) ?
e. What is the estimated failure probability at \(31^{\circ} \mathrm{F}\) ? Notice that there is extrapolation involved in obtaining this estimate. What influence would that have on your recommendation about launching the space shuttle?
f. Calculate and analyze the deviance residuals for this model.
g. Add a quadratic term in temperature to the logistic regression model in part a. Is there any evidence that this term improves the model?
Step by Step Answer:

Introduction To Linear Regression Analysis
ISBN: 9781119578727
6th Edition
Authors: Douglas C. Montgomery, Elizabeth A. Peck, G. Geoffrey Vining




