For separations by settling and centrifugation of bacteria, yeast, fungi, and mixed-culture activated sludge from fermentations and
Question:
For separations by settling and centrifugation of bacteria, yeast, fungi, and mixed-culture activated sludge from fermentations and sewage systems, values of cell density, equivalent diameter, settling velocity, and volume fraction of cells in suspension must be estimated. The data below and procedures used to obtain these values are described in [23].
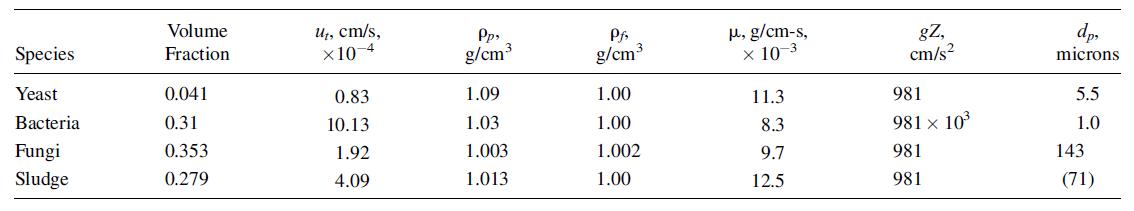
In the above table, gZ is the gravitational constant times the centrifugal field strength. The bacteria-settling study was conducted in centrifuges, while the others were done in simple gravity settlers.
The particle size was observed microscopically, except for the sludge, which was calculated from the settling velocity using Stokes’ law. The authors claim good correlations between microorganism diameters calculated from settling velocities and those determined microscopically. Verify their claim by calculating the diameters from the settling velocities, including a verification of their calculated settling velocity for the sludge. Discuss your results in terms of possible hindered settling, aggregation, and particle shape properties.
Step by Step Answer:

Separation Process Principles Chemical And Biochemical Principles
ISBN: 9780470481837
3rd Edition
Authors: By J. D. Seader, Ernest J. Henley, D. Keith Roper





